Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities using wearable exoskeletons and smart devices, boosting productivity and reducing injury risks in manufacturing environments. Autonomous mobile robots improve operational efficiency through automated material handling, navigation, and real-time decision-making, minimizing downtime and increasing precision. Explore the advantages and applications of human augmentation and autonomous mobile robots to transform modern manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
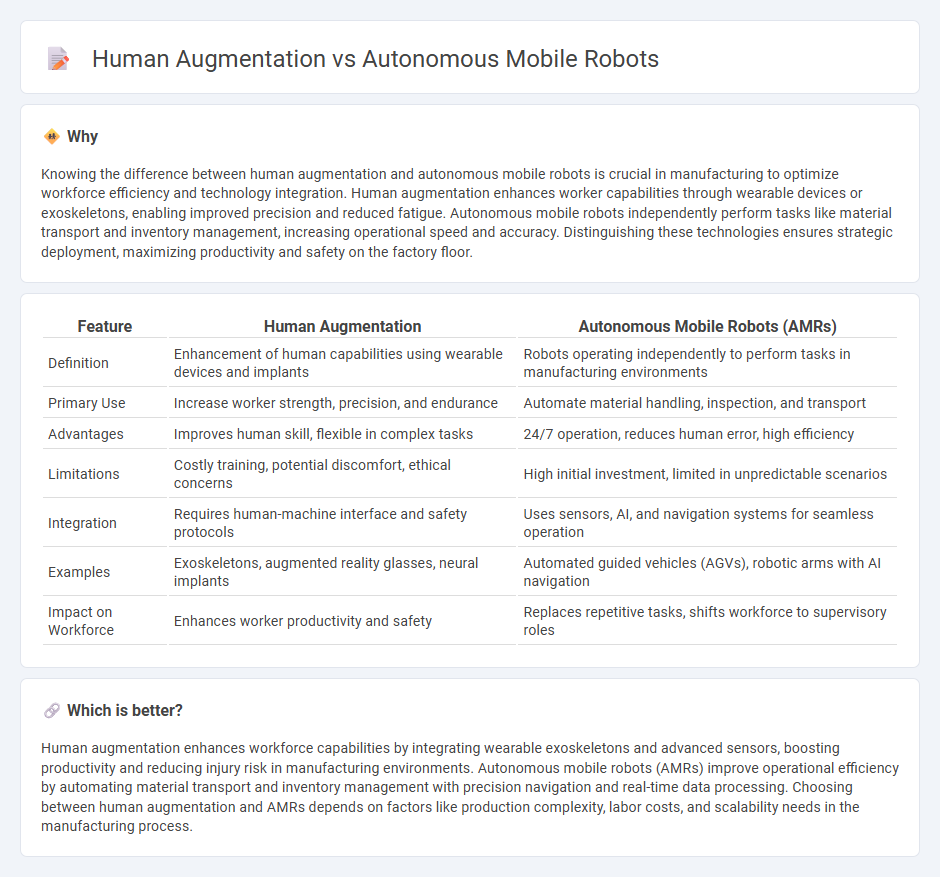
Knowing the difference between human augmentation and autonomous mobile robots is crucial in manufacturing to optimize workforce efficiency and technology integration. Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable devices or exoskeletons, enabling improved precision and reduced fatigue. Autonomous mobile robots independently perform tasks like material transport and inventory management, increasing operational speed and accuracy. Distinguishing these technologies ensures strategic deployment, maximizing productivity and safety on the factory floor.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Human Augmentation | Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancement of human capabilities using wearable devices and implants | Robots operating independently to perform tasks in manufacturing environments |
| Primary Use | Increase worker strength, precision, and endurance | Automate material handling, inspection, and transport |
| Advantages | Improves human skill, flexible in complex tasks | 24/7 operation, reduces human error, high efficiency |
| Limitations | Costly training, potential discomfort, ethical concerns | High initial investment, limited in unpredictable scenarios |
| Integration | Requires human-machine interface and safety protocols | Uses sensors, AI, and navigation systems for seamless operation |
| Examples | Exoskeletons, augmented reality glasses, neural implants | Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic arms with AI navigation |
| Impact on Workforce | Enhances worker productivity and safety | Replaces repetitive tasks, shifts workforce to supervisory roles |
Which is better?
Human augmentation enhances workforce capabilities by integrating wearable exoskeletons and advanced sensors, boosting productivity and reducing injury risk in manufacturing environments. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) improve operational efficiency by automating material transport and inventory management with precision navigation and real-time data processing. Choosing between human augmentation and AMRs depends on factors like production complexity, labor costs, and scalability needs in the manufacturing process.
Connection
Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable exoskeletons and smart sensors, enabling higher precision and reduced fatigue in manufacturing tasks. Autonomous mobile robots navigate factory floors independently, transporting materials and assisting with logistics to streamline production processes. The integration of augmented humans and autonomous robots fosters seamless human-robot collaboration, increasing overall manufacturing efficiency and safety.
Key Terms
Navigation Systems
Autonomous mobile robots utilize advanced navigation systems such as LiDAR, SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), and machine learning algorithms to achieve precise, real-time environment mapping and obstacle avoidance. Human augmentation navigation systems enhance user capabilities through wearable devices like AR glasses and brain-machine interfaces, providing real-time spatial awareness and improved decision-making during navigation tasks. Explore the latest innovations in navigation technology for both autonomous robots and human augmentation to understand their evolving roles in complex environments.
Collaborative Workspaces
Collaborative workspaces benefit significantly from autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) by enhancing efficiency through automated material handling, while human augmentation improves worker performance with wearable exoskeletons and AR interfaces. AMRs optimize logistical workflows and reduce physical strain, whereas human augmentation fosters cognitive and physical capabilities directly at the point of work. Explore the latest innovations in robotics and human-machine collaboration to understand their impact on future workplace productivity.
Ergonomic Exoskeletons
Ergonomic exoskeletons enhance human capabilities by reducing physical strain and improving posture during repetitive tasks, offering significant benefits in industrial and healthcare settings. Autonomous mobile robots automate material handling and logistics, increasing efficiency and safety by performing tasks without human intervention. Explore the latest advancements in ergonomic exoskeletons and autonomous mobile robots to understand their impact on workplace productivity and human welfare.
Source and External Links
Automated & Autonomous Mobile Robots | Robotnik(r) - Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are flexible, versatile platforms that autonomously navigate complex environments for logistics, manufacturing, inspection, agriculture, and retail, adapting quickly without extensive reconfiguration and collaborating efficiently with humans to optimize production and competitiveness.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): A Guide | Built In - AMRs navigate and perform tasks without human control, using sensors to avoid obstacles, with wide applications in warehouses, manufacturing, and even homes, offering more operational flexibility than traditional automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) - ABB AMR/AGV robots - ABB's autonomous mobile robots are designed for load transport across industries, featuring AI-powered navigation, high payload capacities, and robust safety features to enable seamless collaboration with human workers and improve operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com