Hyperautomation integrates AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to streamline manufacturing workflows, reducing human intervention and boosting efficiency. Industrial IoT employs interconnected sensors and devices to collect real-time data, enabling predictive maintenance and enhanced operational visibility. Discover how these technologies transform manufacturing by exploring their unique applications and benefits.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between hyperautomation and industrial IoT is crucial in manufacturing to optimize operational efficiency and cost management. Hyperautomation focuses on automating complex decision-making processes using AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation, while industrial IoT involves connecting physical manufacturing devices to gather real-time data for monitoring and control. Properly distinguishing these technologies enables manufacturers to strategically implement solutions that enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and improve quality control. This knowledge drives informed investment and integration choices that align with specific production goals and digital transformation strategies.
Comparison Table
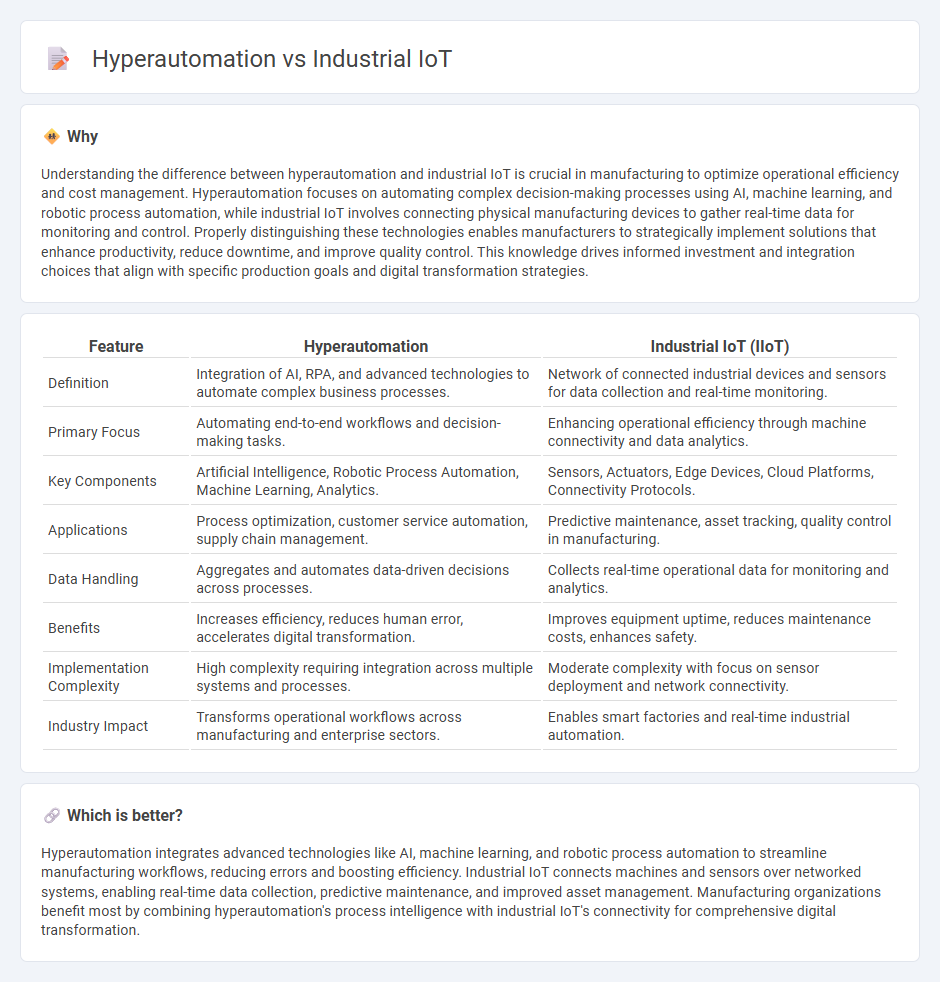
| Feature | Hyperautomation | Industrial IoT (IIoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of AI, RPA, and advanced technologies to automate complex business processes. | Network of connected industrial devices and sensors for data collection and real-time monitoring. |
| Primary Focus | Automating end-to-end workflows and decision-making tasks. | Enhancing operational efficiency through machine connectivity and data analytics. |
| Key Components | Artificial Intelligence, Robotic Process Automation, Machine Learning, Analytics. | Sensors, Actuators, Edge Devices, Cloud Platforms, Connectivity Protocols. |
| Applications | Process optimization, customer service automation, supply chain management. | Predictive maintenance, asset tracking, quality control in manufacturing. |
| Data Handling | Aggregates and automates data-driven decisions across processes. | Collects real-time operational data for monitoring and analytics. |
| Benefits | Increases efficiency, reduces human error, accelerates digital transformation. | Improves equipment uptime, reduces maintenance costs, enhances safety. |
| Implementation Complexity | High complexity requiring integration across multiple systems and processes. | Moderate complexity with focus on sensor deployment and network connectivity. |
| Industry Impact | Transforms operational workflows across manufacturing and enterprise sectors. | Enables smart factories and real-time industrial automation. |
Which is better?
Hyperautomation integrates advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to streamline manufacturing workflows, reducing errors and boosting efficiency. Industrial IoT connects machines and sensors over networked systems, enabling real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and improved asset management. Manufacturing organizations benefit most by combining hyperautomation's process intelligence with industrial IoT's connectivity for comprehensive digital transformation.
Connection
Hyperautomation leverages industrial IoT (IIoT) sensors and devices to collect real-time data from manufacturing processes, enabling advanced analytics and machine learning for predictive maintenance and process optimization. The integration of IIoT with robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI) creates seamless workflows that reduce downtime, improve quality control, and enhance operational efficiency. By connecting disparate systems and automating data-driven decision-making, hyperautomation transforms traditional manufacturing into smart, adaptive, and scalable production environments.
Key Terms
Connectivity
Industrial IoT leverages sensor networks and embedded devices to enable real-time data exchange across manufacturing equipment, enhancing operational visibility and predictive maintenance capabilities. Hyperautomation integrates advanced connectivity solutions with AI-driven workflows to streamline complex processes, reduce manual intervention, and optimize system interactions. Explore how enhanced connectivity shapes the synergy between Industrial IoT and hyperautomation for smarter industrial operations.
Machine Learning
Industrial IoT integrates sensors and devices to collect real-time data, enabling predictive maintenance and operational efficiency through Machine Learning algorithms analyzing vast industrial datasets. Hyperautomation leverages Machine Learning to automate complex workflows, enhancing decision-making and reducing human intervention across manufacturing processes. Explore how Machine Learning drives innovation in both Industrial IoT and hyperautomation for smarter industrial solutions.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Industrial IoT integrates sensors and devices to collect real-time data for monitoring and optimizing manufacturing processes, enhancing machinery efficiency and predictive maintenance. Hyperautomation leverages Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to streamline repetitive tasks, integrate AI-driven decision-making, and accelerate digital transformation across industrial workflows. Discover how combining Industrial IoT with RPA-powered hyperautomation drives unprecedented productivity and operational intelligence.
Source and External Links
Industrial IoT | Digital Transformation - AWS - Industrial IoT (IIoT) integrates machines, cloud computing, analytics, and people to enhance industrial process performance and productivity across industries like manufacturing, energy, and agriculture, enabling predictive quality and maintenance analytics as well as process optimization.
What is industrial IoT - Arm - Industrial IoT enables real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of industrial systems by connecting efficient devices across the production line and supply chain, facilitating automation and smart manufacturing, including robotics and autonomous workloads.
What Is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)? - PTC - IIoT is a key technology for Industry 4.0 that uses connected sensors and smart devices to create smart manufacturing, improving plant operations through reduced downtime, better connectivity, and IT/OT system convergence for advanced analytics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com