Microfactories focus on small-scale, flexible manufacturing units that enable rapid customization and localized production, reducing lead times and inventory costs. Batch production involves producing goods in set quantities, optimizing efficiency for medium to large-scale output but often resulting in longer setup times and higher storage needs. Explore further to understand which manufacturing method best suits your production goals and market demands.
Why it is important
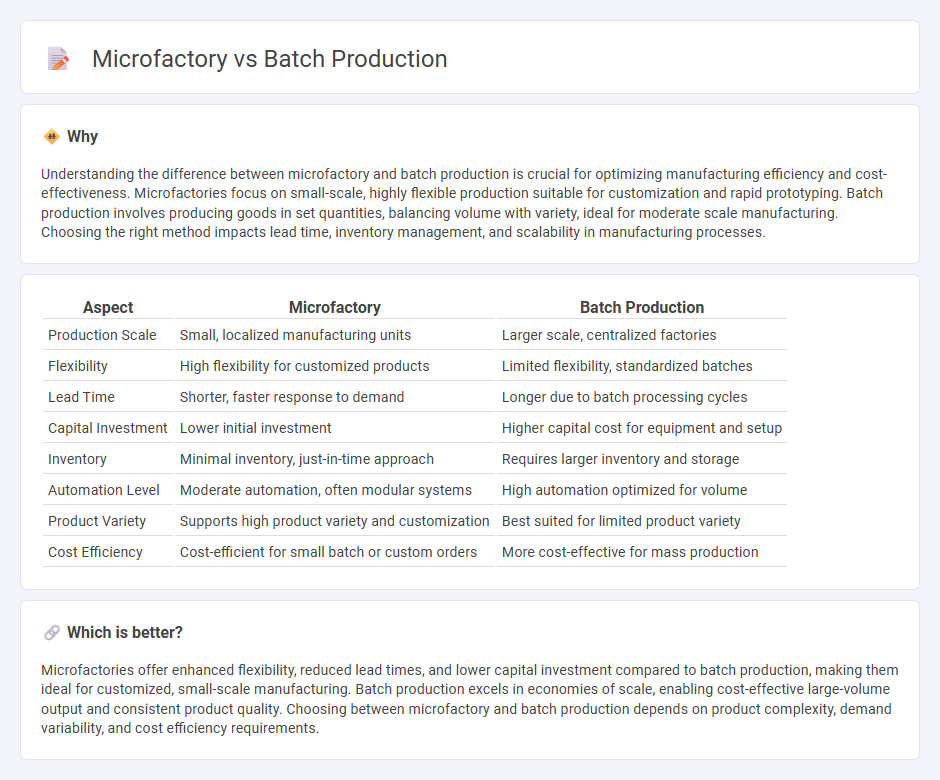
Understanding the difference between microfactory and batch production is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Microfactories focus on small-scale, highly flexible production suitable for customization and rapid prototyping. Batch production involves producing goods in set quantities, balancing volume with variety, ideal for moderate scale manufacturing. Choosing the right method impacts lead time, inventory management, and scalability in manufacturing processes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactory | Batch Production |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small, localized manufacturing units | Larger scale, centralized factories |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for customized products | Limited flexibility, standardized batches |
| Lead Time | Shorter, faster response to demand | Longer due to batch processing cycles |
| Capital Investment | Lower initial investment | Higher capital cost for equipment and setup |
| Inventory | Minimal inventory, just-in-time approach | Requires larger inventory and storage |
| Automation Level | Moderate automation, often modular systems | High automation optimized for volume |
| Product Variety | Supports high product variety and customization | Best suited for limited product variety |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-efficient for small batch or custom orders | More cost-effective for mass production |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer enhanced flexibility, reduced lead times, and lower capital investment compared to batch production, making them ideal for customized, small-scale manufacturing. Batch production excels in economies of scale, enabling cost-effective large-volume output and consistent product quality. Choosing between microfactory and batch production depends on product complexity, demand variability, and cost efficiency requirements.
Connection
Microfactories enhance batch production by enabling small-scale, flexible manufacturing runs that reduce setup times and lower inventory costs. Their compact design supports rapid customization and quick adjustments, aligning perfectly with the batch production model's emphasis on producing limited quantities of goods. This synergy improves efficiency and responsiveness in meeting market demands.
Key Terms
Scalability
Batch production offers scalability by allowing manufacturers to produce large quantities of identical products efficiently, but it requires significant setup time and inventory management. Microfactories enable scalable production through modular, flexible systems that quickly adapt to demand changes with minimal downtime and lower capital investment. Explore how these models impact scalability and operational efficiency to determine the best fit for your manufacturing needs.
Flexibility
Batch production offers limited flexibility due to its reliance on large-scale manufacturing runs and fixed processes, making it less adaptable to sudden changes in product design or demand. In contrast, microfactories utilize modular equipment and agile manufacturing techniques to quickly switch between products, allowing for customization and rapid response to market shifts. Explore how microfactories enhance operational flexibility and responsiveness in modern manufacturing.
Automation
Batch production relies on automated machinery to produce large quantities of identical products, maximizing efficiency through repetition and standardized processes. Microfactories integrate advanced automation and IoT technologies to enable flexible, small-scale manufacturing with rapid customization and minimal setup time. Discover how automation transforms production strategies by exploring the distinct benefits of batch production and microfactory models.
Source and External Links
What is batch production in manufacturing? - OneAdvanced - Batch production is a method where groups of identical products are produced simultaneously in batches through each stage of the manufacturing process, allowing flexibility such as changing specifications between batches and conducting quality checks at each step.
Batch Production - Benefits, Examples, and Tips - MRPeasy - Batch production involves processing sets of identical goods together through different manufacturing stages, offering flexibility, product variety, quality control, and cost advantages, but also leading to higher work-in-progress inventory and potential idle time.
Batch Production: Examples, Advantages and Disadvantages - Batch production produces groups of identical products at the same time, with each batch moving through production stages together, providing quality control and flexibility that distinguish it from other manufacturing processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com