Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in manufacturing focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry and order processing, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Process control involves real-time monitoring and regulation of manufacturing operations through sensors and control systems to maintain product quality and operational stability. Explore the key differences and applications of RPA and process control to optimize manufacturing workflows.
Why it is important
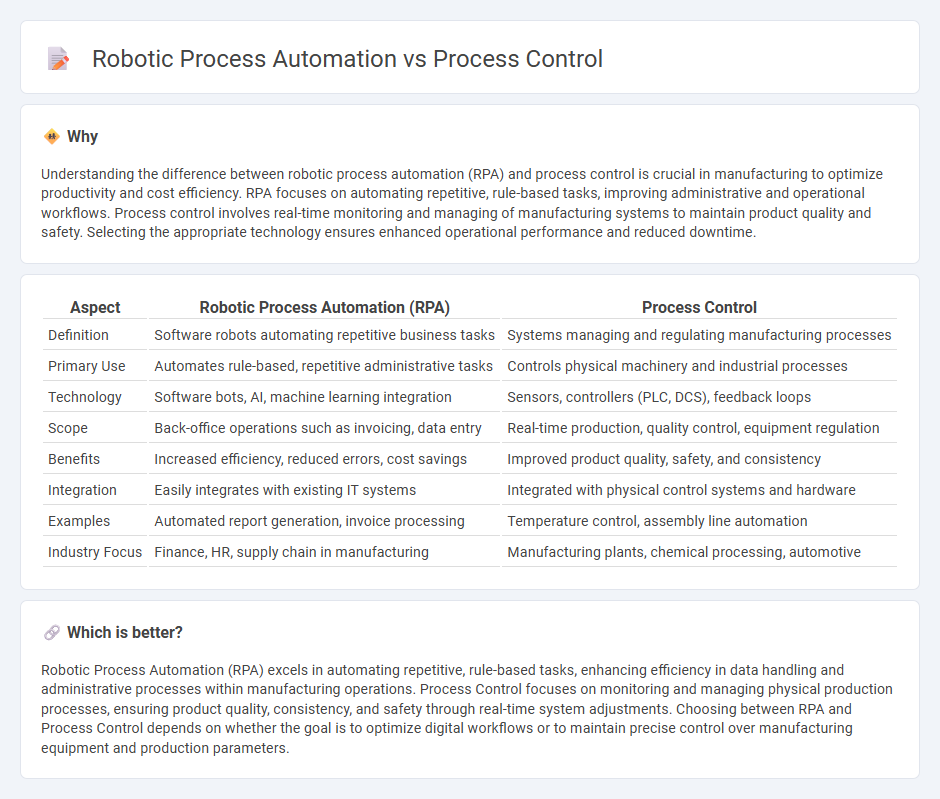
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and process control is crucial in manufacturing to optimize productivity and cost efficiency. RPA focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, improving administrative and operational workflows. Process control involves real-time monitoring and managing of manufacturing systems to maintain product quality and safety. Selecting the appropriate technology ensures enhanced operational performance and reduced downtime.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Process Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive business tasks | Systems managing and regulating manufacturing processes |
| Primary Use | Automates rule-based, repetitive administrative tasks | Controls physical machinery and industrial processes |
| Technology | Software bots, AI, machine learning integration | Sensors, controllers (PLC, DCS), feedback loops |
| Scope | Back-office operations such as invoicing, data entry | Real-time production, quality control, equipment regulation |
| Benefits | Increased efficiency, reduced errors, cost savings | Improved product quality, safety, and consistency |
| Integration | Easily integrates with existing IT systems | Integrated with physical control systems and hardware |
| Examples | Automated report generation, invoice processing | Temperature control, assembly line automation |
| Industry Focus | Finance, HR, supply chain in manufacturing | Manufacturing plants, chemical processing, automotive |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, enhancing efficiency in data handling and administrative processes within manufacturing operations. Process Control focuses on monitoring and managing physical production processes, ensuring product quality, consistency, and safety through real-time system adjustments. Choosing between RPA and Process Control depends on whether the goal is to optimize digital workflows or to maintain precise control over manufacturing equipment and production parameters.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive tasks within Process Control systems, leading to improved accuracy and reduced human error. Integrating RPA with Process Control allows real-time data monitoring and adaptive decision-making, optimizing production workflows. This synergy drives cost savings and increases overall operational productivity in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
**Process control:**
Process control involves monitoring and managing industrial processes to maintain desired output quality, efficiency, and safety by using sensors, controllers, and feedback loops. It is critical in manufacturing industries such as chemical production, automotive assembly, and food processing, where real-time adjustments ensure optimal performance and minimize downtime. Explore detailed insights on how process control systems enhance operational reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Feedback loop
Process control systems maintain operational stability by continuously monitoring feedback loops to adjust variables in real-time, ensuring precise control over industrial processes. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive tasks by integrating software bots without inherent real-time feedback mechanisms, relying on predefined rules rather than dynamic process adjustments. Explore the distinct roles of feedback loops in enhancing efficiency and accuracy within both process control and RPA environments.
Sensors
Process control leverages sensors to monitor variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates, enabling real-time adjustments for optimized system performance in manufacturing and industrial settings. Robotic Process Automation (RPA), on the other hand, primarily utilizes software-based sensors to track digital inputs and user interactions, automating rule-based tasks without physical sensor integration. Explore more about how sensor technologies differentiate process control from robotic process automation and enhance operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Industrial process control - Wikipedia - Process control is a system in manufacturing using control theory and automation to monitor, control, and optimize continuous industrial processes, ensuring smooth, safe operation and energy efficiency via feedback loops and controllers like PLCs and DCSs.
What is Process Control in Manufacturing? - Precognize - Process control involves procedures that automatically manage production conditions using feedback loops and sensors to maintain quality, throughput, and efficiency in manufacturing plants, enhanced today with AI and machine learning technologies.
What is Process Control? - Petrotech Inc - Process control is the monitoring and adjusting of process parameters to achieve desired output, providing benefits such as energy efficiency, increased automation and throughput, quality assurance, and improved safety in industrial processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com