Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products and processes that enable continuous reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials, minimizing waste and resource consumption. Green manufacturing emphasizes eco-friendly practices by reducing energy use, emissions, and pollutants during production to lower environmental impact. Explore in-depth differences and advantages of circular versus green manufacturing to optimize sustainability strategies.
Why it is important
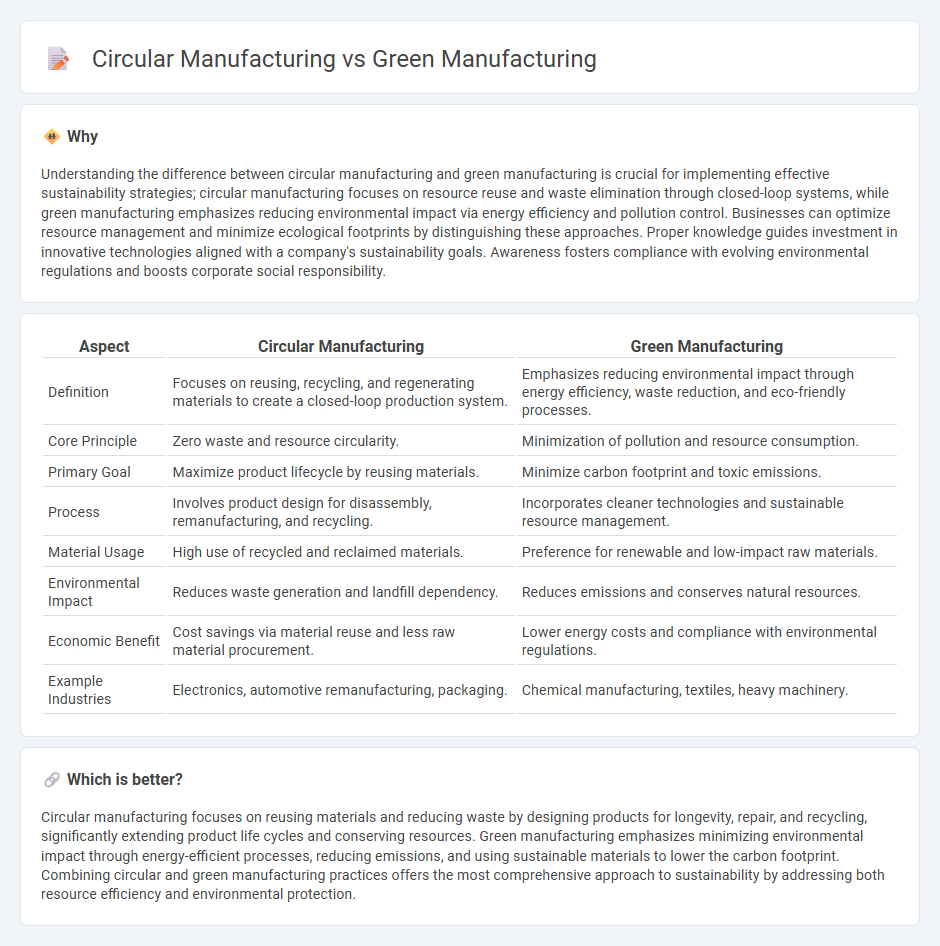
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and green manufacturing is crucial for implementing effective sustainability strategies; circular manufacturing focuses on resource reuse and waste elimination through closed-loop systems, while green manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact via energy efficiency and pollution control. Businesses can optimize resource management and minimize ecological footprints by distinguishing these approaches. Proper knowledge guides investment in innovative technologies aligned with a company's sustainability goals. Awareness fosters compliance with evolving environmental regulations and boosts corporate social responsibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Green Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials to create a closed-loop production system. | Emphasizes reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency, waste reduction, and eco-friendly processes. |
| Core Principle | Zero waste and resource circularity. | Minimization of pollution and resource consumption. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize product lifecycle by reusing materials. | Minimize carbon footprint and toxic emissions. |
| Process | Involves product design for disassembly, remanufacturing, and recycling. | Incorporates cleaner technologies and sustainable resource management. |
| Material Usage | High use of recycled and reclaimed materials. | Preference for renewable and low-impact raw materials. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste generation and landfill dependency. | Reduces emissions and conserves natural resources. |
| Economic Benefit | Cost savings via material reuse and less raw material procurement. | Lower energy costs and compliance with environmental regulations. |
| Example Industries | Electronics, automotive remanufacturing, packaging. | Chemical manufacturing, textiles, heavy machinery. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing focuses on reusing materials and reducing waste by designing products for longevity, repair, and recycling, significantly extending product life cycles and conserving resources. Green manufacturing emphasizes minimizing environmental impact through energy-efficient processes, reducing emissions, and using sustainable materials to lower the carbon footprint. Combining circular and green manufacturing practices offers the most comprehensive approach to sustainability by addressing both resource efficiency and environmental protection.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and green manufacturing both focus on reducing environmental impact by promoting resource efficiency and waste minimization. Circular manufacturing enhances sustainability through product lifecycle extension, reuse, and recycling, directly supporting green manufacturing's goals of lowering carbon emissions and conserving raw materials. Integrating circular principles within green manufacturing processes leads to more sustainable production systems and a reduced ecological footprint.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Green manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact by minimizing waste and using renewable energy, while circular manufacturing focuses on resource efficiency through reuse, recycling, and designing products for longevity and closed-loop systems. Circular manufacturing creates a regenerative supply chain that maximizes material value, whereas green manufacturing aims primarily at lowering emissions and conserving resources. Explore detailed strategies to enhance resource efficiency in both models for sustainable industrial growth.
Waste Minimization
Green manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through efficient resource use and lowering emissions, targeting waste minimization by preventing pollution and conserving materials. Circular manufacturing advances this approach by designing products for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, creating closed-loop systems that eliminate waste generation entirely. Explore how integrating circular principles transforms waste management strategies for sustainable industrial growth.
Closed-Loop Systems
Green manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency and waste minimization, while circular manufacturing centers on closed-loop systems that reclaim, refurbish, and recycle materials to create a regenerative production cycle. Closed-loop systems are integral to circular manufacturing, ensuring that end-of-life products re-enter the supply chain, minimizing resource extraction and landfill waste. Explore how closed-loop strategies can transform sustainability and economic efficiency in modern manufacturing.
Source and External Links
What Is Green Manufacturing? - Green manufacturing is the creation of products in a way that reduces the overall carbon footprint by minimizing negative environmental impacts and conserving energy and resources, using renewable energy, efficient equipment, and sustainable materials.
What is Green Manufacturing? (Plus 5 Steps to a Greener ...) - Green manufacturing focuses on producing goods with minimal environmental impact and resource use by adopting lean manufacturing principles and eco-friendly processes to increase sustainability and cost savings.
Sustainable Manufacturing | US EPA - Sustainable manufacturing involves economically sound processes that reduce environmental impacts and conserve resources while improving operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and market competitiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com