Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to a like-new condition through complete disassembly, inspection, and replacement of worn components, ensuring original performance standards. Reconditioning typically focuses on repairing or refurbishing specific parts to extend product life without full teardown or replacement. Explore more about how these processes impact sustainability and cost-efficiency in manufacturing.
Why it is important
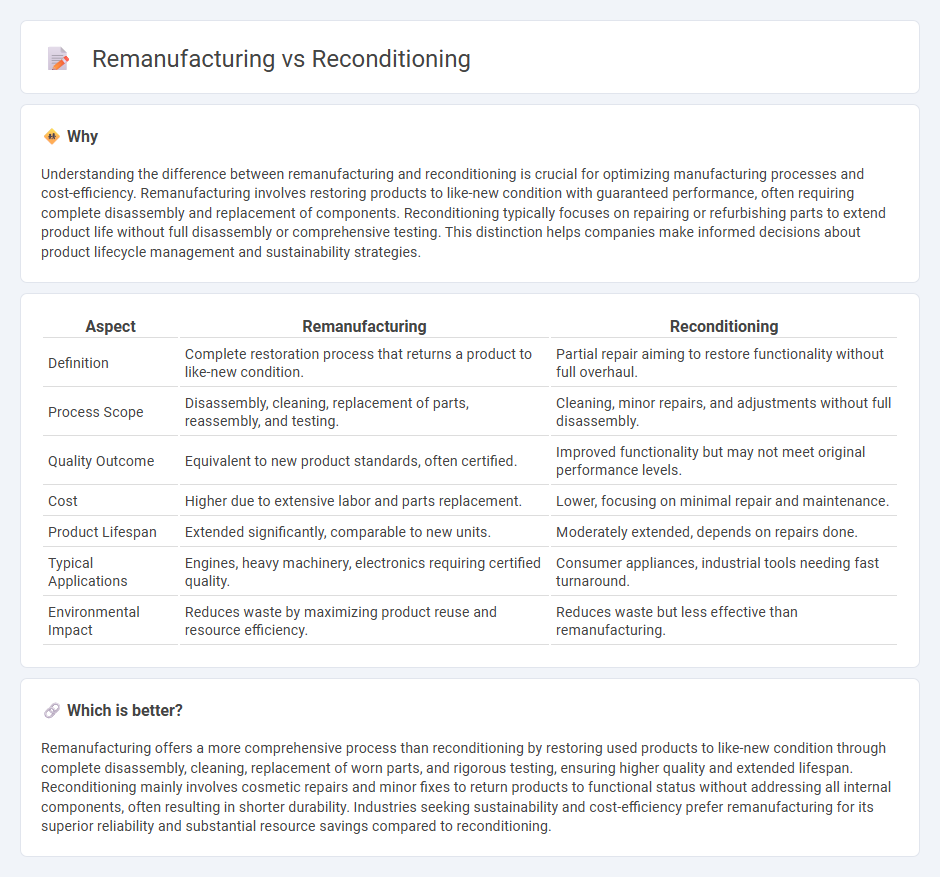
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and reconditioning is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and cost-efficiency. Remanufacturing involves restoring products to like-new condition with guaranteed performance, often requiring complete disassembly and replacement of components. Reconditioning typically focuses on repairing or refurbishing parts to extend product life without full disassembly or comprehensive testing. This distinction helps companies make informed decisions about product lifecycle management and sustainability strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Reconditioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete restoration process that returns a product to like-new condition. | Partial repair aiming to restore functionality without full overhaul. |
| Process Scope | Disassembly, cleaning, replacement of parts, reassembly, and testing. | Cleaning, minor repairs, and adjustments without full disassembly. |
| Quality Outcome | Equivalent to new product standards, often certified. | Improved functionality but may not meet original performance levels. |
| Cost | Higher due to extensive labor and parts replacement. | Lower, focusing on minimal repair and maintenance. |
| Product Lifespan | Extended significantly, comparable to new units. | Moderately extended, depends on repairs done. |
| Typical Applications | Engines, heavy machinery, electronics requiring certified quality. | Consumer appliances, industrial tools needing fast turnaround. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste by maximizing product reuse and resource efficiency. | Reduces waste but less effective than remanufacturing. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing offers a more comprehensive process than reconditioning by restoring used products to like-new condition through complete disassembly, cleaning, replacement of worn parts, and rigorous testing, ensuring higher quality and extended lifespan. Reconditioning mainly involves cosmetic repairs and minor fixes to return products to functional status without addressing all internal components, often resulting in shorter durability. Industries seeking sustainability and cost-efficiency prefer remanufacturing for its superior reliability and substantial resource savings compared to reconditioning.
Connection
Remanufacturing and reconditioning are connected through their focus on extending the life cycle of products by restoring used components to functional condition. Remanufacturing involves a comprehensive process of disassembly, cleaning, repairing, and testing to meet original equipment manufacturer (OEM) standards, while reconditioning typically entails less extensive refurbishment to improve performance or appearance. Both practices contribute significantly to sustainable manufacturing by reducing waste, lowering resource consumption, and promoting circular economy principles.
Key Terms
Restoration
Reconditioning involves restoring a product to its original working condition through cleaning, repairing, and replacing worn parts, typically without disassembling the entire unit. Remanufacturing goes deeper by completely disassembling, inspecting, and rebuilding the product to meet or exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) standards with like-new performance. Explore the key differences and benefits of each process to determine the best restoration method for your needs.
Original Specifications
Reconditioning involves restoring a product to a functional state, typically by cleaning, repairing, or replacing minor parts, but it may not fully meet original specifications. Remanufacturing, by contrast, rebuilds a product to meet or exceed original manufacturer specifications through comprehensive disassembly, inspection, and component replacement. Explore the differences in their processes and outcomes to understand which method best suits your needs.
Component Replacement
Component replacement in reconditioning involves restoring a part to its original working condition by repairing or refurbishing existing components, whereas remanufacturing replaces worn components with new or factory-reset parts to meet original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications. Remanufactured products typically undergo more rigorous testing and quality control to ensure performance parity with new products, while reconditioning may focus on cost-effective fixes without full teardown. To explore the detailed processes and benefits of component replacement in both methods, learn more about industry standards and applications.
Source and External Links
The difference between remanufacturing and reconditioning | Rematec - Reconditioning is a process used to repair and restore auto parts or vehicles to a good condition, distinct from remanufacturing, and often misunderstood despite its environmental and economic benefits in the automotive industry.
What Is Vehicle Reconditioning and Why Should I Care? - Autoweb - Vehicle reconditioning involves inspecting, repairing, cleaning, and preparing a used car to be sellable, including detailed checks, mechanical fixes, and odor removal to improve its market condition.
Reconditioning: Extremely critical and highly misunderstood - Reconditioning is a fundamental but often overlooked part of dealership operations that affects sales, customer retention, and service quality, involving setting clear standards for repairs and maintenance tasks to ensure a vehicle's readiness for sale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com