Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility, reducing transportation costs, and enabling faster local market responses. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste, optimizing workflow, and improving efficiency within a centralized production system to maximize value. Explore the advantages and challenges of both approaches to determine the ideal manufacturing strategy for your business.
Why it is important
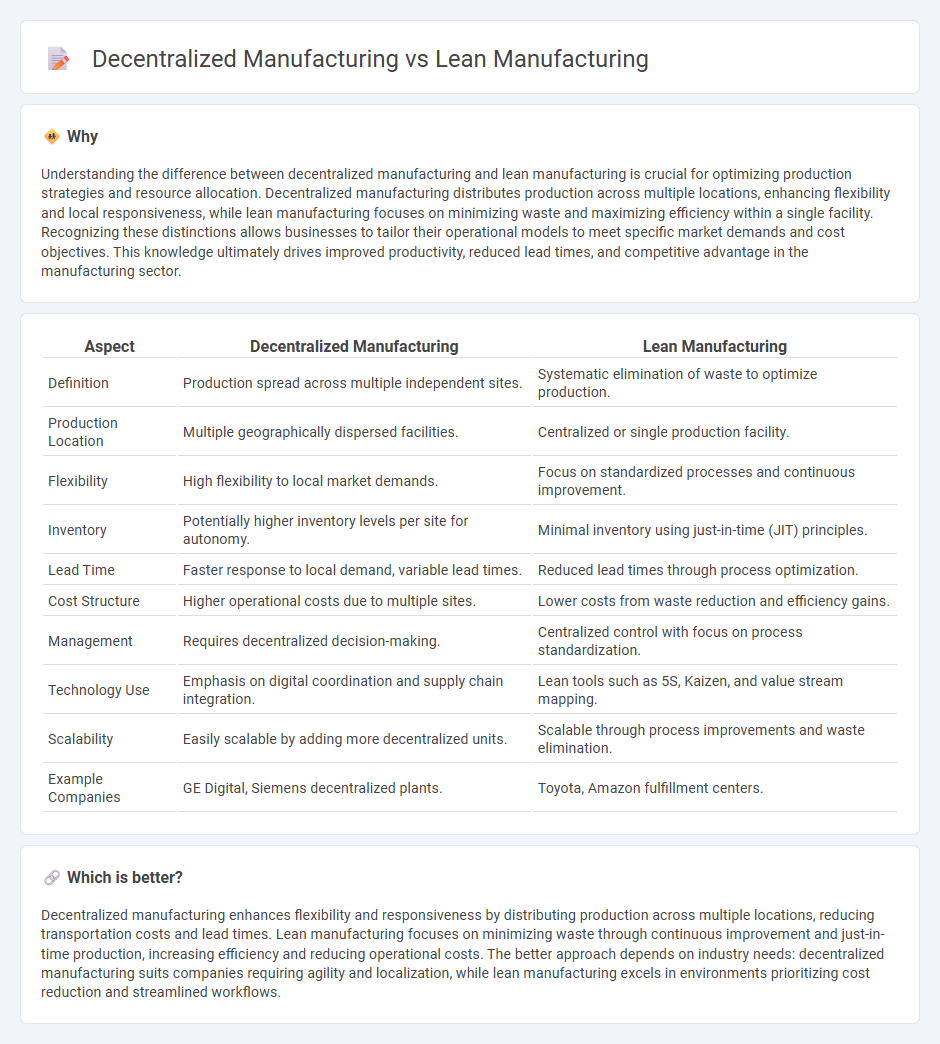
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production strategies and resource allocation. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and local responsiveness, while lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency within a single facility. Recognizing these distinctions allows businesses to tailor their operational models to meet specific market demands and cost objectives. This knowledge ultimately drives improved productivity, reduced lead times, and competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Manufacturing | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production spread across multiple independent sites. | Systematic elimination of waste to optimize production. |
| Production Location | Multiple geographically dispersed facilities. | Centralized or single production facility. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to local market demands. | Focus on standardized processes and continuous improvement. |
| Inventory | Potentially higher inventory levels per site for autonomy. | Minimal inventory using just-in-time (JIT) principles. |
| Lead Time | Faster response to local demand, variable lead times. | Reduced lead times through process optimization. |
| Cost Structure | Higher operational costs due to multiple sites. | Lower costs from waste reduction and efficiency gains. |
| Management | Requires decentralized decision-making. | Centralized control with focus on process standardization. |
| Technology Use | Emphasis on digital coordination and supply chain integration. | Lean tools such as 5S, Kaizen, and value stream mapping. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable by adding more decentralized units. | Scalable through process improvements and waste elimination. |
| Example Companies | GE Digital, Siemens decentralized plants. | Toyota, Amazon fulfillment centers. |
Which is better?
Decentralized manufacturing enhances flexibility and responsiveness by distributing production across multiple locations, reducing transportation costs and lead times. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste through continuous improvement and just-in-time production, increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs. The better approach depends on industry needs: decentralized manufacturing suits companies requiring agility and localization, while lean manufacturing excels in environments prioritizing cost reduction and streamlined workflows.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing enhances lean manufacturing principles by distributing production processes closer to end-users, reducing lead times and minimizing inventory costs. This approach leverages localized supply chains and real-time data, which streamlines workflow efficiency and waste reduction, key tenets of lean methodology. The integration of decentralized systems supports continuous improvement and agility, essential for maintaining lean manufacturing's focus on value creation and resource optimization.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by streamlining processes, minimizing inventory, and eliminating non-value-added activities to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. In contrast, decentralized manufacturing may face challenges in waste control due to varied local practices and less centralized oversight, which can result in inconsistent waste management. Explore more about how lean principles drive operational excellence in manufacturing systems.
Autonomy (Decentralized Manufacturing)
Decentralized manufacturing enhances autonomy by enabling individual units to operate independently, fostering faster decision-making and customized production aligned with local demands. Lean manufacturing emphasizes minimizing waste and streamlining processes across a centralized system to maximize efficiency. Explore how decentralized autonomy transforms production flexibility and responsiveness in modern manufacturing.
Continuous Improvement (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement through systematic waste reduction, streamlined processes, and employee involvement to enhance efficiency and quality. Decentralized manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and local responsiveness but may face challenges in uniformly applying continuous improvement practices across dispersed units. Explore how integrating lean principles within decentralized frameworks can optimize production performance and sustainability.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Lean manufacturing is a method aimed at reducing production and response times by eliminating waste and focusing on just-in-time production, originally developed by Toyota as the Toyota Production System emphasizing continuous improvement and waste elimination.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology to minimize waste while maximizing productivity, based on principles such as Kaizen, and it is widely applied beyond manufacturing in various industries.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing focuses on maximizing productivity and minimizing waste using five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, emphasizing doing more with less.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com