Industrial edge computing processes data locally on manufacturing equipment to reduce latency, enhance real-time decision-making, and improve operational efficiency. Cloud computing centralizes data storage and analytics, offering scalability and extensive computational power but may introduce delays due to data transmission. Explore how these technologies transform manufacturing by balancing speed, cost, and data management needs.
Why it is important
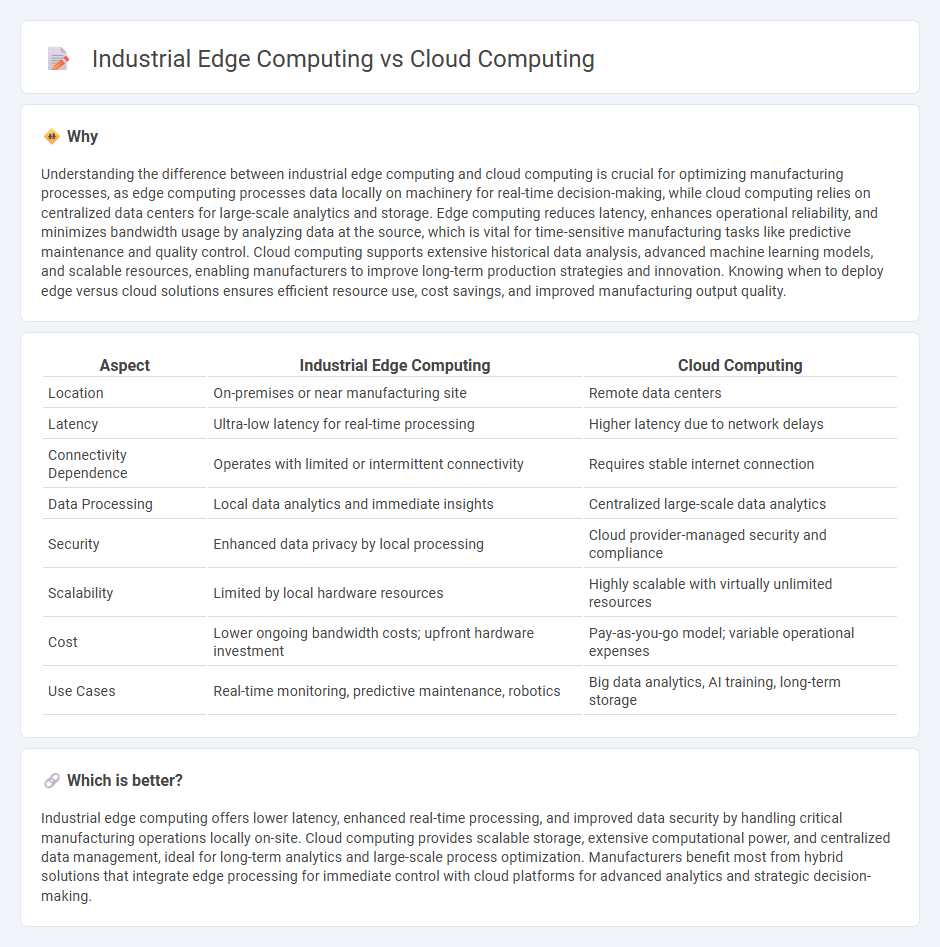
Understanding the difference between industrial edge computing and cloud computing is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as edge computing processes data locally on machinery for real-time decision-making, while cloud computing relies on centralized data centers for large-scale analytics and storage. Edge computing reduces latency, enhances operational reliability, and minimizes bandwidth usage by analyzing data at the source, which is vital for time-sensitive manufacturing tasks like predictive maintenance and quality control. Cloud computing supports extensive historical data analysis, advanced machine learning models, and scalable resources, enabling manufacturers to improve long-term production strategies and innovation. Knowing when to deploy edge versus cloud solutions ensures efficient resource use, cost savings, and improved manufacturing output quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Location | On-premises or near manufacturing site | Remote data centers |
| Latency | Ultra-low latency for real-time processing | Higher latency due to network delays |
| Connectivity Dependence | Operates with limited or intermittent connectivity | Requires stable internet connection |
| Data Processing | Local data analytics and immediate insights | Centralized large-scale data analytics |
| Security | Enhanced data privacy by local processing | Cloud provider-managed security and compliance |
| Scalability | Limited by local hardware resources | Highly scalable with virtually unlimited resources |
| Cost | Lower ongoing bandwidth costs; upfront hardware investment | Pay-as-you-go model; variable operational expenses |
| Use Cases | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, robotics | Big data analytics, AI training, long-term storage |
Which is better?
Industrial edge computing offers lower latency, enhanced real-time processing, and improved data security by handling critical manufacturing operations locally on-site. Cloud computing provides scalable storage, extensive computational power, and centralized data management, ideal for long-term analytics and large-scale process optimization. Manufacturers benefit most from hybrid solutions that integrate edge processing for immediate control with cloud platforms for advanced analytics and strategic decision-making.
Connection
Industrial edge computing processes data near manufacturing equipment, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making crucial for optimizing production workflows. Cloud computing complements this by providing scalable storage, advanced analytics, and centralized management, allowing manufacturers to aggregate and analyze vast datasets from multiple edge devices. The integration of edge and cloud computing enhances operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and quality control in smart manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Data latency
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, often resulting in higher data latency due to physical distance and network congestion. Industrial edge computing processes data locally at or near the source, significantly reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making critical for automation and control systems. Explore how minimizing data latency with edge solutions transforms industrial operations and boosts efficiency.
Processing location
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, offering vast computational resources and scalability ideal for complex analytics and large-scale applications. Industrial edge computing processes data locally near the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making capabilities critical for manufacturing, automation, and IoT environments. Explore how choosing between cloud and edge computing impacts operational efficiency and technology strategies.
Real-time analytics
Cloud computing offers scalable resources and centralized data processing, but latency and bandwidth limitations can hinder real-time analytics performance in industrial environments. Industrial edge computing processes data locally at or near the source, delivering low-latency, high-speed analytics essential for time-sensitive decision-making and automation in manufacturing and IoT applications. Explore the key advantages and use cases to understand which approach best supports your real-time analytics needs.
Source and External Links
What is Cloud Computing? Types, Examples and Benefits - Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of hosted IT services over the internet, using a network of remote data centers and servers managed by cloud providers, enabling users to access resources like storage and applications dynamically with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud computing - Cloud computing is a model for network access to a scalable, elastic pool of shared physical or virtual resources with essential features like on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured services defined by standards such as those from NIST and ISO.
What Is Cloud Computing? - Cloud computing provides users with flexible, scalable access to computing resources such as servers, data storage, and applications hosted in large data centers, allowing customers to use computing power without owning or managing hardware, which is fundamental for services like Gmail, Netflix, and cloud-hosted gaming.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com