Decentralized manufacturing distributes production processes across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and reducing transportation costs by bringing manufacturing closer to end markets. Modular manufacturing uses standardized modules or components that can be easily reconfigured or scaled, promoting efficient customization and rapid assembly. Explore the benefits and applications of both approaches to optimize your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
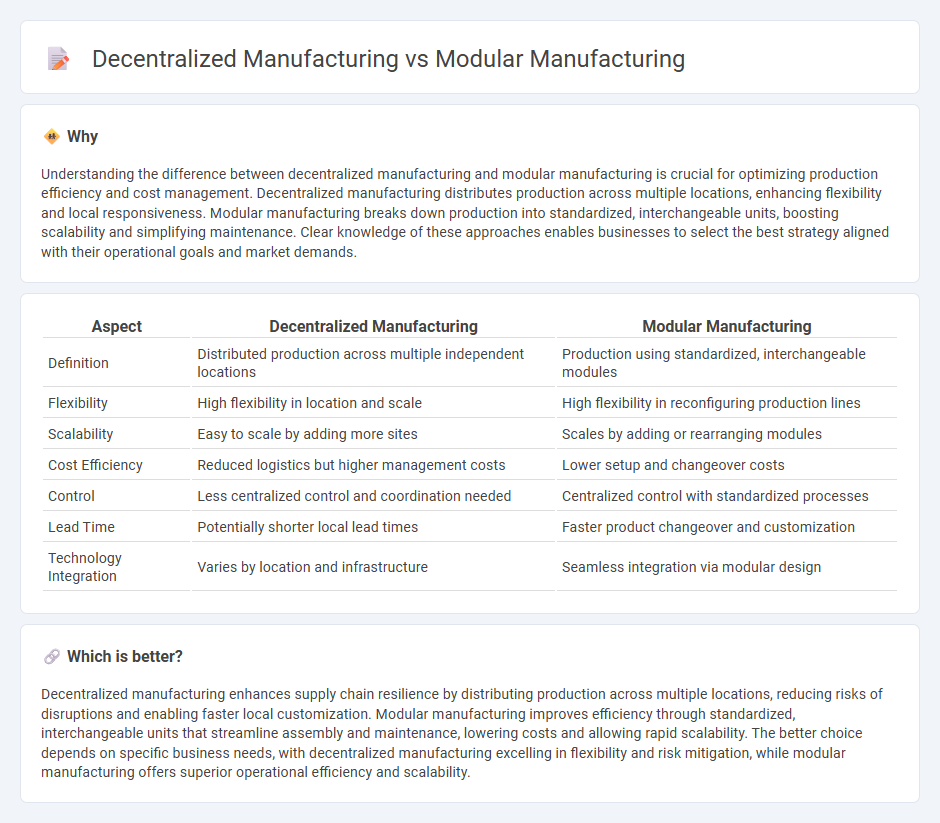
Understanding the difference between decentralized manufacturing and modular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management. Decentralized manufacturing distributes production across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and local responsiveness. Modular manufacturing breaks down production into standardized, interchangeable units, boosting scalability and simplifying maintenance. Clear knowledge of these approaches enables businesses to select the best strategy aligned with their operational goals and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Manufacturing | Modular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed production across multiple independent locations | Production using standardized, interchangeable modules |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in location and scale | High flexibility in reconfiguring production lines |
| Scalability | Easy to scale by adding more sites | Scales by adding or rearranging modules |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced logistics but higher management costs | Lower setup and changeover costs |
| Control | Less centralized control and coordination needed | Centralized control with standardized processes |
| Lead Time | Potentially shorter local lead times | Faster product changeover and customization |
| Technology Integration | Varies by location and infrastructure | Seamless integration via modular design |
Which is better?
Decentralized manufacturing enhances supply chain resilience by distributing production across multiple locations, reducing risks of disruptions and enabling faster local customization. Modular manufacturing improves efficiency through standardized, interchangeable units that streamline assembly and maintenance, lowering costs and allowing rapid scalability. The better choice depends on specific business needs, with decentralized manufacturing excelling in flexibility and risk mitigation, while modular manufacturing offers superior operational efficiency and scalability.
Connection
Decentralized manufacturing enhances flexibility by distributing production across multiple locations, enabling faster response to market demands and reducing supply chain risks. Modular manufacturing complements this by breaking down products into interchangeable modules, allowing for easier customization and scalability within decentralized facilities. Combining both approaches accelerates innovation, lowers costs, and improves efficiency in global manufacturing networks.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Modular manufacturing offers high flexibility by enabling easy reconfiguration of production lines through interchangeable modules, allowing rapid adaptation to changing product designs and volumes. Decentralized manufacturing enhances flexibility by distributing production across multiple locations, reducing dependence on a single facility and facilitating localized customization. Explore the advantages of both approaches to determine the best fit for your manufacturing needs.
Autonomy
Modular manufacturing enhances autonomy by enabling flexible reconfiguration of production units, allowing independent operation and rapid adaptation to changing demands, whereas decentralized manufacturing distributes production geographically to increase local decision-making and resilience. Autonomous systems in modular setups support real-time adjustments, maximizing efficiency with minimal human intervention, while decentralized models empower localized control to reduce supply chain risks. Explore further to understand how autonomy shapes the future of manufacturing landscapes.
Scalability
Modular manufacturing excels in scalability by enabling rapid reconfiguration of production units to meet changing demand without extensive downtime, utilizing standardized modules that streamline expansion. Decentralized manufacturing scales through distributed production facilities closer to end-users, reducing logistics costs and enhancing responsiveness but may face challenges in synchronizing quality and output consistency. Explore further to understand which scalability strategy aligns best with your manufacturing goals.
Source and External Links
The Benefits of Modular Design in Manufacturing - Tencom - Modular manufacturing produces standardized, interchangeable modules that can be simultaneously produced and assembled later, improving efficiency, flexibility, cost savings, and scalability across industries like automotive, electronics, construction, and aerospace.
Modular Manufacturing - Last Energy - Modular manufacturing utilizes standardized, compatible modules produced at different sites to streamline production, reduce waste, and allow rapid response to market changes, enhancing flexibility and innovation in the supply chain and design process.
Modular manufacturing systems - Modular manufacturing systems focus on flexibility by using modular production equipment that can be easily reconfigured and scaled, allowing rapid adaptation to different products and functions, potentially transforming traditional large, complex production lines.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com