Smart factory integrates advanced automation, IoT sensors, and real-time data analytics to optimize production processes and enhance operational efficiency. Industry 4.0 encompasses a broader digital transformation, including cyber-physical systems, big data, and cloud computing, driving interconnected manufacturing ecosystems. Explore the key differences and benefits of smart factories within the Industry 4.0 framework to understand the future of manufacturing.
Why it is important
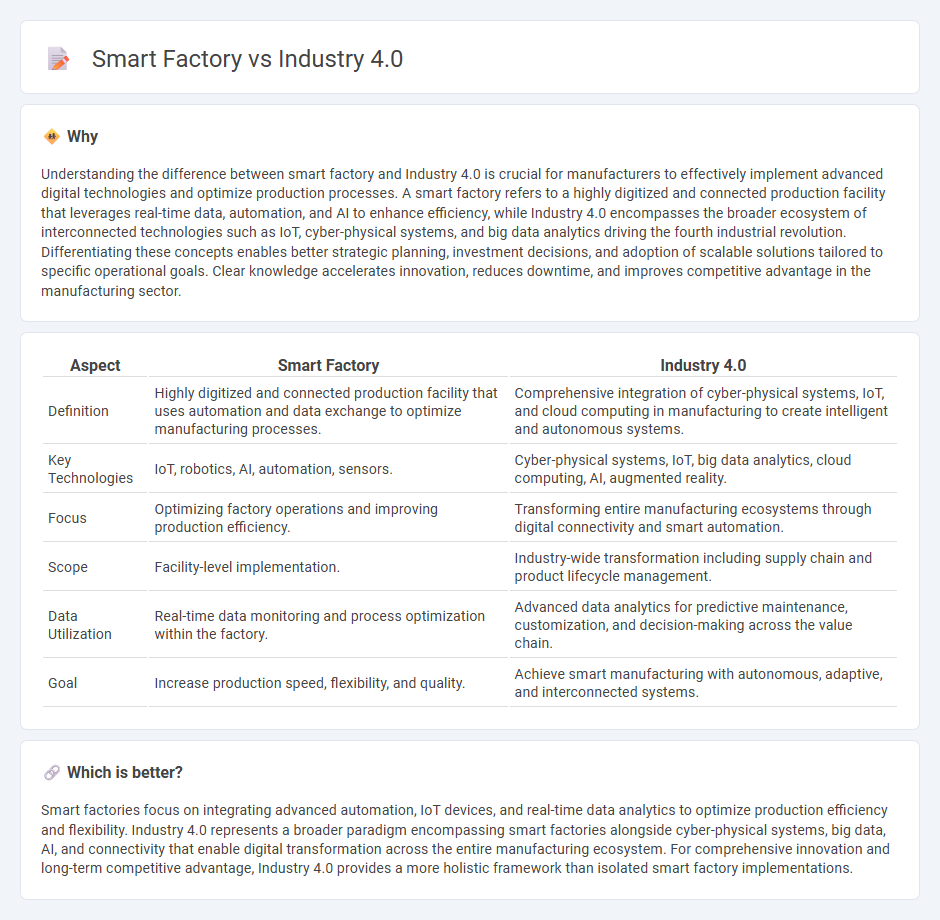
Understanding the difference between smart factory and Industry 4.0 is crucial for manufacturers to effectively implement advanced digital technologies and optimize production processes. A smart factory refers to a highly digitized and connected production facility that leverages real-time data, automation, and AI to enhance efficiency, while Industry 4.0 encompasses the broader ecosystem of interconnected technologies such as IoT, cyber-physical systems, and big data analytics driving the fourth industrial revolution. Differentiating these concepts enables better strategic planning, investment decisions, and adoption of scalable solutions tailored to specific operational goals. Clear knowledge accelerates innovation, reduces downtime, and improves competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Factory | Industry 4.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Highly digitized and connected production facility that uses automation and data exchange to optimize manufacturing processes. | Comprehensive integration of cyber-physical systems, IoT, and cloud computing in manufacturing to create intelligent and autonomous systems. |
| Key Technologies | IoT, robotics, AI, automation, sensors. | Cyber-physical systems, IoT, big data analytics, cloud computing, AI, augmented reality. |
| Focus | Optimizing factory operations and improving production efficiency. | Transforming entire manufacturing ecosystems through digital connectivity and smart automation. |
| Scope | Facility-level implementation. | Industry-wide transformation including supply chain and product lifecycle management. |
| Data Utilization | Real-time data monitoring and process optimization within the factory. | Advanced data analytics for predictive maintenance, customization, and decision-making across the value chain. |
| Goal | Increase production speed, flexibility, and quality. | Achieve smart manufacturing with autonomous, adaptive, and interconnected systems. |
Which is better?
Smart factories focus on integrating advanced automation, IoT devices, and real-time data analytics to optimize production efficiency and flexibility. Industry 4.0 represents a broader paradigm encompassing smart factories alongside cyber-physical systems, big data, AI, and connectivity that enable digital transformation across the entire manufacturing ecosystem. For comprehensive innovation and long-term competitive advantage, Industry 4.0 provides a more holistic framework than isolated smart factory implementations.
Connection
Smart factories are the cornerstone of Industry 4.0, integrating advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and big data to enhance automation and data exchange in manufacturing processes. Industry 4.0 enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and increased operational efficiency through interconnected cyber-physical systems within smart factories. This synergy drives significant improvements in production flexibility, quality, and cost reduction across manufacturing industries.
Key Terms
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
Industry 4.0 integrates Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) to create intelligent networks that autonomously monitor physical processes and optimize production in real time. A smart factory specifically employs CPS to enable seamless communication between machines, sensors, and humans, enhancing flexibility, efficiency, and predictive maintenance. Explore how CPS drives the transformation from traditional manufacturing to intelligent, adaptive environments.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Industry 4.0 integrates advanced digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) to create interconnected manufacturing systems that enhance automation, data exchange, and real-time decision-making. A smart factory applies Industry 4.0 principles by utilizing IoT sensors and devices to monitor equipment performance, optimize production processes, and enable predictive maintenance. Explore in-depth how IoT-driven innovations transform modern manufacturing ecosystems.
Real-Time Data Analytics
Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems, IoT, and cloud computing to enable advanced manufacturing processes, emphasizing extensive data collection and connectivity. Smart factories leverage real-time data analytics to optimize production, enhance decision-making, and improve operational efficiency by processing data instantaneously from various IoT devices and sensors. Explore how real-time data analytics transforms Industry 4.0 implementations and smart factory operations for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Industry 4.0 vs 5.0: What's the Difference? - Rutgers University - Industry 4.0, also called the Fourth Industrial Revolution, involves digital industrial technologies like cyber-physical systems, enabling smart factories through human-machine collaboration and data-driven manufacturing solutions.
What is Industry 4.0? - IBM - Industry 4.0 represents smart manufacturing driven by technologies such as IoT, AI, cloud computing, and advanced sensors, allowing real-time decisions, increased productivity, predictive maintenance, and flexible production.
What are Industry 4.0, the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and 4IR? - McKinsey - Industry 4.0 is the era of connectivity, advanced analytics, and automation that is transforming industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and retail, with adoption varying by existing technology infrastructure and capital investment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com