Lattice structure design in manufacturing offers enhanced strength-to-weight ratios by strategically distributing material in a lightweight framework, contrasting with solid structure design which relies on uniform material distribution for robustness. Advanced additive manufacturing techniques enable the production of complex lattice geometries that optimize mechanical performance and reduce material consumption. Explore the differences and advantages of these design approaches to innovate your manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
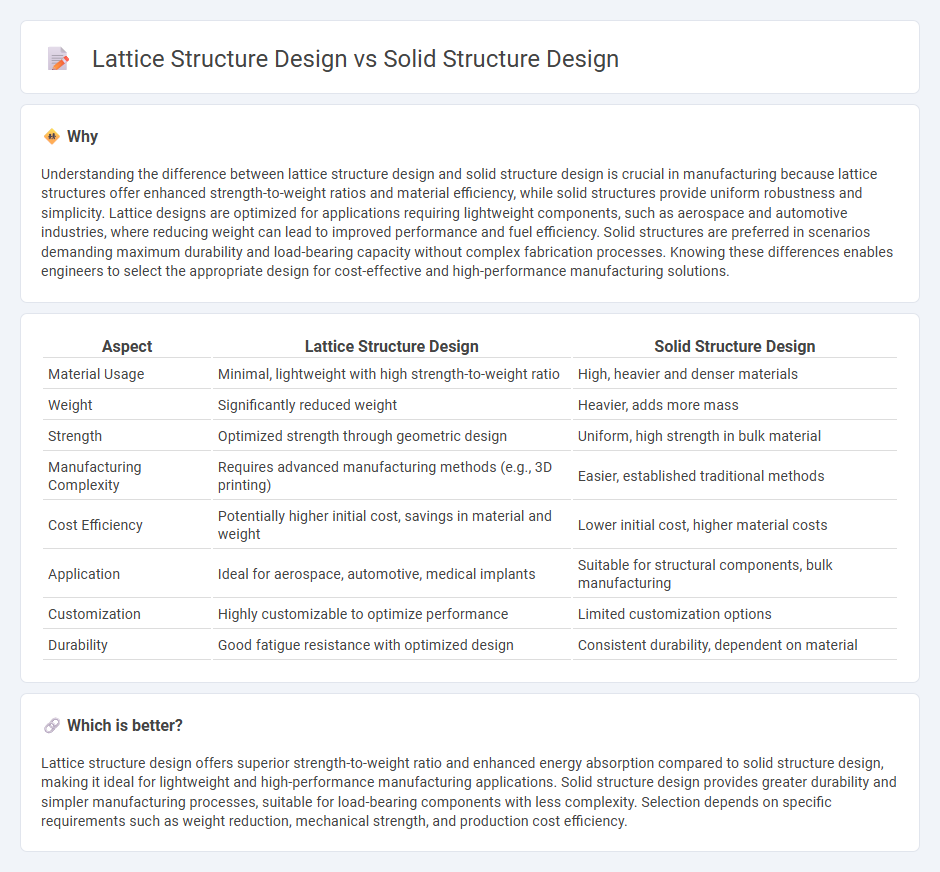
Understanding the difference between lattice structure design and solid structure design is crucial in manufacturing because lattice structures offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and material efficiency, while solid structures provide uniform robustness and simplicity. Lattice designs are optimized for applications requiring lightweight components, such as aerospace and automotive industries, where reducing weight can lead to improved performance and fuel efficiency. Solid structures are preferred in scenarios demanding maximum durability and load-bearing capacity without complex fabrication processes. Knowing these differences enables engineers to select the appropriate design for cost-effective and high-performance manufacturing solutions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lattice Structure Design | Solid Structure Design |
|---|---|---|
| Material Usage | Minimal, lightweight with high strength-to-weight ratio | High, heavier and denser materials |
| Weight | Significantly reduced weight | Heavier, adds more mass |
| Strength | Optimized strength through geometric design | Uniform, high strength in bulk material |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Requires advanced manufacturing methods (e.g., 3D printing) | Easier, established traditional methods |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher initial cost, savings in material and weight | Lower initial cost, higher material costs |
| Application | Ideal for aerospace, automotive, medical implants | Suitable for structural components, bulk manufacturing |
| Customization | Highly customizable to optimize performance | Limited customization options |
| Durability | Good fatigue resistance with optimized design | Consistent durability, dependent on material |
Which is better?
Lattice structure design offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced energy absorption compared to solid structure design, making it ideal for lightweight and high-performance manufacturing applications. Solid structure design provides greater durability and simpler manufacturing processes, suitable for load-bearing components with less complexity. Selection depends on specific requirements such as weight reduction, mechanical strength, and production cost efficiency.
Connection
Lattice structure design and solid structure design are connected through their complementary roles in optimizing material use and mechanical performance in manufacturing. Lattice structures reduce weight while maintaining strength, whereas solid structures provide robustness and support in critical areas. Integrating both designs enhances product efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness in advanced manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
Density
Solid structure design features a uniform, high-density material distribution, resulting in robust mechanical strength but increased weight and material consumption. Lattice structure design optimizes density by incorporating a network of interconnected voids, significantly reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity through efficient load distribution. Explore the advantages of density optimization in both designs to enhance material efficiency and performance.
Mechanical Strength
Solid structure design offers superior mechanical strength due to its continuous material distribution, resulting in high load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation. Lattice structure design reduces weight and material usage while maintaining adequate mechanical strength through strategically arranged geometric patterns that optimize stress distribution. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which design best suits your engineering requirements.
Material Efficiency
Solid structure design typically involves dense, uniform materials that provide high strength but often result in increased material consumption and weight. Lattice structure design utilizes intricate geometric patterns to optimize load distribution while significantly reducing material usage and overall component weight. Explore the advances in lattice structuring to enhance material efficiency and structural performance.
Source and External Links
The Best Way to Build a Solid Structure: Key Principles and Techniques - A solid structure requires a strong foundation, high-quality materials, design for structural integrity including load distribution and seismic resistance, and strict adherence to building codes and safety regulations.
Solid construction - The German's favorite - Solid structures are made from non-flammable materials offering better sound protection and longevity than timber, but timber can also last centuries if well constructed and maintained.
Structural Steel Design with SOLIDWORKS - Structural steel design can be optimized and detailed using SOLIDWORKS software, facilitating efficient construction processes and manufacturing integration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com