Digital twin technology creates a precise virtual replica of physical manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize production efficiency. In contrast, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, fabricates physical objects layer by layer directly from digital models, allowing for rapid prototyping and complex designs. Explore how these technologies revolutionize manufacturing workflows and enhance operational capabilities.
Why it is important
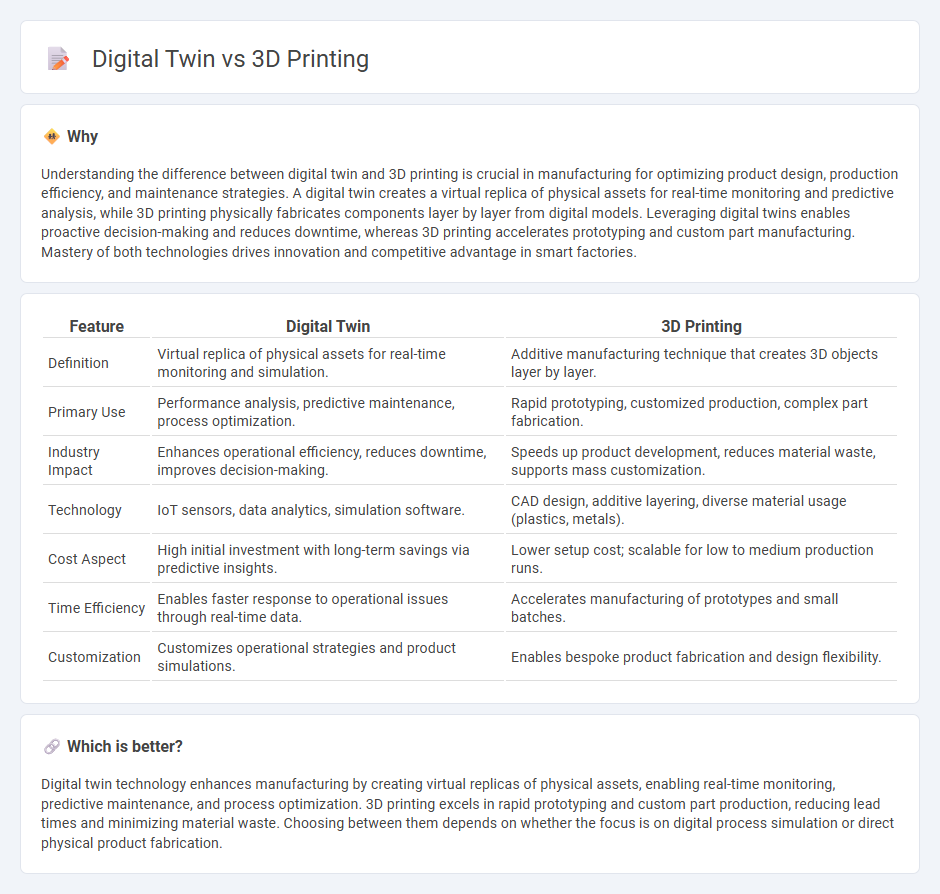
Understanding the difference between digital twin and 3D printing is crucial in manufacturing for optimizing product design, production efficiency, and maintenance strategies. A digital twin creates a virtual replica of physical assets for real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, while 3D printing physically fabricates components layer by layer from digital models. Leveraging digital twins enables proactive decision-making and reduces downtime, whereas 3D printing accelerates prototyping and custom part manufacturing. Mastery of both technologies drives innovation and competitive advantage in smart factories.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twin | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets for real-time monitoring and simulation. | Additive manufacturing technique that creates 3D objects layer by layer. |
| Primary Use | Performance analysis, predictive maintenance, process optimization. | Rapid prototyping, customized production, complex part fabrication. |
| Industry Impact | Enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, improves decision-making. | Speeds up product development, reduces material waste, supports mass customization. |
| Technology | IoT sensors, data analytics, simulation software. | CAD design, additive layering, diverse material usage (plastics, metals). |
| Cost Aspect | High initial investment with long-term savings via predictive insights. | Lower setup cost; scalable for low to medium production runs. |
| Time Efficiency | Enables faster response to operational issues through real-time data. | Accelerates manufacturing of prototypes and small batches. |
| Customization | Customizes operational strategies and product simulations. | Enables bespoke product fabrication and design flexibility. |
Which is better?
Digital twin technology enhances manufacturing by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. 3D printing excels in rapid prototyping and custom part production, reducing lead times and minimizing material waste. Choosing between them depends on whether the focus is on digital process simulation or direct physical product fabrication.
Connection
Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical manufacturing processes, allowing real-time simulation and analysis to optimize production. 3D printing leverages these digital models to fabricate complex parts with precision, reducing prototyping time and material waste. Integrating digital twins with 3D printing enhances product customization, accelerates design iterations, and improves overall manufacturing efficiency.
Key Terms
3D Printing:
3D printing revolutionizes manufacturing by enabling rapid prototyping and complex geometries with materials like plastics, metals, and ceramics, significantly reducing production time and cost. This additive manufacturing process supports customization in industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive, enhancing product innovation and functionality. Explore further to understand the transformative impact of 3D printing technologies across various sectors.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing leverages 3D printing technology to create physical objects layer by layer, enabling rapid prototyping and complex geometries. Digital twins complement this process by providing virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization of manufacturing workflows. Explore how integrating 3D printing with digital twin technology can revolutionize additive manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Layer-by-Layer Fabrication
Layer-by-layer fabrication distinguishes 3D printing by physically constructing objects through additive manufacturing, enabling complex geometries and rapid prototyping. Digital twins employ virtual layer-by-layer modeling to simulate and optimize physical processes without material waste. Explore how these technologies uniquely leverage layer-layer fabrication for innovation and efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is 3D Printing? | 3D Printing Software - 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that builds objects layer by layer from heated or melted material controlled by a print head, used for everything from small prototypes to large structures like houses and cars, with cost and build time depending on size, complexity, and material.
3D printing - Wikipedia - 3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, constructs three-dimensional objects from digital 3D models by depositing material layer by layer, enabling creation of complex geometries not possible with traditional methods, and has evolved from rapid prototyping to industrial production.
3D printing: What is it & how does it work? - 3D printing is widely used for prototyping and customized production in aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing, leveraging design freedom and material innovations to produce complex, lightweight, or consolidated parts quickly and cost-effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com