Soft robotics offers enhanced flexibility and adaptability by utilizing compliant materials and biomimetic designs, enabling delicate interactions in complex environments. Pneumatic actuators rely on compressed air to generate movement, providing high force-to-weight ratios and rapid response but often lack the nuanced control found in soft robotic components. Explore the latest advancements in manufacturing technologies to understand how these systems impact automation efficiency.
Why it is important
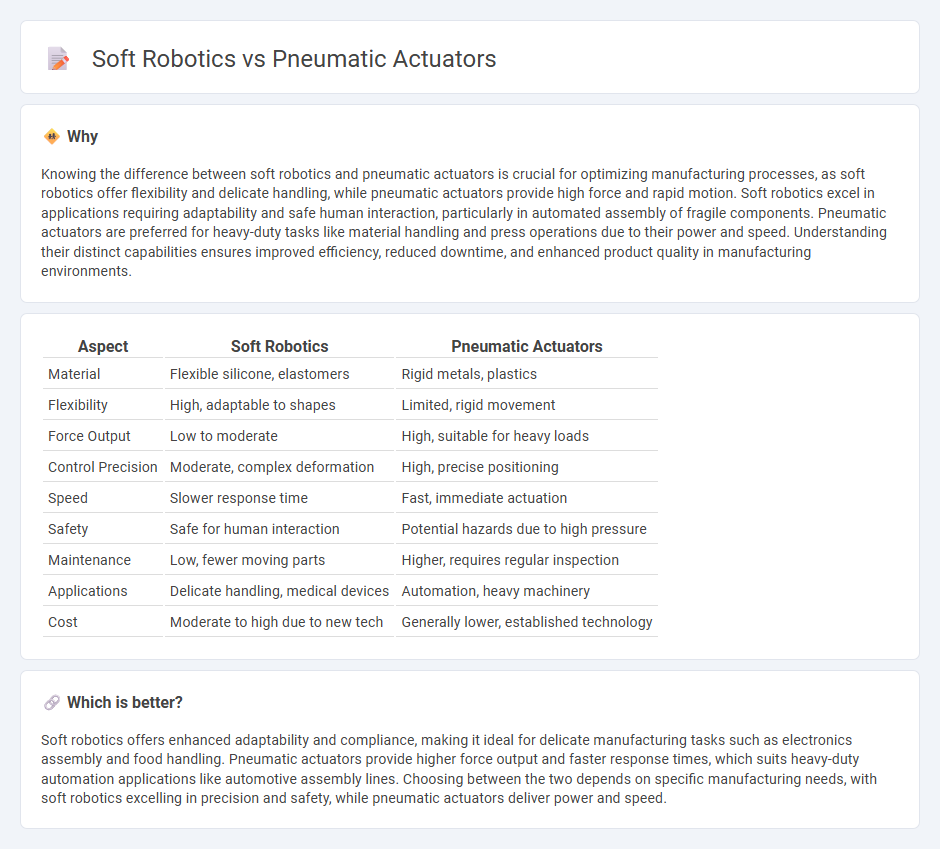
Knowing the difference between soft robotics and pneumatic actuators is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as soft robotics offer flexibility and delicate handling, while pneumatic actuators provide high force and rapid motion. Soft robotics excel in applications requiring adaptability and safe human interaction, particularly in automated assembly of fragile components. Pneumatic actuators are preferred for heavy-duty tasks like material handling and press operations due to their power and speed. Understanding their distinct capabilities ensures improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced product quality in manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Robotics | Pneumatic Actuators |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Flexible silicone, elastomers | Rigid metals, plastics |
| Flexibility | High, adaptable to shapes | Limited, rigid movement |
| Force Output | Low to moderate | High, suitable for heavy loads |
| Control Precision | Moderate, complex deformation | High, precise positioning |
| Speed | Slower response time | Fast, immediate actuation |
| Safety | Safe for human interaction | Potential hazards due to high pressure |
| Maintenance | Low, fewer moving parts | Higher, requires regular inspection |
| Applications | Delicate handling, medical devices | Automation, heavy machinery |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to new tech | Generally lower, established technology |
Which is better?
Soft robotics offers enhanced adaptability and compliance, making it ideal for delicate manufacturing tasks such as electronics assembly and food handling. Pneumatic actuators provide higher force output and faster response times, which suits heavy-duty automation applications like automotive assembly lines. Choosing between the two depends on specific manufacturing needs, with soft robotics excelling in precision and safety, while pneumatic actuators deliver power and speed.
Connection
Soft robotics leverages pneumatic actuators to enable flexible, lightweight, and safe manipulation in manufacturing processes. Pneumatic actuators provide precise control through compressed air, allowing soft robots to perform delicate tasks such as assembling fragile components and handling irregular objects. This synergy enhances automation efficiency by combining softness with strength, reducing damage risks and improving operational adaptability in industrial environments.
Key Terms
Compressed Air
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to create linear or rotary motion, offering high power-to-weight ratios and rapid response times in industrial automation settings. Soft robotics leverages flexible, inflatable materials that also operate on compressed air but prioritize adaptability, safe interaction, and gentle object manipulation over pure actuation force. Explore more about the advantages and applications of compressed air technology within these innovative actuator systems.
Flexibility
Pneumatic actuators deliver high force and precision but often lack the adaptability required for complex or delicate tasks, whereas soft robotics excels in flexibility and safe interaction with unstructured environments due to its compliant materials. Soft robotic systems use elastomers and advanced polymers to mimic biological movements, offering superior flexibility and adaptability compared to rigid pneumatic designs. Discover how these technologies are evolving to meet the demands of diverse applications by exploring their unique capabilities and integration challenges.
End-Effector
Pneumatic actuators provide precise, high-force motion control ideal for rigid end-effectors, excelling in industrial automation tasks requiring speed and strength. Soft robotics leverage flexible, compliant materials to create adaptable, safe end-effectors capable of gentle grasping and handling of delicate objects in medical or agricultural settings. Explore the distinctions in end-effector design and application to understand their impact on robotic performance and versatility.
Source and External Links
What are pneumatic actuators - ABB Measurement & Analytics Blog - Pneumatic actuators convert compressed air or gas energy into mechanical motion, which can be linear or rotary, to regulate control elements automatically, commonly used for modulation and emergency shutdowns.
What is a Pneumatic Actuator? | Types & Applications - YouTube - Pneumatic actuators typically use piston or spring/diaphragm mechanisms to convert air pressure into valve movement, enabling precise control by either air-to-extend or air-to-retract motions.
Pneumatic Linear Actuators | Industrial Cylinders - Tolomatic - Pneumatic linear actuators utilize compressed air for fast, cost-effective linear motion, with types including band cylinders, cable cylinders, and magnetic cylinders suited for various industrial applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com