Smart dust technology revolutionizes manufacturing by deploying networks of tiny, wireless sensors that enable real-time, granular data collection across production lines. SCADA systems provide centralized control and monitoring through integrated software and hardware, optimizing process automation and operational efficiency. Discover how combining smart dust with SCADA can transform manufacturing intelligence and performance.
Why it is important
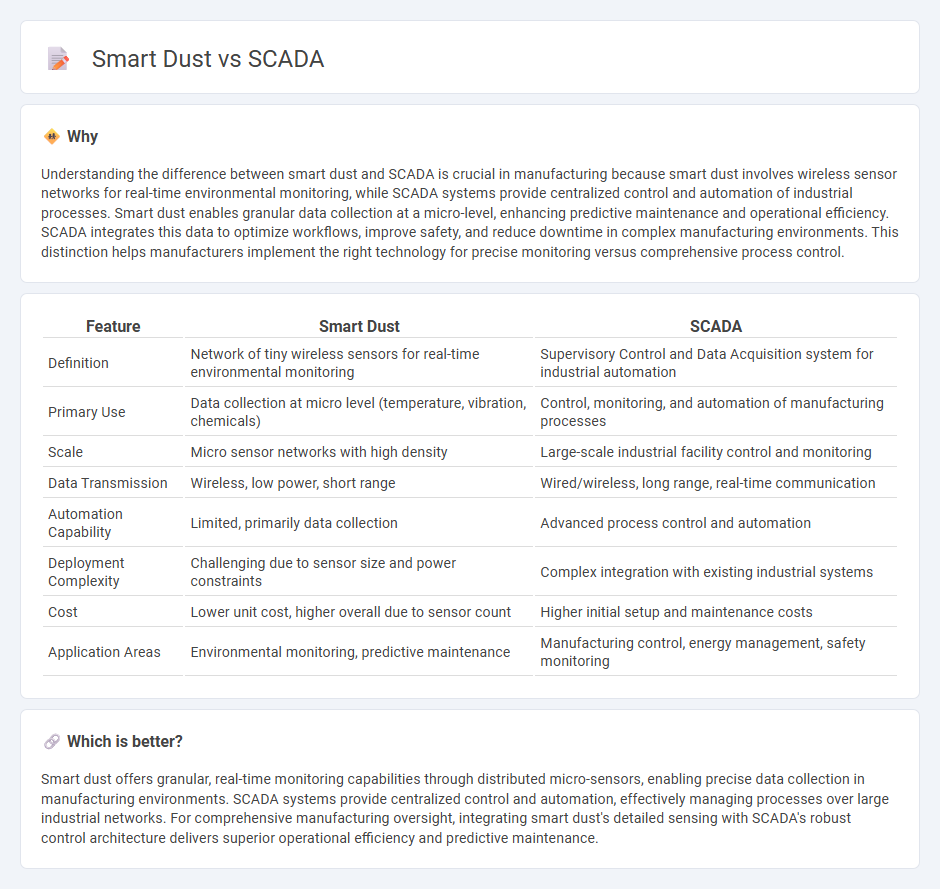
Understanding the difference between smart dust and SCADA is crucial in manufacturing because smart dust involves wireless sensor networks for real-time environmental monitoring, while SCADA systems provide centralized control and automation of industrial processes. Smart dust enables granular data collection at a micro-level, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. SCADA integrates this data to optimize workflows, improve safety, and reduce downtime in complex manufacturing environments. This distinction helps manufacturers implement the right technology for precise monitoring versus comprehensive process control.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | SCADA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of tiny wireless sensors for real-time environmental monitoring | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system for industrial automation |
| Primary Use | Data collection at micro level (temperature, vibration, chemicals) | Control, monitoring, and automation of manufacturing processes |
| Scale | Micro sensor networks with high density | Large-scale industrial facility control and monitoring |
| Data Transmission | Wireless, low power, short range | Wired/wireless, long range, real-time communication |
| Automation Capability | Limited, primarily data collection | Advanced process control and automation |
| Deployment Complexity | Challenging due to sensor size and power constraints | Complex integration with existing industrial systems |
| Cost | Lower unit cost, higher overall due to sensor count | Higher initial setup and maintenance costs |
| Application Areas | Environmental monitoring, predictive maintenance | Manufacturing control, energy management, safety monitoring |
Which is better?
Smart dust offers granular, real-time monitoring capabilities through distributed micro-sensors, enabling precise data collection in manufacturing environments. SCADA systems provide centralized control and automation, effectively managing processes over large industrial networks. For comprehensive manufacturing oversight, integrating smart dust's detailed sensing with SCADA's robust control architecture delivers superior operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Connection
Smart dust enhances SCADA systems by providing real-time, granular data from microscopic sensors dispersed throughout manufacturing environments. This integration enables improved monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource management by collecting and transmitting critical operational metrics. As a result, SCADA systems become more responsive and precise, optimizing manufacturing processes and reducing downtime.
Key Terms
Real-time monitoring
SCADA systems enable real-time monitoring through centralized control and data acquisition from industrial equipment, ensuring efficient process management. Smart dust employs networks of microelectromechanical sensors to provide granular, real-time environmental data in hard-to-reach areas. Explore the key differences and applications of SCADA and smart dust for advanced real-time monitoring solutions.
Wireless sensor networks
Wireless sensor networks in SCADA systems enable real-time monitoring and control across industrial environments with high reliability and scalability. Smart dust technology, comprising miniature wireless sensors, offers granular data collection with minimal power consumption, making it ideal for distributed sensing in challenging or inaccessible areas. Explore the detailed advantages and applications of SCADA and smart dust in wireless sensor networks for optimized industrial solutions.
Data acquisition
SCADA systems excel in centralized data acquisition by collecting, processing, and monitoring large-scale industrial process data through sensors and control devices. Smart dust leverages distributed microelectromechanical sensors for highly granular, real-time environmental data collection, enhancing spatial resolution and scalability. Explore more to understand how these technologies revolutionize data acquisition in automated monitoring.
Source and External Links
What is SCADA? Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition - SCADA is a system combining software and hardware that allows organizations to monitor and control industrial processes in real time by directly interfacing with plant-floor machinery and displaying critical data for operational decisions.
SCADA - Wikipedia - SCADA is a control system architecture using computers and networked communications to manage and monitor physical processes such as electricity transmission, pipeline transport, water distribution, and traffic control, with security being a critical concern due to its impact on essential infrastructure.
SCADA Systems: What They Are & How They Work - Splunk - SCADA systems enable organizations to control, monitor, and analyze industrial devices and processes, relying on sensors, actuators, PLCs, RTUs, and layered networks to gather, transmit, and process real-time operational data for efficient decision-making.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com