Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers a flexible, on-demand manufacturing model that leverages cloud-based solutions to optimize production without heavy upfront investment, contrasting with traditional industrial automation which relies on pre-installed equipment and fixed processes for efficiency. FaaS integrates digital platforms, IoT, and real-time data analytics to enable scalable and adaptive factory operations, whereas industrial automation emphasizes consistent output through robotics and automated machinery. Explore the differences and benefits of each approach to transform your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
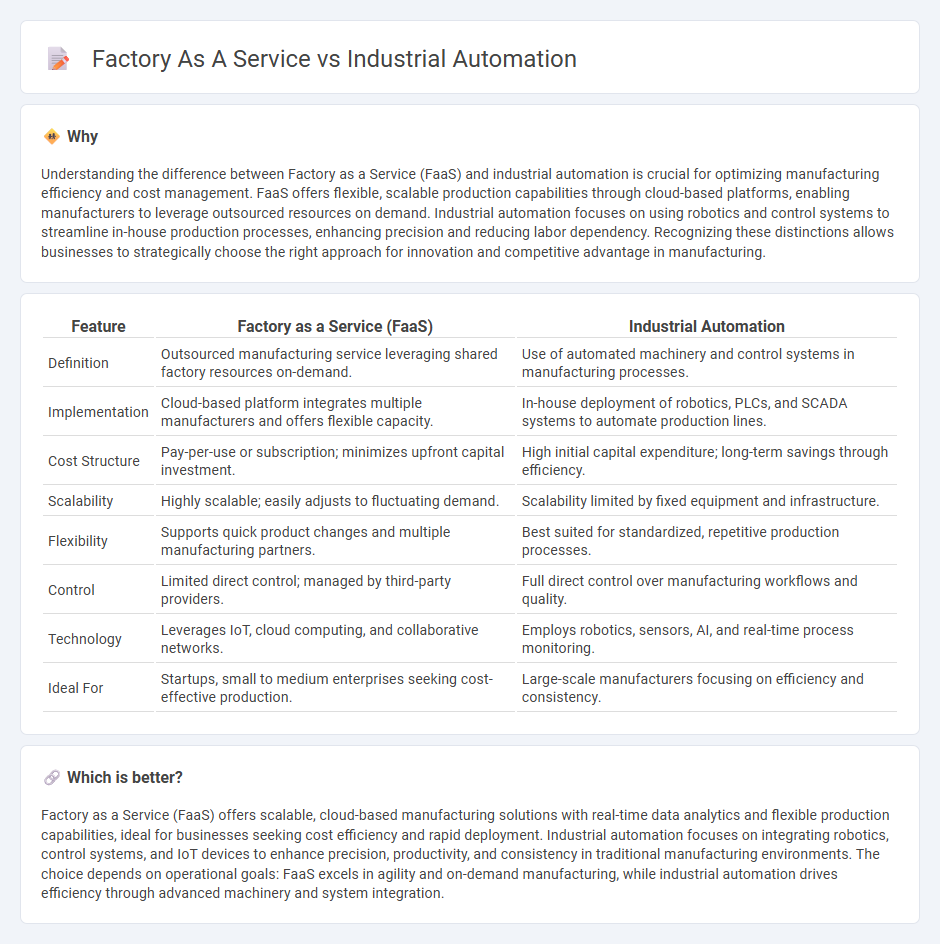
Understanding the difference between Factory as a Service (FaaS) and industrial automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and cost management. FaaS offers flexible, scalable production capabilities through cloud-based platforms, enabling manufacturers to leverage outsourced resources on demand. Industrial automation focuses on using robotics and control systems to streamline in-house production processes, enhancing precision and reducing labor dependency. Recognizing these distinctions allows businesses to strategically choose the right approach for innovation and competitive advantage in manufacturing.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Factory as a Service (FaaS) | Industrial Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourced manufacturing service leveraging shared factory resources on-demand. | Use of automated machinery and control systems in manufacturing processes. |
| Implementation | Cloud-based platform integrates multiple manufacturers and offers flexible capacity. | In-house deployment of robotics, PLCs, and SCADA systems to automate production lines. |
| Cost Structure | Pay-per-use or subscription; minimizes upfront capital investment. | High initial capital expenditure; long-term savings through efficiency. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; easily adjusts to fluctuating demand. | Scalability limited by fixed equipment and infrastructure. |
| Flexibility | Supports quick product changes and multiple manufacturing partners. | Best suited for standardized, repetitive production processes. |
| Control | Limited direct control; managed by third-party providers. | Full direct control over manufacturing workflows and quality. |
| Technology | Leverages IoT, cloud computing, and collaborative networks. | Employs robotics, sensors, AI, and real-time process monitoring. |
| Ideal For | Startups, small to medium enterprises seeking cost-effective production. | Large-scale manufacturers focusing on efficiency and consistency. |
Which is better?
Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers scalable, cloud-based manufacturing solutions with real-time data analytics and flexible production capabilities, ideal for businesses seeking cost efficiency and rapid deployment. Industrial automation focuses on integrating robotics, control systems, and IoT devices to enhance precision, productivity, and consistency in traditional manufacturing environments. The choice depends on operational goals: FaaS excels in agility and on-demand manufacturing, while industrial automation drives efficiency through advanced machinery and system integration.
Connection
Factory as a Service (FaaS) leverages industrial automation by integrating advanced robotics, IoT sensors, and real-time data analytics to deliver scalable, on-demand manufacturing solutions. Industrial automation enables seamless operation, monitoring, and control of FaaS environments, optimizing production efficiency and reducing downtime. Both technologies drive Industry 4.0 advancements by creating flexible, customizable, and cost-effective manufacturing ecosystems.
Key Terms
**Industrial Automation:**
Industrial automation involves the integration of advanced control systems, robotics, and software to streamline manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency, precision, and consistency in production environments. Key technologies include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and industrial IoT sensors, which work collectively to monitor and optimize operations in real-time. Explore the evolving landscape of industrial automation to understand how it revolutionizes modern manufacturing.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) serve as the backbone of industrial automation by enabling precise control over manufacturing processes through real-time monitoring and programmable input/output operations. In contrast, Factory as a Service (FaaS) integrates PLCs within a cloud-based ecosystem, offering scalable, on-demand automation solutions that reduce upfront capital expenditures and improve operational flexibility. Explore how the evolution of PLC technology is redefining industrial automation and FaaS paradigms for smarter manufacturing.
Robotics
Industrial automation integrates robotics to streamline manufacturing processes, enhance precision, and reduce operational costs. Factory as a Service (FaaS) leverages on-demand robotic solutions, enabling scalable and flexible production without heavy upfront investments in automation infrastructure. Explore the evolving role of robotics in both models to optimize your manufacturing strategy.
Source and External Links
What is Industrial Automation? -- INDUSTLABS - Industrial automation uses robotics, machines, and control systems to perform tasks traditionally done by humans, improving productivity, quality, and safety in manufacturing and industrial applications, with technologies like PLCs, CNC systems, and sensors.
Industrial Automation: What Is It? - Sure Controls - Industrial automation involves control systems, computers, robots, and IT to manage processes and machinery, increasingly focused on quality and flexibility besides productivity and cost reduction.
Industrial automation system: What is it? Types, and benefits - Industrial automation systems, enhanced by IIoT, provide high precision and consistent product quality, with types ranging from programmable automation for batch production to flexible automation in discrete manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com