Dark factories utilize advanced automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs in manufacturing processes. Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items such as automobiles or electronics, focusing on assembly lines and customization. Explore the differences and benefits of these manufacturing methods to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark factory and discrete manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and resource allocation. Dark factories operate fully automated systems with minimal human intervention, enhancing continuous operation and reducing labor costs. Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items, allowing for customization and flexibility in product design. Correctly identifying the manufacturing type enables businesses to implement appropriate technologies and workflows, boosting overall productivity and competitiveness.
Comparison Table
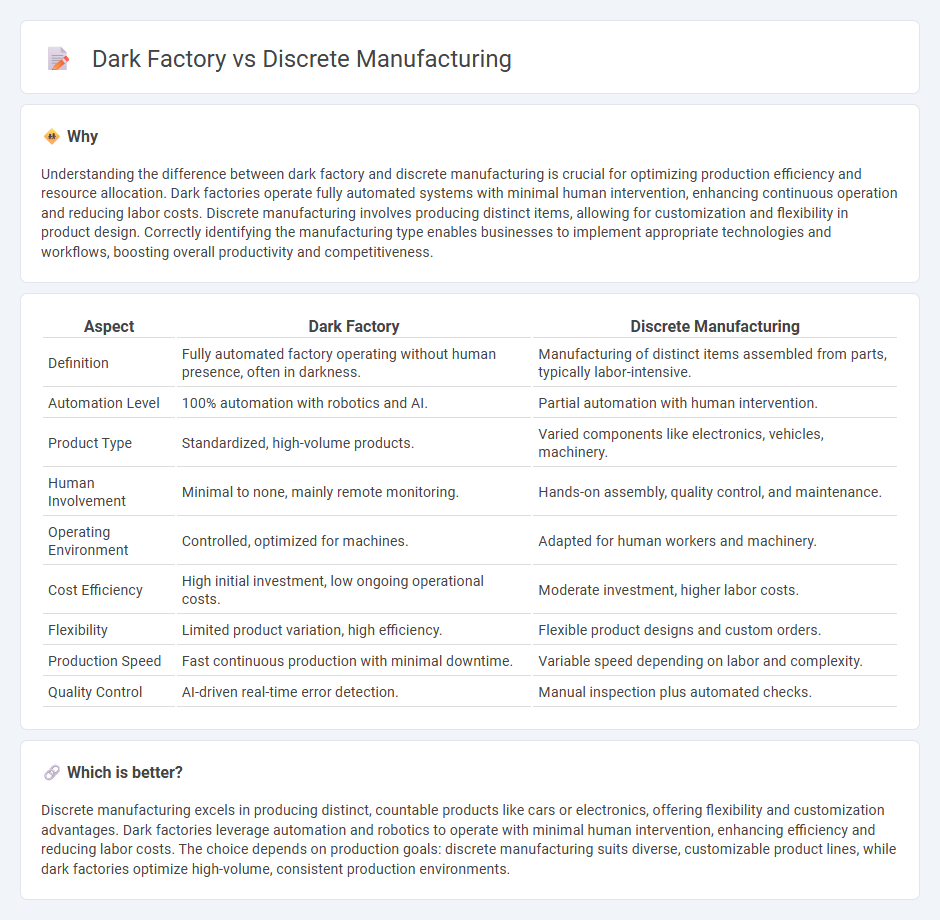
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Discrete Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence, often in darkness. | Manufacturing of distinct items assembled from parts, typically labor-intensive. |
| Automation Level | 100% automation with robotics and AI. | Partial automation with human intervention. |
| Product Type | Standardized, high-volume products. | Varied components like electronics, vehicles, machinery. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none, mainly remote monitoring. | Hands-on assembly, quality control, and maintenance. |
| Operating Environment | Controlled, optimized for machines. | Adapted for human workers and machinery. |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment, low ongoing operational costs. | Moderate investment, higher labor costs. |
| Flexibility | Limited product variation, high efficiency. | Flexible product designs and custom orders. |
| Production Speed | Fast continuous production with minimal downtime. | Variable speed depending on labor and complexity. |
| Quality Control | AI-driven real-time error detection. | Manual inspection plus automated checks. |
Which is better?
Discrete manufacturing excels in producing distinct, countable products like cars or electronics, offering flexibility and customization advantages. Dark factories leverage automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. The choice depends on production goals: discrete manufacturing suits diverse, customizable product lines, while dark factories optimize high-volume, consistent production environments.
Connection
Dark factories use advanced automation and robotics to enable continuous, unmanned production, optimizing efficiency and reducing human intervention. Discrete manufacturing, which produces distinct items such as automobiles or electronics, benefits from dark factory technology through enhanced precision, scalability, and real-time process monitoring. Integrating dark factory systems within discrete manufacturing streamlines operations, minimizes defects, and accelerates production cycles.
Key Terms
Unit Production
Discrete manufacturing focuses on producing distinct items such as cars, appliances, and electronics through assembly lines, emphasizing unit production and customization. Dark factories utilize advanced automation and robotics to operate without human presence, optimizing unit production efficiency and consistency in discrete manufacturing processes. Explore more to understand how integrating dark factory technologies revolutionizes unit production in discrete manufacturing.
Automation
Discrete manufacturing relies on automation systems such as robotics, CNC machines, and PLCs to enhance production efficiency and precision in assembling distinct units or components. Dark factories represent the next evolution, operating fully automated without human workers onsite, leveraging AI-driven robotics, IoT sensors, and advanced machine learning for continuous, error-free production. Explore how these automation technologies reshape industrial processes and reduce operational costs by learning more about their practical implementations.
Human Labor
Discrete manufacturing relies heavily on human labor for tasks like assembly, quality control, and machine operation, ensuring flexibility and quick adaptation to design changes. Dark factories minimize or eliminate human presence through automation and robotics, aiming for continuous, 24/7 production with reduced labor costs and fewer errors. Explore more about how these approaches impact efficiency and workforce dynamics in modern manufacturing environments.
Source and External Links
Discrete manufacturing - Wikipedia - Discrete manufacturing is the production of distinct, identifiable items such as automobiles, furniture, and smartphones, characterized by separate unit production and non-continuous processes, contrasting with process manufacturing of undifferentiated products like oil or salt.
Discrete vs. Process Manufacturing - How Do They Differ? - MRPeasy - Discrete manufacturing produces goods from individual components assembled along a production line, such as cars made with a bill of materials and sequential assembly steps.
Discrete Manufacturing - Oracle Help Center - Discrete manufacturing typically uses work orders for specific quantities and completion dates, involves routing instructions for independent operations, and is applied in environments like make-to-stock and engineer-to-order to produce items such as cars, furniture, and electronics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com