Lights out factories operate with minimal human intervention, leveraging automation and robotics to maximize efficiency and reduce operational costs. Hybrid manufacturing combines traditional manual processes with advanced automation, enabling flexibility and scalability while improving quality control. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of both approaches to optimize your production system.
Why it is important
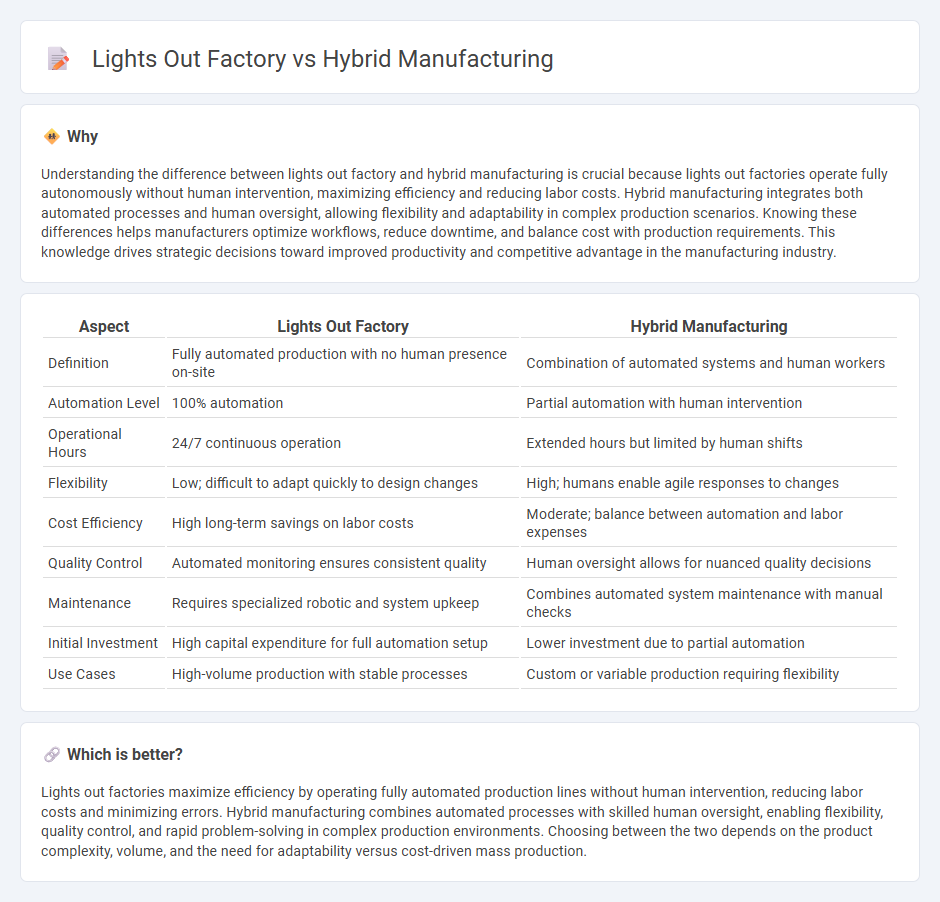
Understanding the difference between lights out factory and hybrid manufacturing is crucial because lights out factories operate fully autonomously without human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Hybrid manufacturing integrates both automated processes and human oversight, allowing flexibility and adaptability in complex production scenarios. Knowing these differences helps manufacturers optimize workflows, reduce downtime, and balance cost with production requirements. This knowledge drives strategic decisions toward improved productivity and competitive advantage in the manufacturing industry.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Hybrid Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with no human presence on-site | Combination of automated systems and human workers |
| Automation Level | 100% automation | Partial automation with human intervention |
| Operational Hours | 24/7 continuous operation | Extended hours but limited by human shifts |
| Flexibility | Low; difficult to adapt quickly to design changes | High; humans enable agile responses to changes |
| Cost Efficiency | High long-term savings on labor costs | Moderate; balance between automation and labor expenses |
| Quality Control | Automated monitoring ensures consistent quality | Human oversight allows for nuanced quality decisions |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized robotic and system upkeep | Combines automated system maintenance with manual checks |
| Initial Investment | High capital expenditure for full automation setup | Lower investment due to partial automation |
| Use Cases | High-volume production with stable processes | Custom or variable production requiring flexibility |
Which is better?
Lights out factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production lines without human intervention, reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. Hybrid manufacturing combines automated processes with skilled human oversight, enabling flexibility, quality control, and rapid problem-solving in complex production environments. Choosing between the two depends on the product complexity, volume, and the need for adaptability versus cost-driven mass production.
Connection
Lights out factories leverage automation and robotics to operate without human intervention, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Hybrid manufacturing integrates additive and subtractive processes, enabling versatile production capabilities essential for complex designs. Combining lights out factory principles with hybrid manufacturing technologies drives continuous, high-precision production while minimizing downtime and labor dependency.
Key Terms
**Hybrid Manufacturing:**
Hybrid manufacturing combines additive and subtractive processes within a single system, enabling enhanced precision and material efficiency in producing complex parts. This approach reduces lead times and allows for greater design flexibility compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Discover more about how hybrid manufacturing revolutionizes production efficiency and innovation.
Additive-Subtractive Integration
Hybrid manufacturing integrates additive and subtractive processes within a single system, enabling complex geometries and enhanced precision in production. Lights out factories operate fully automated manufacturing environments requiring minimal human intervention but typically focus on optimizing singular processes for efficiency. Explore how the synergy of additive-subtractive integration can revolutionize manufacturing workflows and operational efficiency.
Multi-Process Machine
Hybrid manufacturing integrates additive and subtractive processes within a single Multi-Process Machine, enabling precise, efficient production of complex components with reduced setup times. Lights out factories utilize fully automated Multi-Process Machines to facilitate continuous, unattended manufacturing, enhancing productivity and minimizing human intervention. Explore how Multi-Process Machines revolutionize modern manufacturing workflows and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Hybrid Manufacturing? - Firetrace International - Hybrid manufacturing combines additive (like 3D printing) and subtractive (like CNC machining) processes within a single machine, enabling both building and finishing parts in one setup for greater precision and efficiency.
Ultimate Guide to Hybrid Manufacturing (and Importance of CAD Data) - Hybrid manufacturing merges 3D printing with traditional machining (such as milling or turning) on the same equipment, streamlining production, reducing errors, and allowing for more complex and intricate part designs.
What is hybrid manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Hybrid manufacturing integrates additive and subtractive techniques in one system to achieve both fabrication and high precision, offering greater design freedom and the ability to produce parts with complex geometries not possible through conventional methods alone.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com