Industrial Internet integrates vast networks of connected devices for real-time data collection and centralized analysis, enhancing manufacturing processes through predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Edge Computing processes data locally at the source, minimizing latency and bandwidth usage, enabling faster decision-making and improved machine performance on the factory floor. Discover how these technologies revolutionize manufacturing by unlocking new possibilities in automation and smart production.
Why it is important
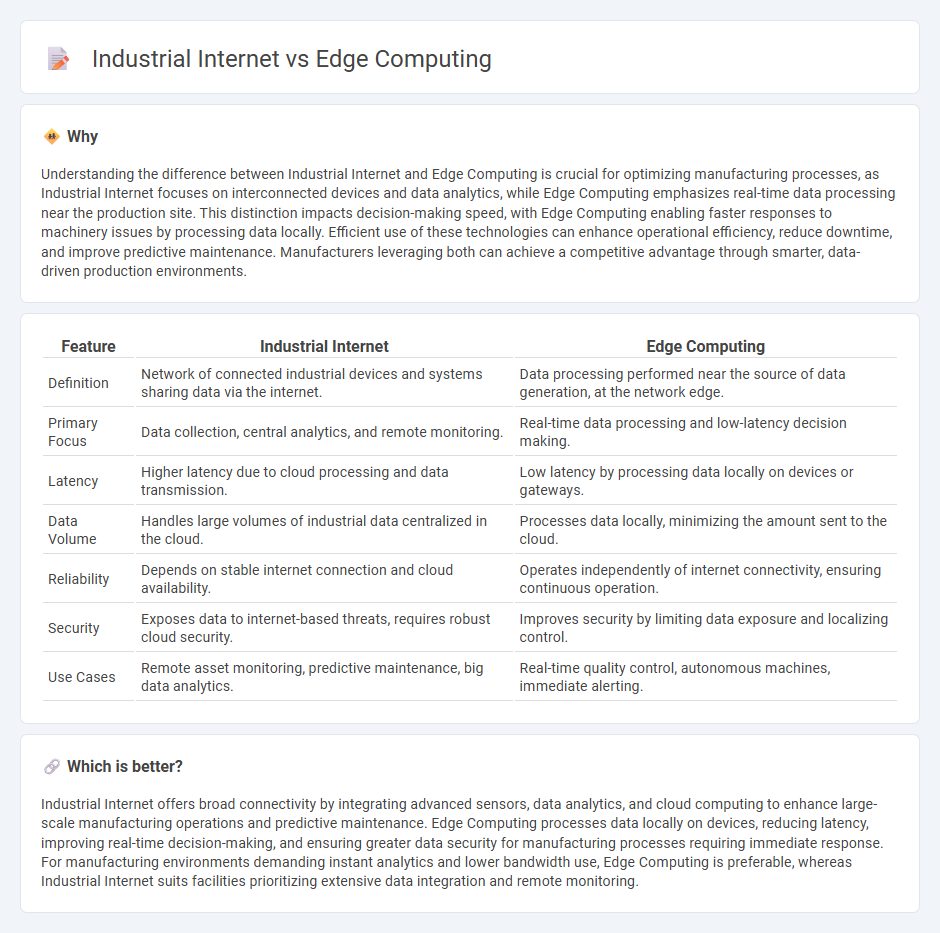
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Edge Computing is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as Industrial Internet focuses on interconnected devices and data analytics, while Edge Computing emphasizes real-time data processing near the production site. This distinction impacts decision-making speed, with Edge Computing enabling faster responses to machinery issues by processing data locally. Efficient use of these technologies can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve predictive maintenance. Manufacturers leveraging both can achieve a competitive advantage through smarter, data-driven production environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Internet | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of connected industrial devices and systems sharing data via the internet. | Data processing performed near the source of data generation, at the network edge. |
| Primary Focus | Data collection, central analytics, and remote monitoring. | Real-time data processing and low-latency decision making. |
| Latency | Higher latency due to cloud processing and data transmission. | Low latency by processing data locally on devices or gateways. |
| Data Volume | Handles large volumes of industrial data centralized in the cloud. | Processes data locally, minimizing the amount sent to the cloud. |
| Reliability | Depends on stable internet connection and cloud availability. | Operates independently of internet connectivity, ensuring continuous operation. |
| Security | Exposes data to internet-based threats, requires robust cloud security. | Improves security by limiting data exposure and localizing control. |
| Use Cases | Remote asset monitoring, predictive maintenance, big data analytics. | Real-time quality control, autonomous machines, immediate alerting. |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet offers broad connectivity by integrating advanced sensors, data analytics, and cloud computing to enhance large-scale manufacturing operations and predictive maintenance. Edge Computing processes data locally on devices, reducing latency, improving real-time decision-making, and ensuring greater data security for manufacturing processes requiring immediate response. For manufacturing environments demanding instant analytics and lower bandwidth use, Edge Computing is preferable, whereas Industrial Internet suits facilities prioritizing extensive data integration and remote monitoring.
Connection
The Industrial Internet leverages Edge Computing to process data generated by manufacturing equipment at or near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use. Edge Computing enables real-time analytics and rapid decision-making on the factory floor, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. Integrating these technologies drives smarter manufacturing systems with improved productivity and reduced downtime.
Key Terms
Real-time data processing
Edge computing enables real-time data processing by bringing computation and storage closer to the data source, reducing latency and enhancing decision-making speed in industrial environments. Industrial Internet relies on interconnected sensors and devices to collect massive data streams, but processing often occurs in centralized cloud systems, potentially introducing delays. Explore how integrating edge computing with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can optimize real-time analytics and operational efficiency.
Connectivity and interoperability
Edge computing enhances industrial internet connectivity by processing data locally at or near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use compared to cloud-only systems. Industrial internet relies on seamless interoperability between diverse devices and protocols, integrating sensors, machines, and enterprise systems for real-time analytics and decision-making. Explore how optimizing connectivity and interoperability in these technologies drives smarter, more efficient industrial operations.
Decentralized architecture
Edge computing in industrial internet environments emphasizes decentralized architecture by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making capabilities in smart factories and industrial automation. This approach distributes computing resources across multiple nodes, enhancing system resilience and minimizing bandwidth usage compared to centralized cloud models. Explore further to understand how decentralized edge solutions transform industrial operations and drive Industry 4.0 advancements.
Source and External Links
What is edge computing? | Glossary | HPE - Edge computing stores and processes data close to the user instead of a remote data center, reducing latency and enabling real-time processing with devices like IoT sensors and local servers.
What is edge computing? | Benefits of the edge - Cloudflare - Edge computing brings data processing near the source, minimizing long-distance communication and reducing latency and bandwidth usage for internet-connected devices and applications.
What Is Edge Computing? | Microsoft Azure - Edge computing allows devices in remote locations to process data locally or via nearby servers to ensure real-time actions with minimal latency, sending only critical data to central datacenters.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com