Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems to continuously monitor and adjust production processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, flexible units that focus on specific product components, promoting quicker response times and improved workflow. Explore the advantages and applications of both manufacturing strategies to determine the best fit for your production goals.
Why it is important
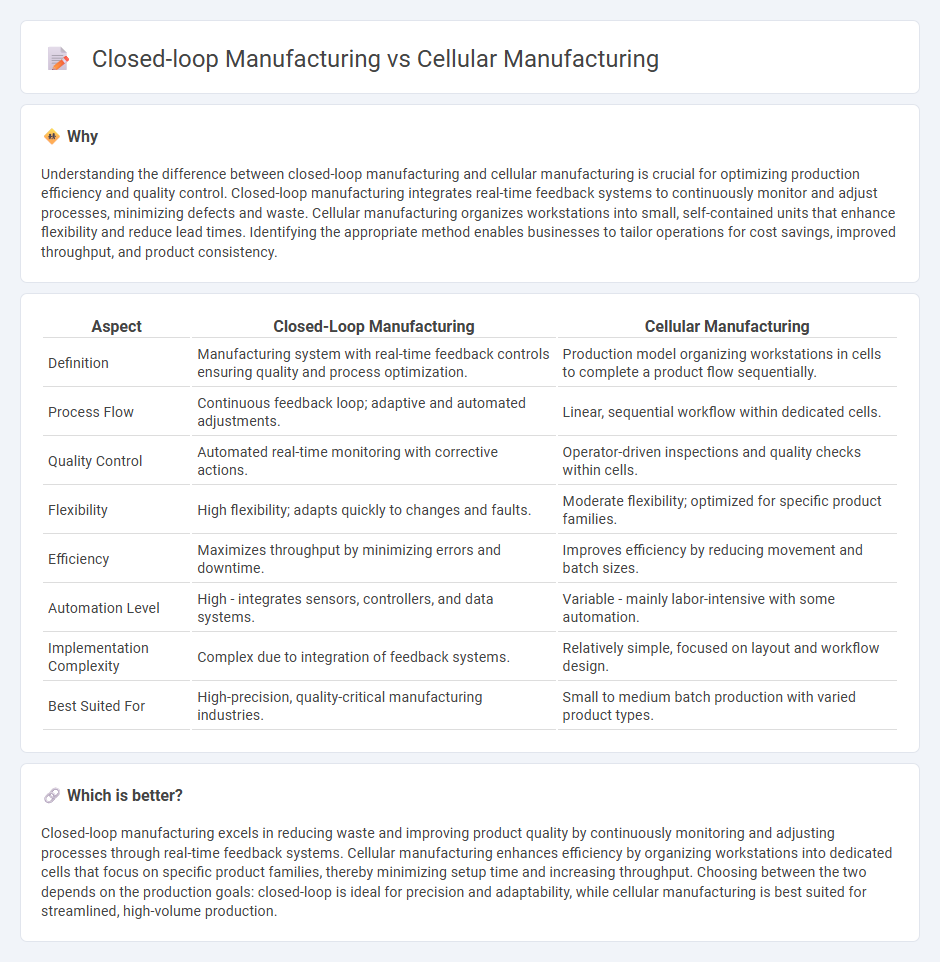
Understanding the difference between closed-loop manufacturing and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and quality control. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems to continuously monitor and adjust processes, minimizing defects and waste. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, self-contained units that enhance flexibility and reduce lead times. Identifying the appropriate method enables businesses to tailor operations for cost savings, improved throughput, and product consistency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Closed-Loop Manufacturing | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing system with real-time feedback controls ensuring quality and process optimization. | Production model organizing workstations in cells to complete a product flow sequentially. |
| Process Flow | Continuous feedback loop; adaptive and automated adjustments. | Linear, sequential workflow within dedicated cells. |
| Quality Control | Automated real-time monitoring with corrective actions. | Operator-driven inspections and quality checks within cells. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; adapts quickly to changes and faults. | Moderate flexibility; optimized for specific product families. |
| Efficiency | Maximizes throughput by minimizing errors and downtime. | Improves efficiency by reducing movement and batch sizes. |
| Automation Level | High - integrates sensors, controllers, and data systems. | Variable - mainly labor-intensive with some automation. |
| Implementation Complexity | Complex due to integration of feedback systems. | Relatively simple, focused on layout and workflow design. |
| Best Suited For | High-precision, quality-critical manufacturing industries. | Small to medium batch production with varied product types. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing excels in reducing waste and improving product quality by continuously monitoring and adjusting processes through real-time feedback systems. Cellular manufacturing enhances efficiency by organizing workstations into dedicated cells that focus on specific product families, thereby minimizing setup time and increasing throughput. Choosing between the two depends on the production goals: closed-loop is ideal for precision and adaptability, while cellular manufacturing is best suited for streamlined, high-volume production.
Connection
Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback and data-driven adjustments to optimize production efficiency, directly complementing cellular manufacturing's focus on arranging workstations for streamlined, flexible workflows. Both approaches reduce waste and enhance product quality by continuously monitoring and adapting processes within self-contained manufacturing cells. The synergy between closed-loop systems and cellular layouts drives agility and precision in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Work cells
Cellular manufacturing organizes work cells into small, self-contained units that optimize product flow, reduce lead time, and enhance worker flexibility, improving overall production efficiency. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates these work cells with real-time feedback systems to monitor quality and process variables, enabling dynamic adjustments and minimizing defects throughout the production cycle. Explore the distinctions and benefits between these approaches to maximize manufacturing performance.
Feedback control
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into small, self-contained units optimizing workflow and reducing lead times through localized material and information flow. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback control systems to continuously monitor and adjust processes, ensuring precision, quality, and adaptive response to production variations. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how feedback control shapes these manufacturing paradigms for enhanced operational efficiency.
Material flow
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into small, self-contained units to optimize material flow by minimizing transportation and reducing work-in-progress inventory, enhancing efficiency through streamlined workflows. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems and sensors to monitor material flow continuously, enabling dynamic adjustments that reduce waste and improve production accuracy. Explore the differences in material flow strategies to choose the best manufacturing approach for your operations.
Source and External Links
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - Deskera - Cellular manufacturing organizes production into unified cells, each performing a specific sequence of tasks, requiring assessment, cell design, process mapping, resource assignment, and ongoing performance analysis for efficiency.
Cellular manufacturing - Wikipedia - Cellular manufacturing is a subsection of lean manufacturing that arranges workstations in dedicated cells, enabling flexible, efficient, and waste-reducing production by allowing rapid adjustments and streamlined communication among team members.
Lean Thinking and Methods - Cellular Manufacturing | US EPA - This approach shifts industry from traditional batch-and-queue mass production to a product-aligned, one-piece-flow system, reducing work-in-process and lead times while responding better to actual customer demand.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com