Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical sensors that enable real-time environmental monitoring and data collection within manufacturing processes, enhancing precision and responsiveness. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are industrial digital computers used for automation of electromechanical processes, offering robust control and reliability in manufacturing lines. Discover how integrating smart dust and PLC technology transforms industrial automation and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between smart dust and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is crucial in manufacturing because smart dust enables wireless, microscopic sensor networks for real-time environmental monitoring, while PLCs provide centralized, programmable automation control for industrial machinery. Smart dust allows for detailed, distributed data collection that enhances predictive maintenance and process optimization. PLCs offer robust and reliable automation critical for controlling assembly lines and ensuring operational consistency. Selecting the appropriate technology impacts efficiency, cost, and system scalability in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
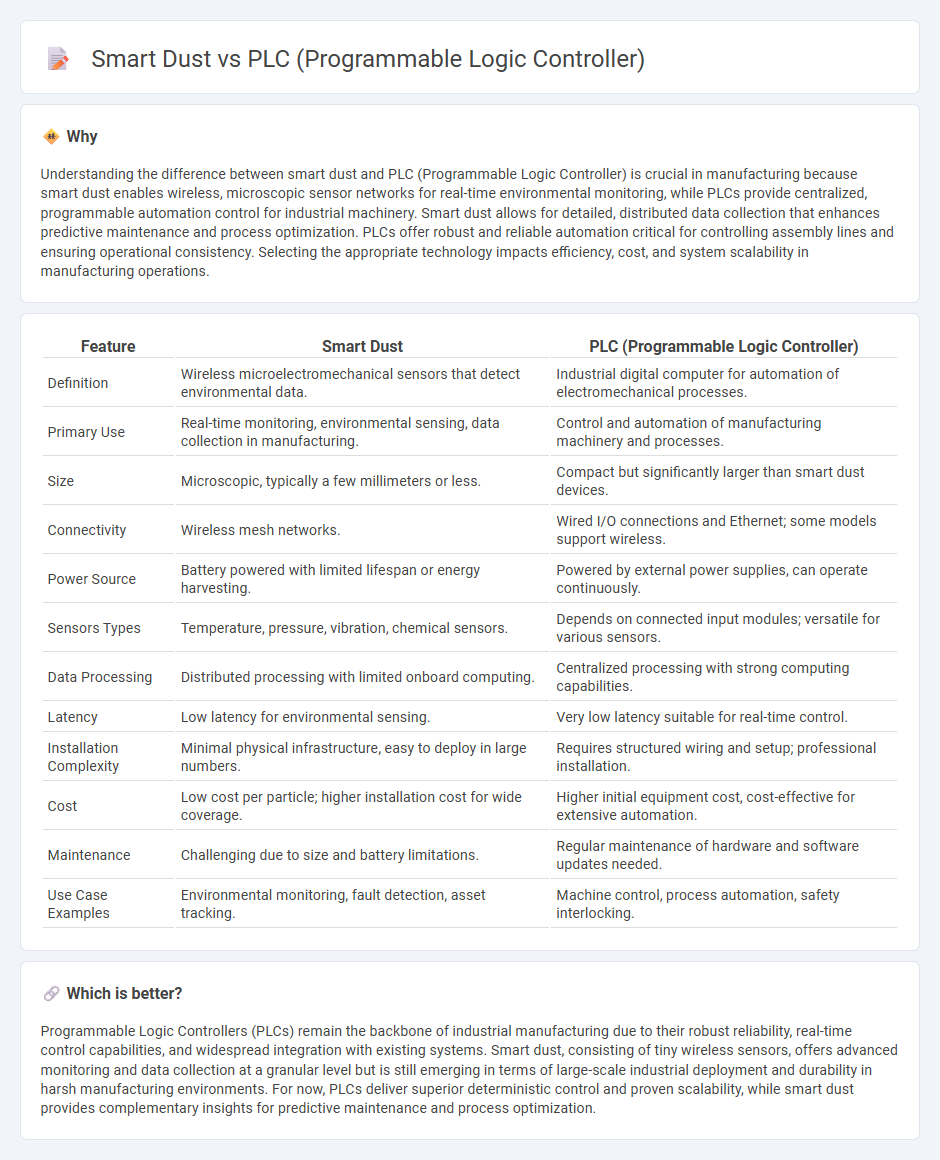
| Feature | Smart Dust | PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wireless microelectromechanical sensors that detect environmental data. | Industrial digital computer for automation of electromechanical processes. |
| Primary Use | Real-time monitoring, environmental sensing, data collection in manufacturing. | Control and automation of manufacturing machinery and processes. |
| Size | Microscopic, typically a few millimeters or less. | Compact but significantly larger than smart dust devices. |
| Connectivity | Wireless mesh networks. | Wired I/O connections and Ethernet; some models support wireless. |
| Power Source | Battery powered with limited lifespan or energy harvesting. | Powered by external power supplies, can operate continuously. |
| Sensors Types | Temperature, pressure, vibration, chemical sensors. | Depends on connected input modules; versatile for various sensors. |
| Data Processing | Distributed processing with limited onboard computing. | Centralized processing with strong computing capabilities. |
| Latency | Low latency for environmental sensing. | Very low latency suitable for real-time control. |
| Installation Complexity | Minimal physical infrastructure, easy to deploy in large numbers. | Requires structured wiring and setup; professional installation. |
| Cost | Low cost per particle; higher installation cost for wide coverage. | Higher initial equipment cost, cost-effective for extensive automation. |
| Maintenance | Challenging due to size and battery limitations. | Regular maintenance of hardware and software updates needed. |
| Use Case Examples | Environmental monitoring, fault detection, asset tracking. | Machine control, process automation, safety interlocking. |
Which is better?
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) remain the backbone of industrial manufacturing due to their robust reliability, real-time control capabilities, and widespread integration with existing systems. Smart dust, consisting of tiny wireless sensors, offers advanced monitoring and data collection at a granular level but is still emerging in terms of large-scale industrial deployment and durability in harsh manufacturing environments. For now, PLCs deliver superior deterministic control and proven scalability, while smart dust provides complementary insights for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
Connection
Smart dust sensors collect real-time environmental and operational data on manufacturing floors, enabling precise monitoring of equipment and processes. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) integrate this data to automate control tasks, enhance predictive maintenance, and optimize production efficiency. The synergy between smart dust and PLCs drives advanced industrial automation through granular data acquisition and intelligent system responses.
Key Terms
Automation
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have been the backbone of industrial automation, providing reliable, real-time control and monitoring of machinery and processes through programmable software and hardware integration. Smart dust, consisting of micro-scale sensor nodes capable of wireless communication, introduces a paradigm shift by enabling distributed, pervasive sensing and data collection in automation systems, enhancing precision and scalability. Explore how integrating PLCs and smart dust technologies can revolutionize automation environments and improve operational efficiency.
Sensor Networks
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) coordinate industrial sensor networks by processing discrete input signals and managing real-time automation tasks with high reliability and robustness. In contrast, smart dust consists of minuscule, wireless sensor nodes capable of forming highly distributed, self-organizing networks that monitor environmental variables at a granular level. Explore how these technologies redefine sensor network applications and efficiencies in diverse industries.
Real-time Control
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) excel in real-time control by providing deterministic, reliable, and high-speed automation for industrial processes, ensuring precise timing and fault tolerance in complex systems. Smart dust comprises microelectromechanical sensors with adaptive wireless communication capable of environmental monitoring but faces latency and energy constraints that hinder instantaneous real-time control. Explore more about integrating PLCs and smart dust to optimize real-time control applications across smart manufacturing and IoT ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What is PLC ? Programmable Logic Controller - Unitronics - A PLC is a ruggedized computer used for industrial automation, capable of controlling specific processes, machines, or entire production lines by receiving data from sensors, processing it with programmed logic, and triggering outputs to manage machinery and alarms.
What is a programmable logic controller (PLC)? - TechTarget - A PLC is a small, modular, solid-state computer designed with customized instructions for automating industrial tasks, using input/output modules to monitor sensors and control devices, and it can be programmed in several standard languages defined by IEC 61131.
What Is a Programmable Logic Controller? | UTI - A PLC is a robust digital computer that executes programmed instructions to automate tasks such as turning on lights, controlling motors, or running assembly lines by continuously monitoring inputs, processing data, and activating outputs without human intervention.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com