Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable devices, exoskeletons, and neural interfaces, improving precision and reducing fatigue in manufacturing processes. Industrial IoT integrates smart sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated systems to optimize production efficiency, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management. Discover how these advanced technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing by exploring their distinct applications and benefits.
Why it is important
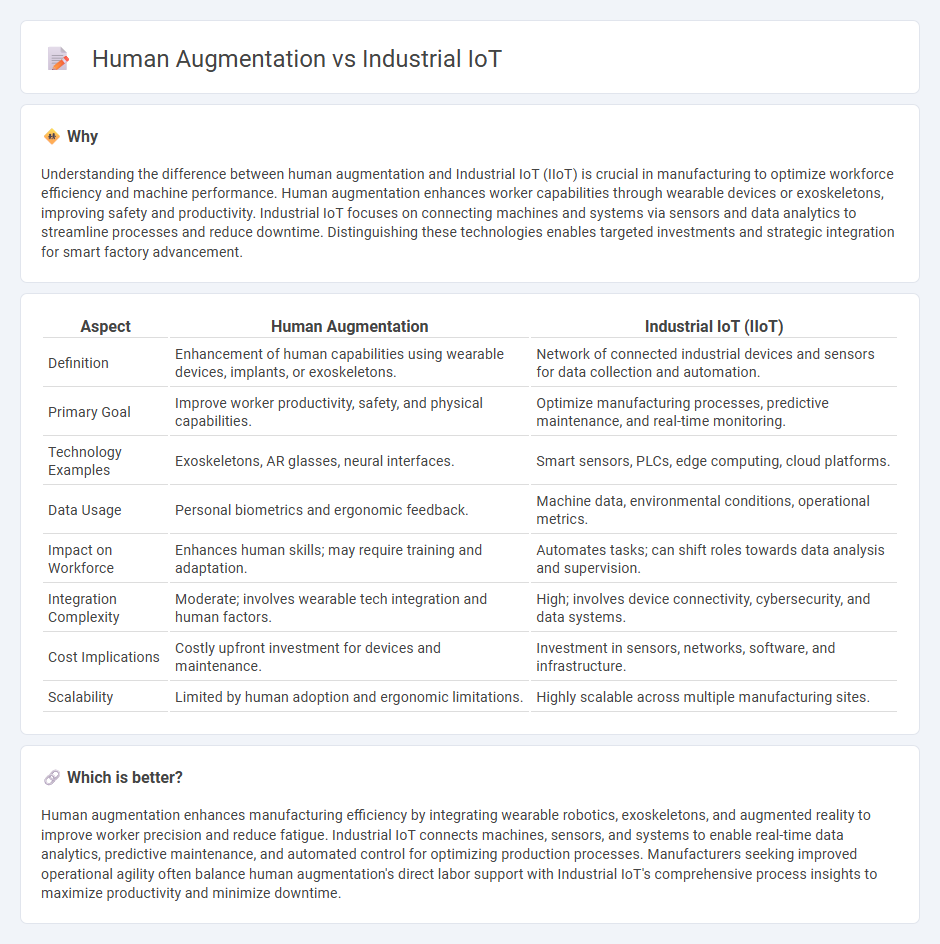
Understanding the difference between human augmentation and Industrial IoT (IIoT) is crucial in manufacturing to optimize workforce efficiency and machine performance. Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable devices or exoskeletons, improving safety and productivity. Industrial IoT focuses on connecting machines and systems via sensors and data analytics to streamline processes and reduce downtime. Distinguishing these technologies enables targeted investments and strategic integration for smart factory advancement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Human Augmentation | Industrial IoT (IIoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancement of human capabilities using wearable devices, implants, or exoskeletons. | Network of connected industrial devices and sensors for data collection and automation. |
| Primary Goal | Improve worker productivity, safety, and physical capabilities. | Optimize manufacturing processes, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring. |
| Technology Examples | Exoskeletons, AR glasses, neural interfaces. | Smart sensors, PLCs, edge computing, cloud platforms. |
| Data Usage | Personal biometrics and ergonomic feedback. | Machine data, environmental conditions, operational metrics. |
| Impact on Workforce | Enhances human skills; may require training and adaptation. | Automates tasks; can shift roles towards data analysis and supervision. |
| Integration Complexity | Moderate; involves wearable tech integration and human factors. | High; involves device connectivity, cybersecurity, and data systems. |
| Cost Implications | Costly upfront investment for devices and maintenance. | Investment in sensors, networks, software, and infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Limited by human adoption and ergonomic limitations. | Highly scalable across multiple manufacturing sites. |
Which is better?
Human augmentation enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating wearable robotics, exoskeletons, and augmented reality to improve worker precision and reduce fatigue. Industrial IoT connects machines, sensors, and systems to enable real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and automated control for optimizing production processes. Manufacturers seeking improved operational agility often balance human augmentation's direct labor support with Industrial IoT's comprehensive process insights to maximize productivity and minimize downtime.
Connection
Human augmentation enhances workforce capabilities by integrating wearable devices and smart sensors that collect real-time data within manufacturing environments. Industrial IoT (IIoT) enables seamless connectivity and communication between augmented workers and machines, optimizing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. This synergy drives increased productivity, improved safety, and data-driven decision-making across manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
Sensor Networks
Sensor networks in industrial IoT enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced automation by connecting machines and processes across factories. In human augmentation, sensor networks gather biometric and environmental data to enhance human capabilities, improve safety, and support health monitoring through wearable devices. Explore the latest advancements in sensor network technologies to understand their transformative impact on both industrial and human-centered applications.
Wearable Exoskeletons
Wearable exoskeletons play a crucial role in industrial IoT by enhancing worker productivity and safety through real-time data integration and ergonomic support. These devices leverage IoT sensors to monitor movement, reduce fatigue, and prevent injuries in manufacturing and construction environments. Explore the advancements in wearable exoskeleton technology and its impact on the future of industrial workforces.
Predictive Maintenance
Industrial IoT leverages sensor networks and real-time data analytics to enable predictive maintenance, reducing equipment downtime by forecasting failures before they occur. Human augmentation enhances maintenance tasks by integrating wearable technology and AI-driven decision support systems, improving technician accuracy and response times. Explore in-depth how these technologies transform predictive maintenance strategies across industries.
Source and External Links
Industrial IoT | Digital Transformation - AWS - Industrial IoT (IIoT) integrates machines, cloud computing, analytics, and people to enhance industrial process performance and productivity across sectors like manufacturing, energy, and transportation, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization.
What is industrial IoT - Arm - Industrial IoT enables real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of industrial processes with connected devices that operate reliably in harsh environments, driving automation, smart manufacturing, and flexible production lines.
What Is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)? - PTC - IIoT underpins Industry 4.0 by connecting sensors, actuators, and machines to create smart manufacturing solutions that reduce downtime, improve operations, and enable IT/OT convergence for enhanced data visibility and analytics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com