Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing efficiency by promoting the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between different industries, reducing waste and environmental impact. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, conserving resources and lowering production costs through systematic disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of components. Explore how integrating industrial symbiosis with remanufacturing can drive sustainable growth in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and remanufacturing is crucial for optimizing sustainable manufacturing processes and resource efficiency. Industrial symbiosis involves the collaborative exchange of waste or by-products between industries to reduce environmental impact. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, extending product life cycles and reducing raw material consumption. Recognizing their distinct roles enables manufacturers to implement targeted strategies for waste reduction, cost savings, and circular economy advancement.
Comparison Table
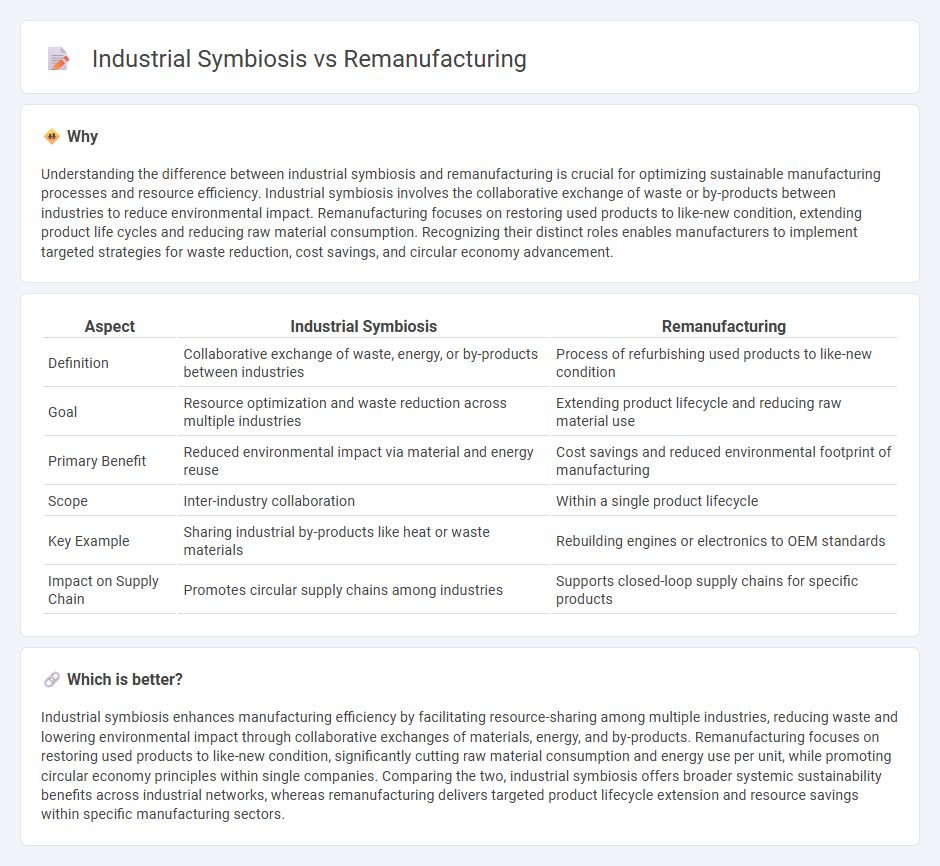
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Remanufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative exchange of waste, energy, or by-products between industries | Process of refurbishing used products to like-new condition |
| Goal | Resource optimization and waste reduction across multiple industries | Extending product lifecycle and reducing raw material use |
| Primary Benefit | Reduced environmental impact via material and energy reuse | Cost savings and reduced environmental footprint of manufacturing |
| Scope | Inter-industry collaboration | Within a single product lifecycle |
| Key Example | Sharing industrial by-products like heat or waste materials | Rebuilding engines or electronics to OEM standards |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Promotes circular supply chains among industries | Supports closed-loop supply chains for specific products |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing efficiency by facilitating resource-sharing among multiple industries, reducing waste and lowering environmental impact through collaborative exchanges of materials, energy, and by-products. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, significantly cutting raw material consumption and energy use per unit, while promoting circular economy principles within single companies. Comparing the two, industrial symbiosis offers broader systemic sustainability benefits across industrial networks, whereas remanufacturing delivers targeted product lifecycle extension and resource savings within specific manufacturing sectors.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis and remanufacturing are interconnected through their focus on resource efficiency and waste reduction within manufacturing processes. Industrial symbiosis promotes the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between companies to minimize waste, while remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, reducing the need for virgin materials. Both strategies support circular economy principles, enabling sustainable manufacturing ecosystems that lower environmental impact and enhance economic value.
Key Terms
Resource Recovery
Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, extending product life cycles and reducing raw material consumption, whereas industrial symbiosis focuses on collaboration between industries to utilize waste or by-products as resources. Both approaches enhance resource recovery by minimizing waste and maximizing material efficiency, contributing to circular economy goals. Explore further to understand how these strategies drive sustainable industrial practices and optimize resource utilization.
Closed-Loop Systems
Remanufacturing restores used products to like-new condition by disassembling, cleaning, and replacing parts within a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and resource consumption. Industrial symbiosis integrates multiple industries to exchange materials, energy, and by-products, creating a network that optimizes resource efficiency and supports circular economy goals. Explore how combining remanufacturing and industrial symbiosis fosters sustainable closed-loop systems for maximal environmental impact.
By-product Exchange
Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, reducing waste and resource consumption, while industrial symbiosis focuses on collaborative by-product exchange among industries to optimize resource efficiency and minimize environmental impact. By-product exchange in industrial symbiosis transforms waste streams from one company into valuable inputs for another, promoting circular economy principles. Explore how integrating remanufacturing and industrial symbiosis can enhance sustainable production and resource management.
Source and External Links
Remanufacturing - Wikipedia - Remanufacturing is the rebuilding of a product to original specifications using reused, repaired, and new parts, resulting in a product that meets the same performance standards as a new one and is significant for waste reduction and resource conservation.
Remanufacturing 101: Reviving parts, reclaiming value - McKinsey - Remanufacturing is a complex process involving multiple steps to restore used parts for a second life, helping mitigate supply chain shortages, reduce raw material dependence, and extend product life cycles across industries like automotive and electronics.
What Does Remanufactured Mean? - TWI - This industrial process disassembles, cleans, repairs, and replaces worn components to return products to a "like-new" condition, supporting a circular economy by reducing waste and environmental impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com