Condition-based monitoring uses real-time data and sensor technology to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Planned maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and part replacements regardless of equipment condition, often leading to unnecessary maintenance or unexpected breakdowns. Discover how integrating these strategies can enhance operational efficiency and asset longevity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Condition-based Monitoring (CBM) and Planned Maintenance is crucial for optimizing asset performance and reducing operational costs in manufacturing. CBM relies on real-time data and diagnostics to perform maintenance only when needed, preventing unexpected failures. Planned Maintenance follows a fixed schedule regardless of equipment condition, which may lead to unnecessary downtime and expenses. Accurate knowledge of these approaches enables manufacturers to implement predictive maintenance strategies that maximize equipment uptime and efficiency.
Comparison Table
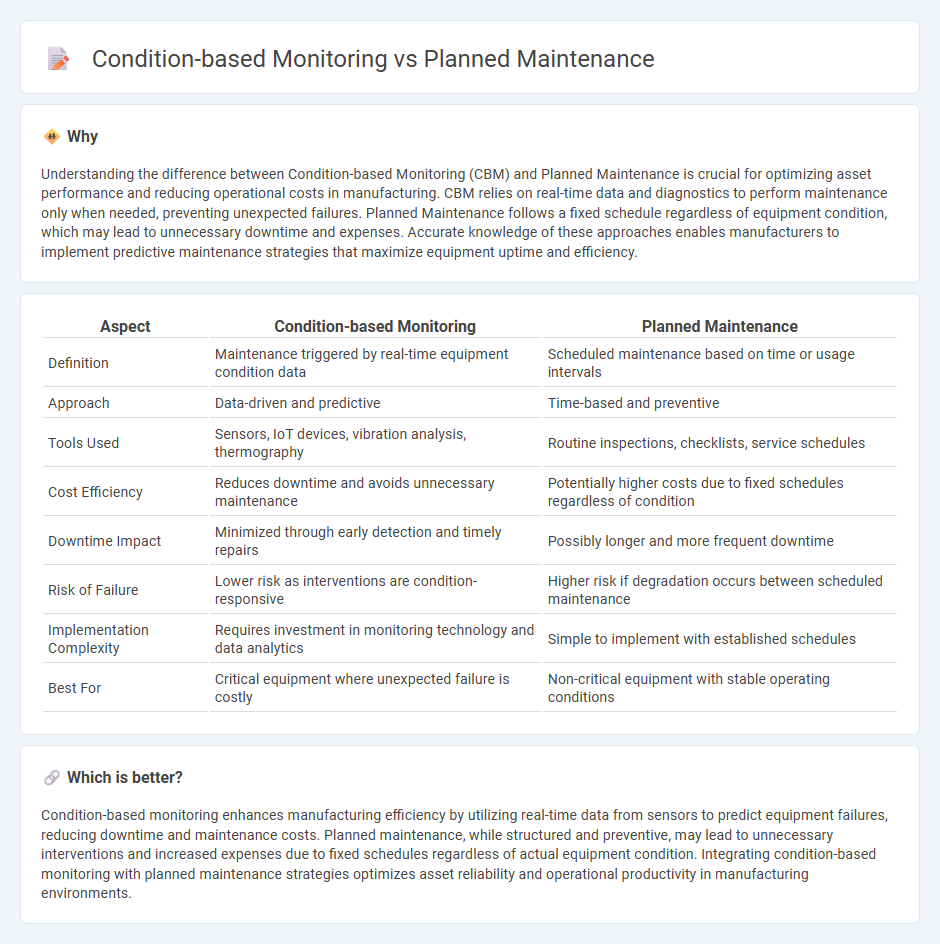
| Aspect | Condition-based Monitoring | Planned Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance triggered by real-time equipment condition data | Scheduled maintenance based on time or usage intervals |
| Approach | Data-driven and predictive | Time-based and preventive |
| Tools Used | Sensors, IoT devices, vibration analysis, thermography | Routine inspections, checklists, service schedules |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces downtime and avoids unnecessary maintenance | Potentially higher costs due to fixed schedules regardless of condition |
| Downtime Impact | Minimized through early detection and timely repairs | Possibly longer and more frequent downtime |
| Risk of Failure | Lower risk as interventions are condition-responsive | Higher risk if degradation occurs between scheduled maintenance |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires investment in monitoring technology and data analytics | Simple to implement with established schedules |
| Best For | Critical equipment where unexpected failure is costly | Non-critical equipment with stable operating conditions |
Which is better?
Condition-based monitoring enhances manufacturing efficiency by utilizing real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Planned maintenance, while structured and preventive, may lead to unnecessary interventions and increased expenses due to fixed schedules regardless of actual equipment condition. Integrating condition-based monitoring with planned maintenance strategies optimizes asset reliability and operational productivity in manufacturing environments.
Connection
Condition-based monitoring uses real-time data from sensors to assess equipment health and predict failures, enabling maintenance activities to be scheduled only when necessary. Planned maintenance relies on this data-driven insight to optimize maintenance intervals, reducing downtime and extending machinery lifespan. Together, they improve operational efficiency by preventing unexpected breakdowns and minimizing maintenance costs in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Scheduled Intervals
Planned maintenance relies on predetermined schedules to service equipment, ensuring routine checks regardless of condition, which helps prevent unexpected failures but may lead to unnecessary part replacements. Condition-based monitoring uses real-time data and sensor technology to assess equipment health, triggering maintenance only when specific indicators suggest potential issues, optimizing resource use and reducing downtime. Explore how integrating both strategies can enhance operational efficiency and extend asset lifespan.
Real-time Sensors
Real-time sensors enable condition-based monitoring by continuously tracking equipment performance, detecting anomalies, and predicting failures before they escalate, reducing unplanned downtime and costly repairs. Planned maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and replacements regardless of actual equipment health, potentially leading to unnecessary maintenance or unexpected breakdowns. Explore how real-time sensor technology revolutionizes maintenance strategies for improved efficiency and asset longevity.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics leverages condition-based monitoring to analyze real-time data from sensors, enabling accurate forecasts of equipment failures and optimizing maintenance schedules. Unlike traditional planned maintenance, which relies on fixed intervals, condition-based monitoring reduces downtime and maintenance costs by addressing issues only when specific conditions indicate potential problems. Discover how integrating predictive analytics transforms maintenance strategies and enhances operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Planned Maintenance? | IBM - Planned maintenance is a proactive strategy involving scheduled upkeep tasks such as preventive, predictive, reliability-centered, and run-to-failure maintenance to avoid equipment breakdowns and extend asset life.
Planned Maintenance: From Reactive to Organized and Scheduled - Planned maintenance is a maintenance strategy that uses proactive planning, documentation, and scheduling to reduce equipment downtime and costs by ensuring timely inspections, spare parts ordering, and task prioritization.
Planned Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide | SafetyCulture - Planned maintenance is a scheduled approach for maintaining equipment based on historical data and organized schedules aimed at preventing breakdowns and ensuring continuous operation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com