Remanufacturing involves completely disassembling, inspecting, and restoring products to like-new condition using original specifications and replacing worn components, while refurbishing typically includes cleaning, repairing, and updating products without full teardown. Remanufactured products often meet or exceed original quality standards and include warranties similar to new items, whereas refurbished goods may vary in quality and offer limited guarantees. Discover more about how these processes impact sustainability and cost-efficiency in manufacturing.
Why it is important
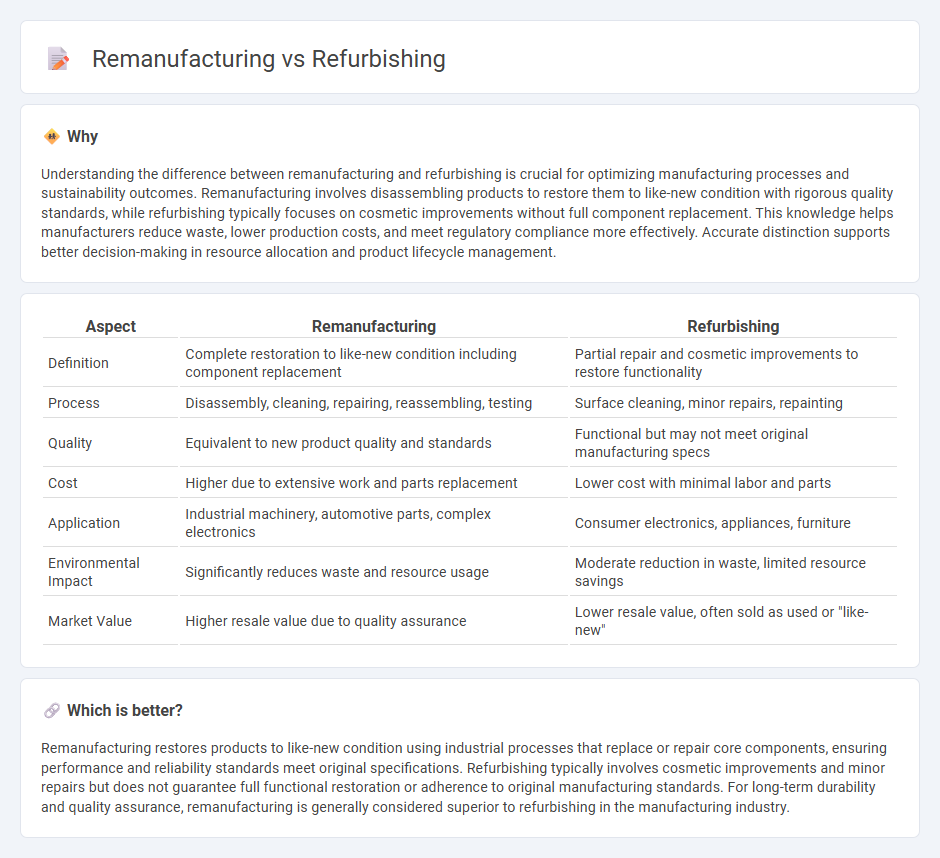
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and refurbishing is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and sustainability outcomes. Remanufacturing involves disassembling products to restore them to like-new condition with rigorous quality standards, while refurbishing typically focuses on cosmetic improvements without full component replacement. This knowledge helps manufacturers reduce waste, lower production costs, and meet regulatory compliance more effectively. Accurate distinction supports better decision-making in resource allocation and product lifecycle management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Refurbishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete restoration to like-new condition including component replacement | Partial repair and cosmetic improvements to restore functionality |
| Process | Disassembly, cleaning, repairing, reassembling, testing | Surface cleaning, minor repairs, repainting |
| Quality | Equivalent to new product quality and standards | Functional but may not meet original manufacturing specs |
| Cost | Higher due to extensive work and parts replacement | Lower cost with minimal labor and parts |
| Application | Industrial machinery, automotive parts, complex electronics | Consumer electronics, appliances, furniture |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduces waste and resource usage | Moderate reduction in waste, limited resource savings |
| Market Value | Higher resale value due to quality assurance | Lower resale value, often sold as used or "like-new" |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing restores products to like-new condition using industrial processes that replace or repair core components, ensuring performance and reliability standards meet original specifications. Refurbishing typically involves cosmetic improvements and minor repairs but does not guarantee full functional restoration or adherence to original manufacturing standards. For long-term durability and quality assurance, remanufacturing is generally considered superior to refurbishing in the manufacturing industry.
Connection
Remanufacturing and refurbishing share a common goal of extending the lifecycle of products by restoring used items to a functional or like-new condition. Remanufacturing involves a complete disassembly, thorough inspection, and replacement of worn components to meet original specifications, primarily applied in automotive and industrial machinery sectors. Refurbishing typically focuses on repairing and cosmetic improvements to enhance appearance and usability, often used for electronics and consumer goods.
Key Terms
Restoration Process
Refurbishing involves repairing and restoring used products by replacing worn parts and improving cosmetic condition to extend lifecycle without altering original design; remanufacturing goes further by disassembling, inspecting, and rebuilding components to meet original factory specifications, often resulting in a product indistinguishable from new. Both processes reduce waste and lower environmental impact, but remanufacturing typically requires more technical expertise and stringent quality controls. Explore detailed insights on how these restoration processes enhance product sustainability and value.
Quality Standards
Refurbishing restores used products by cleaning and repairing to meet basic functional standards, often resulting in variable quality outcomes depending on the extent of repairs. Remanufacturing follows stringent quality standards set by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), involving complete disassembly, inspection, replacement of worn parts, and rigorous testing to ensure performance equivalent to new products. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how quality benchmarks impact product lifecycle and customer trust.
Warranty/Certification
Refurbishing typically involves repairing and restoring products to a functional condition, often with limited or no warranty compared to the original, while remanufacturing restores products to like-new condition and includes full warranties and certifications that meet original equipment manufacturer (OEM) standards. Remanufactured items undergo thorough testing and quality control processes to ensure reliability and compliance, providing customers with assurance similar to new products. Explore deeper insights into warranty and certification differences between refurbishing and remanufacturing to enhance procurement decisions.
Source and External Links
Refinishing vs. Refurbishing - Refurbishing is a comprehensive process that restores both the appearance and structural integrity of furniture, including repairing damage, replacing upholstery, and restoring hardware for a complete overhaul.
Refurbish - Meaning and Importance in the Maintenance - Refurbishing involves cleaning, repairing, and replacing parts to restore equipment or machinery to optimal working condition, extending asset life and reducing operational costs.
REFURBISH | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - To refurbish means to make a building or object look new again by painting, repairing, and cleaning, often without major structural changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com