Mass customization leverages flexible manufacturing systems and advanced digital technologies to produce personalized products at near mass production efficiency, balancing variety with cost-effectiveness. Make-to-Order focuses on producing goods specifically based on individual customer orders, minimizing inventory and reducing waste through tailored production schedules. Explore the key differences and benefits of each approach to optimize your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
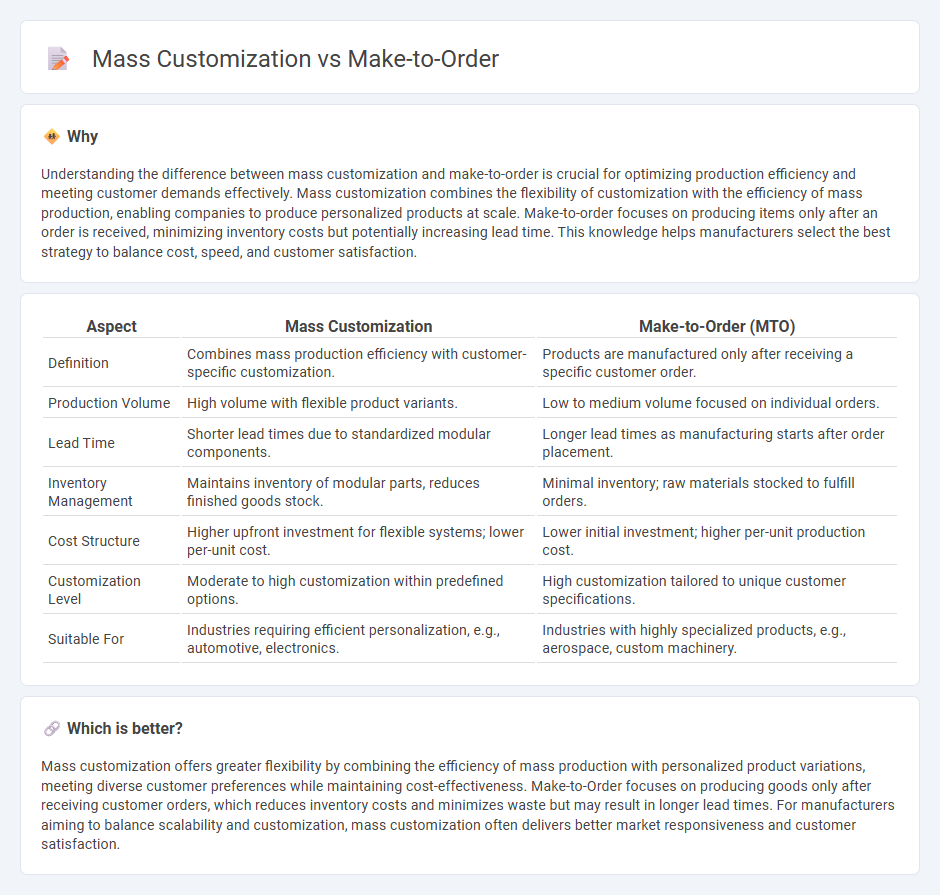
Understanding the difference between mass customization and make-to-order is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and meeting customer demands effectively. Mass customization combines the flexibility of customization with the efficiency of mass production, enabling companies to produce personalized products at scale. Make-to-order focuses on producing items only after an order is received, minimizing inventory costs but potentially increasing lead time. This knowledge helps manufacturers select the best strategy to balance cost, speed, and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Mass Customization | Make-to-Order (MTO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines mass production efficiency with customer-specific customization. | Products are manufactured only after receiving a specific customer order. |
| Production Volume | High volume with flexible product variants. | Low to medium volume focused on individual orders. |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times due to standardized modular components. | Longer lead times as manufacturing starts after order placement. |
| Inventory Management | Maintains inventory of modular parts, reduces finished goods stock. | Minimal inventory; raw materials stocked to fulfill orders. |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront investment for flexible systems; lower per-unit cost. | Lower initial investment; higher per-unit production cost. |
| Customization Level | Moderate to high customization within predefined options. | High customization tailored to unique customer specifications. |
| Suitable For | Industries requiring efficient personalization, e.g., automotive, electronics. | Industries with highly specialized products, e.g., aerospace, custom machinery. |
Which is better?
Mass customization offers greater flexibility by combining the efficiency of mass production with personalized product variations, meeting diverse customer preferences while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Make-to-Order focuses on producing goods only after receiving customer orders, which reduces inventory costs and minimizes waste but may result in longer lead times. For manufacturers aiming to balance scalability and customization, mass customization often delivers better market responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
Connection
Mass customization and Make-to-Order manufacturing are intrinsically connected through their focus on producing personalized products tailored to specific customer requirements. Both strategies leverage flexible production systems and advanced technologies like CAD/CAM and digital supply chain integration to minimize inventory costs and reduce lead times. This synergy enables manufacturers to efficiently deliver customized solutions while maintaining scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Key Terms
Lead Time
Make-to-Order (MTO) systems typically offer longer lead times as products are manufactured only after receiving customer orders, ensuring personalized specifications. Mass customization blends the efficiency of mass production with customization, resulting in shorter lead times by using modular designs and flexible manufacturing processes. Explore how optimizing lead time impacts customer satisfaction and operational efficiency in both production strategies.
Flexibility
Make-to-Order (MTO) offers high flexibility by producing goods only after receiving customer orders, allowing tailored products and minimal inventory risk. Mass customization combines the efficiency of mass production with personalization features, enabling customers to choose specific options within standardized processes. Explore the benefits and challenges of both approaches to determine the best fit for your business needs.
Customer Specification
Make-to-Order (MTO) production strictly adheres to individual customer specifications, creating unique products only after an order is received, which ensures high customization but longer lead times. In contrast, Mass Customization blends standardized processes with modular design to offer customers personalized options while maintaining economies of scale and faster delivery. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to optimize your production strategy and meet diverse customer demands effectively.
Source and External Links
Make-to-Order workflow | Katana - Make-to-Order (MTO) is a business approach where products are manufactured only after receiving a customer order, enabling efficient production planning and minimizing finished goods inventory.
What Is Make-to-Order? Make-to-Order Definition & Meaning - MTO is a manufacturing strategy focusing on producing customized products based on specific customer orders rather than stockpiling products in advance.
Make To Order (MTO) - Overview, Advantage/Disadvantage - Make-to-Order is a production technique where manufacturing starts only after an order is received, reducing waste and inventory costs, common in specialized sectors like aircraft and construction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com