Green steel is produced using renewable energy sources and hydrogen, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional steel manufacturing. Blue steel involves capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions during production, offering a cleaner alternative without completely eliminating fossil fuels. Explore the environmental benefits and industrial applications of green and blue steel to understand their impact on sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
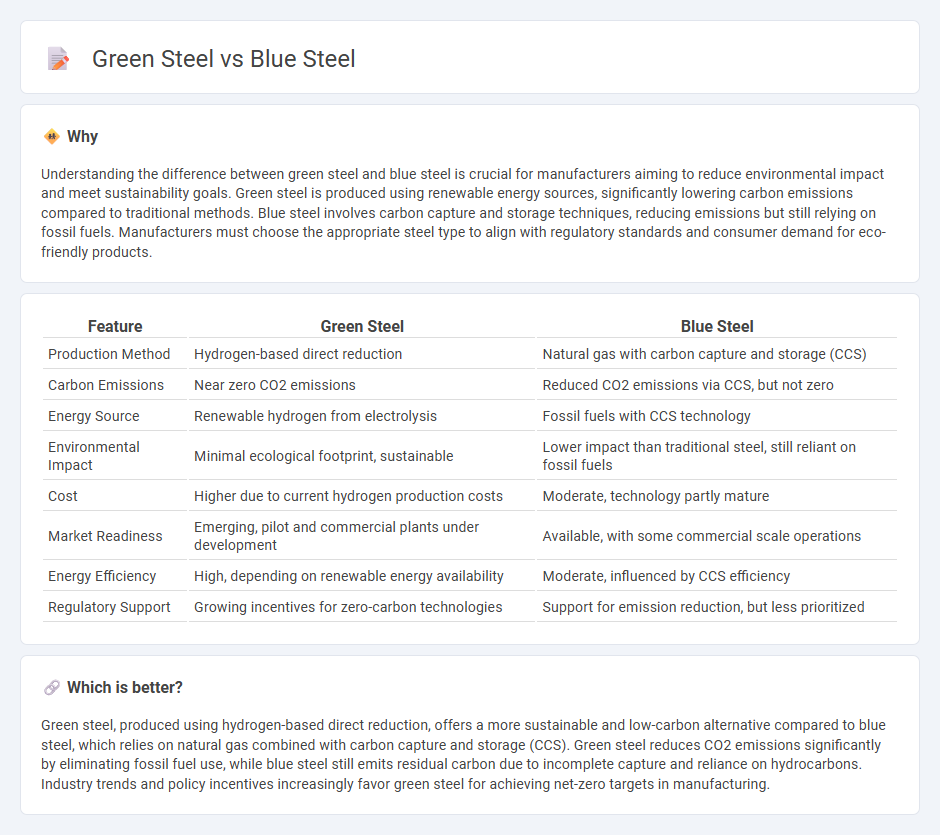
Understanding the difference between green steel and blue steel is crucial for manufacturers aiming to reduce environmental impact and meet sustainability goals. Green steel is produced using renewable energy sources, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional methods. Blue steel involves carbon capture and storage techniques, reducing emissions but still relying on fossil fuels. Manufacturers must choose the appropriate steel type to align with regulatory standards and consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Green Steel | Blue Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Hydrogen-based direct reduction | Natural gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS) |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | Reduced CO2 emissions via CCS, but not zero |
| Energy Source | Renewable hydrogen from electrolysis | Fossil fuels with CCS technology |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal ecological footprint, sustainable | Lower impact than traditional steel, still reliant on fossil fuels |
| Cost | Higher due to current hydrogen production costs | Moderate, technology partly mature |
| Market Readiness | Emerging, pilot and commercial plants under development | Available, with some commercial scale operations |
| Energy Efficiency | High, depending on renewable energy availability | Moderate, influenced by CCS efficiency |
| Regulatory Support | Growing incentives for zero-carbon technologies | Support for emission reduction, but less prioritized |
Which is better?
Green steel, produced using hydrogen-based direct reduction, offers a more sustainable and low-carbon alternative compared to blue steel, which relies on natural gas combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS). Green steel reduces CO2 emissions significantly by eliminating fossil fuel use, while blue steel still emits residual carbon due to incomplete capture and reliance on hydrocarbons. Industry trends and policy incentives increasingly favor green steel for achieving net-zero targets in manufacturing.
Connection
Green steel and blue steel are connected through their shared goal of reducing carbon emissions in the steel manufacturing industry. Green steel production relies on renewable energy and hydrogen from sustainable sources, while blue steel incorporates carbon capture and storage to lower its environmental impact. Both technologies represent critical steps toward decarbonizing steel manufacturing and achieving sustainable industrial practices.
Key Terms
Carbon Emissions
Blue steel production utilizes natural gas reforming with carbon capture and storage (CCS) to significantly reduce carbon emissions, achieving up to 70% lower CO2 output compared to traditional steelmaking. Green steel relies on hydrogen produced via renewable energy sources for the reduction process, resulting in near-zero carbon emissions and representing the industry's cleanest pathway to decarbonization. Explore the advancements and environmental impacts of blue and green steel technologies for a comprehensive understanding of sustainable steel production.
Raw Materials
Blue steel production relies heavily on high-grade iron ore and natural gas, serving as a critical raw material for the hydrogen-based reduction process. Green steel primarily sources renewable hydrogen and scrap steel, drastically reducing dependency on fossil fuels and raw iron ore mining. Explore more about how raw material choices impact the environmental footprint of blue and green steel production.
Production Process
Blue steel production involves hydrogen-based direct reduction of iron ore combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS) to minimize CO2 emissions, making it a near-zero carbon alternative to traditional steelmaking. Green steel utilizes green hydrogen produced via electrolysis powered by renewable energy, further reducing environmental impact by eliminating fossil fuels entirely in the reduction process. Explore the detailed technologies and environmental benefits behind these innovative steel production methods to understand their role in sustainable manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Blue Steel - Wikipedia - Blue Steel refers to a tempering color of steel, a rust-protection process called bluing, a crystalline steel form, a British Cold War missile, as well as several films, a guitar string brand, and other uses in culture and technology.
Blue Steel (1990 film) - Wikipedia - Blue Steel is a 1990 American action thriller directed by Kathryn Bigelow, starring Jamie Lee Curtis as a rookie cop who becomes the target of a violent obsession after shooting a robber.
Blue Steel (1934) - IMDb - Blue Steel (1934) is a western film starring John Wayne as a U.S. marshal caught in a robbery investigation and small-town corruption.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com