Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) enable rapid adaptation to changing product designs through computer-controlled machinery and automated processes, enhancing production efficiency and reducing downtime. Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into dedicated cells focused on specific product families, minimizing material handling and improving workflow. Explore the differences between these manufacturing approaches to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
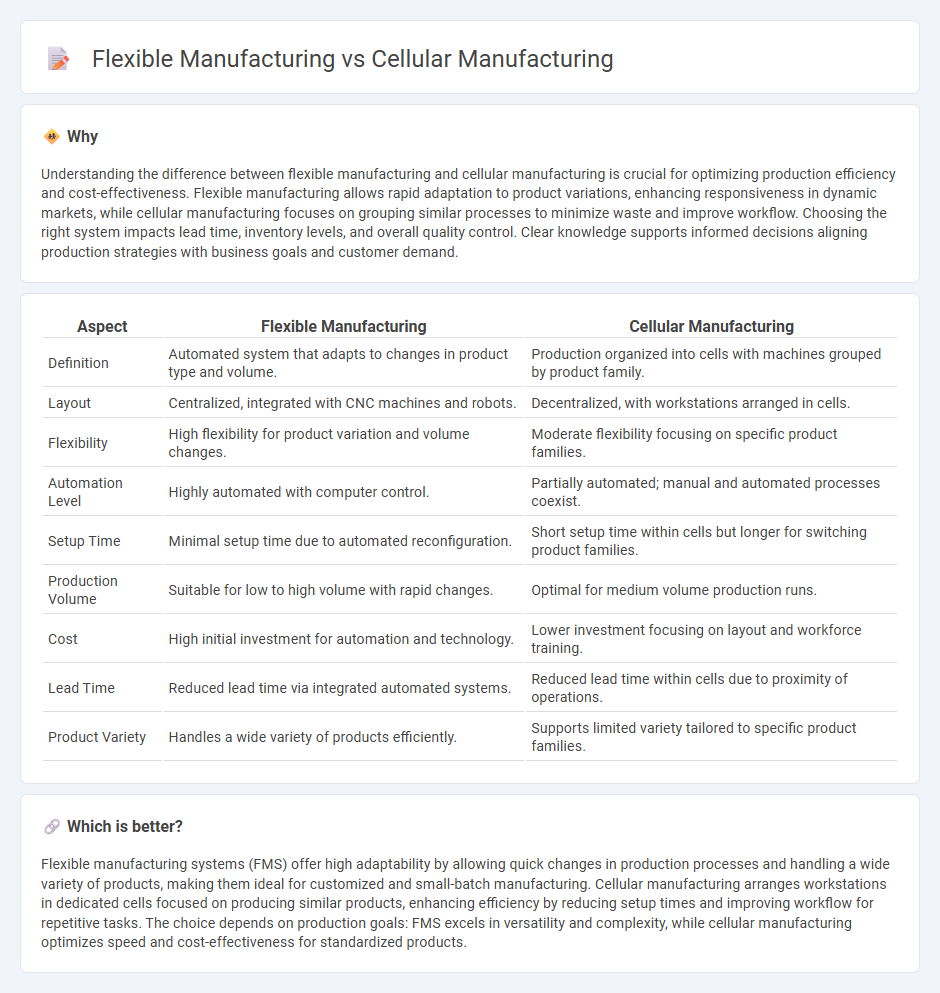
Understanding the difference between flexible manufacturing and cellular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Flexible manufacturing allows rapid adaptation to product variations, enhancing responsiveness in dynamic markets, while cellular manufacturing focuses on grouping similar processes to minimize waste and improve workflow. Choosing the right system impacts lead time, inventory levels, and overall quality control. Clear knowledge supports informed decisions aligning production strategies with business goals and customer demand.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flexible Manufacturing | Cellular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated system that adapts to changes in product type and volume. | Production organized into cells with machines grouped by product family. |
| Layout | Centralized, integrated with CNC machines and robots. | Decentralized, with workstations arranged in cells. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for product variation and volume changes. | Moderate flexibility focusing on specific product families. |
| Automation Level | Highly automated with computer control. | Partially automated; manual and automated processes coexist. |
| Setup Time | Minimal setup time due to automated reconfiguration. | Short setup time within cells but longer for switching product families. |
| Production Volume | Suitable for low to high volume with rapid changes. | Optimal for medium volume production runs. |
| Cost | High initial investment for automation and technology. | Lower investment focusing on layout and workforce training. |
| Lead Time | Reduced lead time via integrated automated systems. | Reduced lead time within cells due to proximity of operations. |
| Product Variety | Handles a wide variety of products efficiently. | Supports limited variety tailored to specific product families. |
Which is better?
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) offer high adaptability by allowing quick changes in production processes and handling a wide variety of products, making them ideal for customized and small-batch manufacturing. Cellular manufacturing arranges workstations in dedicated cells focused on producing similar products, enhancing efficiency by reducing setup times and improving workflow for repetitive tasks. The choice depends on production goals: FMS excels in versatility and complexity, while cellular manufacturing optimizes speed and cost-effectiveness for standardized products.
Connection
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) integrate automated machinery and computer-controlled processes to adapt quickly to varying product demands, while cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into discrete cells optimized for a specific set of tasks. The connection lies in the ability of cellular manufacturing to support FMS by grouping related processes and enabling rapid changeovers, enhancing production efficiency and responsiveness. Combining these approaches reduces lead times and inventory costs, promoting lean manufacturing principles within dynamic production environments.
Key Terms
**Cellular Manufacturing:**
Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into small, manageable units called cells, each dedicated to producing a specific family of parts. This method enhances production efficiency by reducing setup times, minimizing transportation waste, and improving communication among team members. Explore more about how cellular manufacturing streamlines processes and boosts productivity.
Work Cells
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into dedicated work cells that group machines and operators based on product families, enabling streamlined workflow and reduced setup times. Flexible manufacturing systems utilize adaptable work cells equipped with programmable machines to handle a variety of products, enhancing responsiveness to market changes. Explore the advantages and applications of work cells in both manufacturing approaches to optimize efficiency and productivity.
Group Technology
Cellular manufacturing organizes production into cells based on group technology, where similar parts or products sharing common processes are grouped together to minimize setup times and enhance workflow efficiency. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) utilize automated machines capable of producing different products with minimal changeover, offering adaptability but often at a higher investment and complexity level compared to cellular setups. Explore further to understand how integrating group technology principles in manufacturing boosts productivity and reduces operational costs.
Source and External Links
Cellular Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide - Cellular manufacturing is a production system that integrates multiple manufacturing processes within a single cell, designed by assessing the production environment, creating production cells, and monitoring their performance for efficiency improvements.
Cellular manufacturing - This manufacturing method is part of lean and just-in-time manufacturing, uses cells composed of machines arranged often in a U-shape to enable fast, flexible production and reduce waste, improving productivity, quality, and reducing inventory and lead times.
What Is Cellular Manufacturing? - Cellular manufacturing organizes workstations into self-sufficient production cells tailored for specific product processes, improving communication, lead times, reducing work-in-progress, space, and waste, applicable in diverse industries like automotive and electronics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com