Digital twinning enhances manufacturing by creating virtual replicas of physical systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. PLC automation focuses on controlling machinery through programmable logic controllers for efficient, reliable process execution. Explore how integrating digital twins with PLC automation can revolutionize industrial operations.
Why it is important
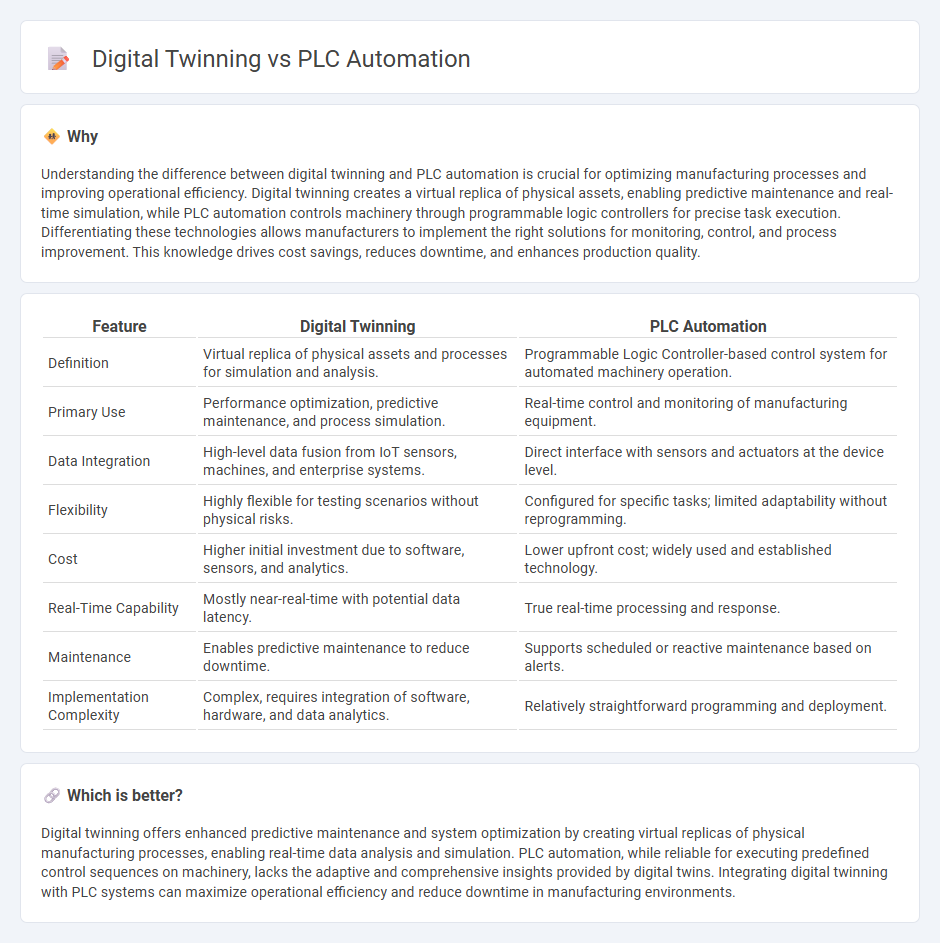
Understanding the difference between digital twinning and PLC automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and improving operational efficiency. Digital twinning creates a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time simulation, while PLC automation controls machinery through programmable logic controllers for precise task execution. Differentiating these technologies allows manufacturers to implement the right solutions for monitoring, control, and process improvement. This knowledge drives cost savings, reduces downtime, and enhances production quality.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twinning | PLC Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets and processes for simulation and analysis. | Programmable Logic Controller-based control system for automated machinery operation. |
| Primary Use | Performance optimization, predictive maintenance, and process simulation. | Real-time control and monitoring of manufacturing equipment. |
| Data Integration | High-level data fusion from IoT sensors, machines, and enterprise systems. | Direct interface with sensors and actuators at the device level. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for testing scenarios without physical risks. | Configured for specific tasks; limited adaptability without reprogramming. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to software, sensors, and analytics. | Lower upfront cost; widely used and established technology. |
| Real-Time Capability | Mostly near-real-time with potential data latency. | True real-time processing and response. |
| Maintenance | Enables predictive maintenance to reduce downtime. | Supports scheduled or reactive maintenance based on alerts. |
| Implementation Complexity | Complex, requires integration of software, hardware, and data analytics. | Relatively straightforward programming and deployment. |
Which is better?
Digital twinning offers enhanced predictive maintenance and system optimization by creating virtual replicas of physical manufacturing processes, enabling real-time data analysis and simulation. PLC automation, while reliable for executing predefined control sequences on machinery, lacks the adaptive and comprehensive insights provided by digital twins. Integrating digital twinning with PLC systems can maximize operational efficiency and reduce downtime in manufacturing environments.
Connection
Digital twinning and PLC automation are interconnected through the creation of virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems that allow real-time monitoring and control. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) send data to digital twins, enabling precise simulation, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. This integration enhances production efficiency, reduces downtime, and optimizes operational workflows in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Real-time Control
PLC automation enables real-time control by executing precise, predefined sequences of machine operations with minimal latency, ensuring consistent and reliable performance in industrial environments. Digital twinning enhances real-time control through continuous data integration and simulation, allowing dynamic process adjustments and predictive maintenance based on virtual replicas of physical systems. Explore how digital twinning and PLC automation converge to optimize industrial control systems and elevate operational efficiency.
Virtual Simulation
PLC automation enables precise control of industrial processes through programmable logic controllers, optimizing real-time operations and enhancing system efficiency. Digital twinning, with its virtual simulation capabilities, creates a dynamic, real-time digital counterpart of physical assets, allowing predictive maintenance and process optimization before implementation. Explore further to understand how integrating virtual simulation in PLC automation can revolutionize industrial workflows.
Data Integration
PLC automation relies on real-time data acquisition from sensors and devices to execute precise control commands across manufacturing processes, ensuring operational efficiency. Digital twinning integrates diverse data streams, including IoT inputs, historical records, and simulation models, to create a virtual replica that enhances predictive analytics and system optimization. Explore how advanced data integration transforms industrial automation by bridging PLC control systems with digital twin technologies for smarter decision-making.
Source and External Links
What is Industrial Automation? Programmable Logic ... - A PLC is a ruggedized industrial computer that continuously monitors inputs, processes preprogrammed commands, and controls output in industrial processes to automate tasks, improving reliability and reducing human error in manufacturing.
PLC automation: what is it and what is its role? - PLCs are industrial computers managing automated equipment via sensors and actuators, often working with SCADA systems and HMIs to control and monitor processes efficiently in industrial and logistics environments.
What is PLC Programming and Automation? - PLCs replace mechanical relays in automation by digitally processing inputs and outputs with high scan speeds, greatly reducing maintenance and costs while enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com