Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products and processes that maximize resource efficiency by promoting reuse, recycling, and minimizing waste throughout the product lifecycle. Remanufacturing, a key component of circular manufacturing, involves restoring used products to like-new condition, significantly reducing material consumption and energy use compared to new production. Explore more to understand how integrating circular manufacturing and remanufacturing can drive sustainable industrial innovation.
Why it is important
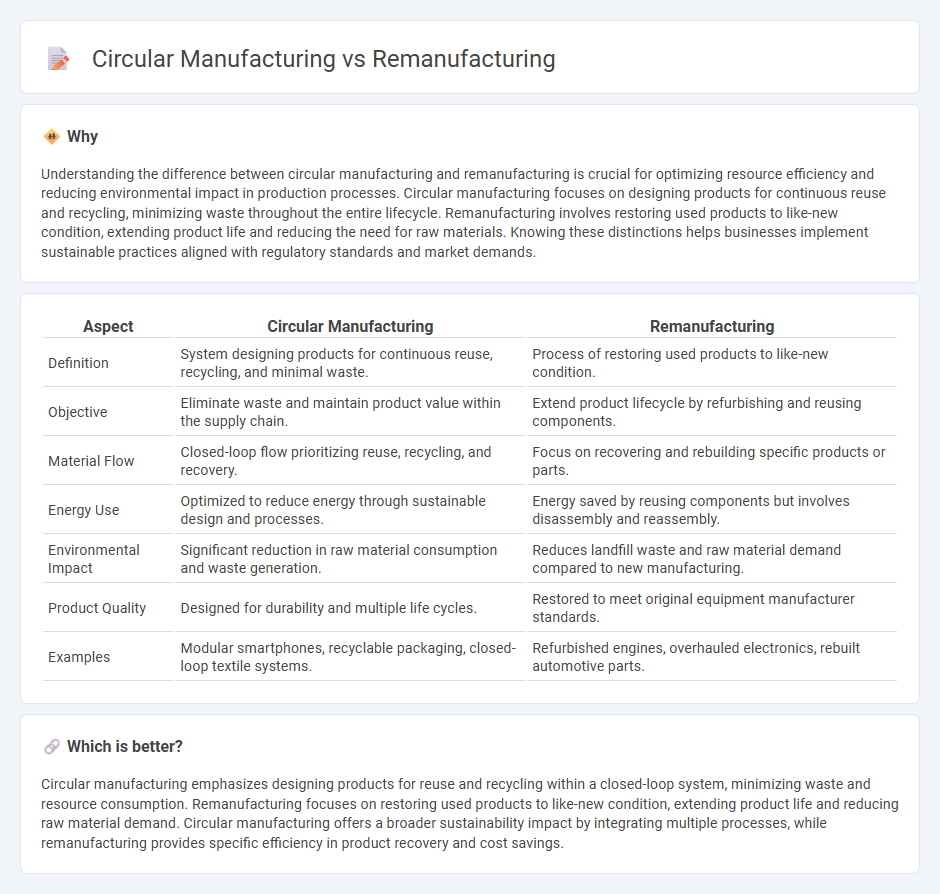
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and remanufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact in production processes. Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products for continuous reuse and recycling, minimizing waste throughout the entire lifecycle. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, extending product life and reducing the need for raw materials. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses implement sustainable practices aligned with regulatory standards and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Remanufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System designing products for continuous reuse, recycling, and minimal waste. | Process of restoring used products to like-new condition. |
| Objective | Eliminate waste and maintain product value within the supply chain. | Extend product lifecycle by refurbishing and reusing components. |
| Material Flow | Closed-loop flow prioritizing reuse, recycling, and recovery. | Focus on recovering and rebuilding specific products or parts. |
| Energy Use | Optimized to reduce energy through sustainable design and processes. | Energy saved by reusing components but involves disassembly and reassembly. |
| Environmental Impact | Significant reduction in raw material consumption and waste generation. | Reduces landfill waste and raw material demand compared to new manufacturing. |
| Product Quality | Designed for durability and multiple life cycles. | Restored to meet original equipment manufacturer standards. |
| Examples | Modular smartphones, recyclable packaging, closed-loop textile systems. | Refurbished engines, overhauled electronics, rebuilt automotive parts. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing emphasizes designing products for reuse and recycling within a closed-loop system, minimizing waste and resource consumption. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, extending product life and reducing raw material demand. Circular manufacturing offers a broader sustainability impact by integrating multiple processes, while remanufacturing provides specific efficiency in product recovery and cost savings.
Connection
Circular manufacturing integrates remanufacturing by emphasizing the reuse and restoration of products to extend their lifecycle, thereby reducing waste and resource consumption. Remanufacturing plays a crucial role within circular manufacturing by rebuilding used products to like-new condition, supporting sustainability and economic efficiency. This synergy enhances material circularity, lowers environmental impact, and promotes a closed-loop production system.
Key Terms
Product Lifecycle
Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to a like-new condition by disassembling, cleaning, repairing, and replacing components, extending the product lifecycle significantly. Circular manufacturing emphasizes designing products and processes for continuous reuse, recycling, and minimal waste, aiming to close the loop in the product lifecycle. Explore detailed strategies to optimize product longevity and sustainability in circular manufacturing.
Resource Recovery
Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, emphasizing material and component reuse to minimize waste and energy consumption, while circular manufacturing integrates resource recovery strategies to maintain continuous material flow through recycling and refurbishment. Resource recovery in circular manufacturing prioritizes reclaiming raw materials from end-of-life products, reducing dependence on virgin resources, and enhancing overall sustainability. Explore the differences and synergies between these approaches to optimize resource efficiency and environmental impact.
Closed-Loop System
Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, emphasizing product lifespan extension and resource efficiency within a closed-loop system where materials and components are repeatedly cycled. Circular manufacturing expands on this by integrating design, production, and recovery processes, ensuring minimal waste through continuous reuse and recycling, fostering sustainability at the system level. Explore the intricate dynamics of closed-loop systems in remanufacturing and circular manufacturing to fully understand their impact on sustainable industrial practices.
Source and External Links
Remanufacturing - Wikipedia - Remanufacturing is the rebuilding of a product to original specifications using a combination of reused, repaired, and new parts, ensuring the remanufactured item performs like new, and it plays a growing role in waste reduction and resource conservation in industries such as automotive parts.
What Is Remanufacturing? Definition, Benefits and Types | Indeed.com - Remanufacturing involves disassembling used products, replacing or repairing degraded components, and reassembling them to meet original manufacturing standards, effectively extending product lifecycles and reducing waste.
Remanufacturing 101: Reviving parts, reclaiming value - McKinsey - The remanufacturing process, important for reducing supply chain issues and raw material dependency, includes steps like disassembly, inspection, reconditioning, and reassembly, offering cost savings and environmental benefits especially in automotive and medical sectors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com