Servitization transforms manufacturing companies by integrating services into traditional product offerings, enhancing customer value and creating new revenue streams. Outsourcing focuses on delegating specific production processes or components to external suppliers to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Explore how these strategies reshape competitive advantages in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between servitization and outsourcing is crucial for manufacturing companies to optimize operational efficiency and enhance customer value. Servitization transforms product offerings into integrated solutions with added services, while outsourcing delegates specific tasks to external providers. Identifying the right strategy drives innovation, cost management, and competitive advantage in the manufacturing sector. Clear differentiation aids in aligning business models with corporate goals and market demands.
Comparison Table
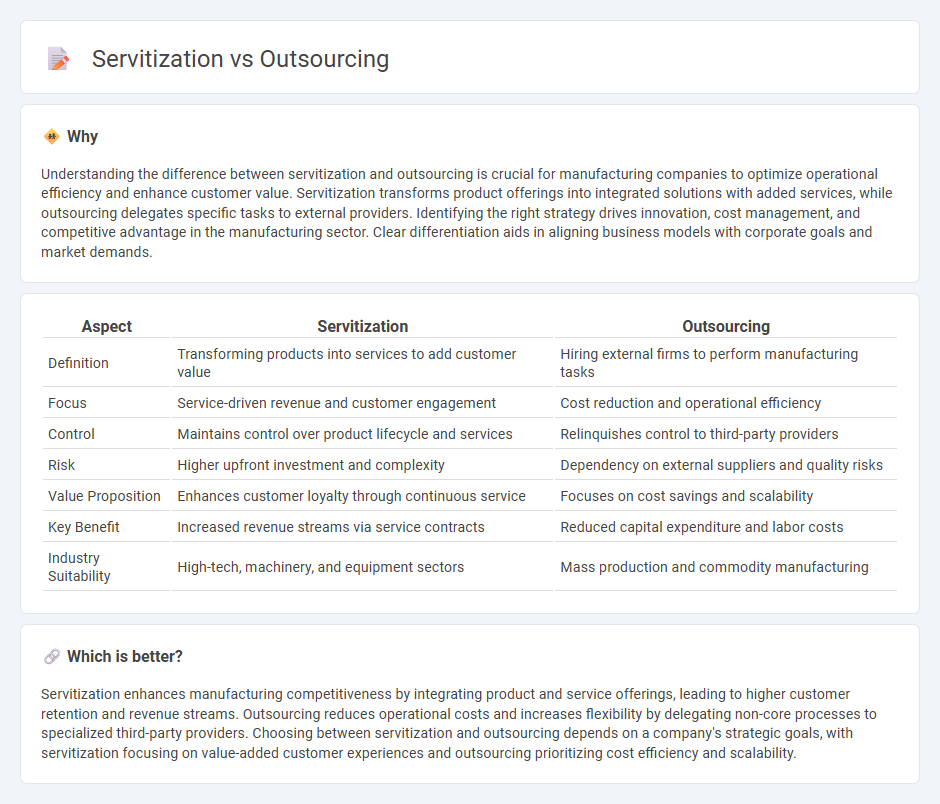
| Aspect | Servitization | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforming products into services to add customer value | Hiring external firms to perform manufacturing tasks |
| Focus | Service-driven revenue and customer engagement | Cost reduction and operational efficiency |
| Control | Maintains control over product lifecycle and services | Relinquishes control to third-party providers |
| Risk | Higher upfront investment and complexity | Dependency on external suppliers and quality risks |
| Value Proposition | Enhances customer loyalty through continuous service | Focuses on cost savings and scalability |
| Key Benefit | Increased revenue streams via service contracts | Reduced capital expenditure and labor costs |
| Industry Suitability | High-tech, machinery, and equipment sectors | Mass production and commodity manufacturing |
Which is better?
Servitization enhances manufacturing competitiveness by integrating product and service offerings, leading to higher customer retention and revenue streams. Outsourcing reduces operational costs and increases flexibility by delegating non-core processes to specialized third-party providers. Choosing between servitization and outsourcing depends on a company's strategic goals, with servitization focusing on value-added customer experiences and outsourcing prioritizing cost efficiency and scalability.
Connection
Servitization in manufacturing transforms traditional product-based companies into service-oriented providers, enhancing customer value through integrated solutions. Outsourcing supports servitization by enabling manufacturers to delegate non-core activities to specialized partners, optimizing resource allocation and operational efficiency. This strategic collaboration fosters innovation, reduces costs, and accelerates time-to-market for advanced manufacturing services.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Management
Outsourcing in supply chain management involves delegating specific logistics, procurement, or manufacturing functions to third-party providers to reduce costs and enhance operational efficiency. Servitization transforms traditional supply chains by integrating value-added services, such as maintenance and customer support, generating new revenue streams and fostering closer customer relationships. Explore the advantages and strategic implications of both approaches to optimize your supply chain performance.
Product-Service Systems (PSS)
Product-Service Systems (PSS) integrate products and services to enhance customer value and drive innovation, contrasting with traditional outsourcing that focuses on cost reduction by delegating business functions. PSS emphasizes collaboration between manufacturers and service providers to create sustainable, customized solutions, promoting long-term customer relationships and competitive advantage. Explore how PSS transforms business models and fosters sustainable growth in various industries.
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing often reduces operational costs by leveraging external expertise and economies of scale, allowing companies to focus on core activities while minimizing fixed expenses. Servitization transforms traditional product-based firms into service-oriented businesses, enhancing revenue streams through continuous customer engagement but requiring higher initial investments and management complexity. Explore in-depth comparisons to determine which strategy best aligns with your cost efficiency goals.
Source and External Links
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - Outsourcing is a business practice where a company hires a third party to perform tasks, handle operations, or provide services, often to reduce costs or access specialized skills.
Outsourcing - Outsourcing involves companies using external providers to carry out business processes that would otherwise be handled internally, and can include both domestic and foreign contracting.
What is outsourcing? | Definition and examples - Outsourcing refers to passing individual tasks, specific areas, or entire business processes to an external contractor, with common examples including customer service, IT, and manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com