Closed-loop manufacturing focuses on recycling materials within the production process to minimize waste and reduce raw material consumption, enhancing resource efficiency. Sustainable manufacturing extends beyond waste reduction by integrating eco-friendly practices, energy efficiency, and social responsibility into the entire lifecycle of products. Explore the key differences and benefits of closed-loop versus sustainable manufacturing to optimize your production strategy.
Why it is important
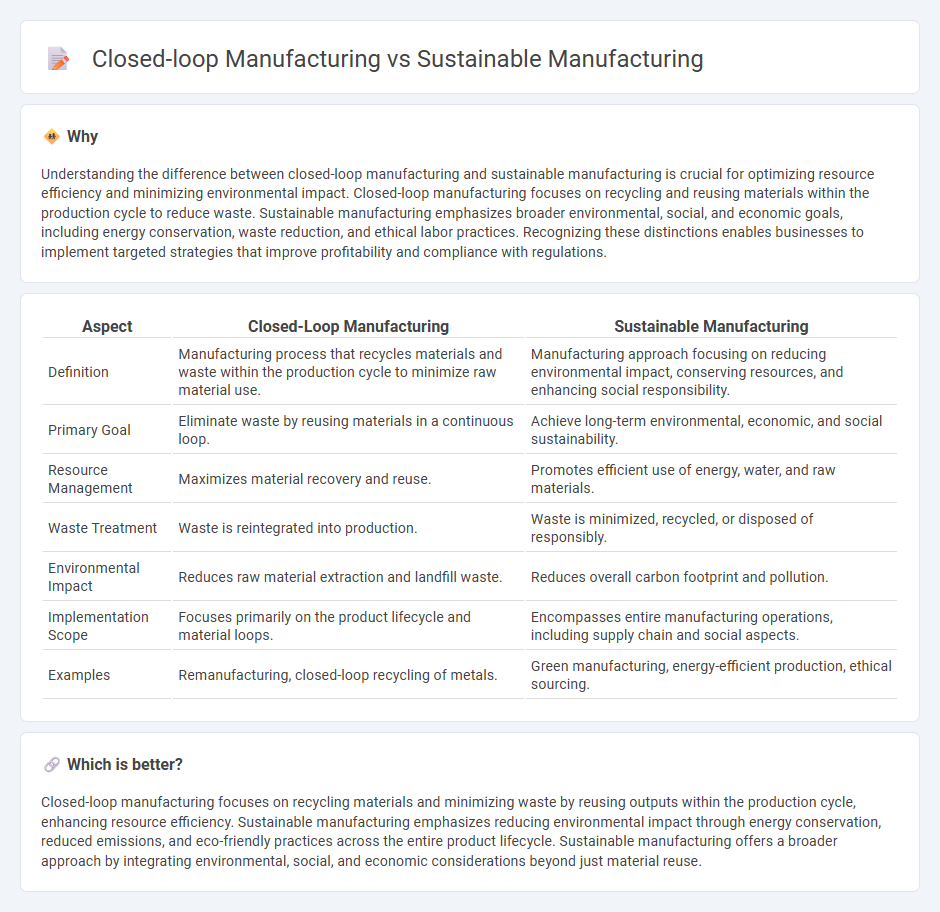
Understanding the difference between closed-loop manufacturing and sustainable manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. Closed-loop manufacturing focuses on recycling and reusing materials within the production cycle to reduce waste. Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes broader environmental, social, and economic goals, including energy conservation, waste reduction, and ethical labor practices. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to implement targeted strategies that improve profitability and compliance with regulations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Closed-Loop Manufacturing | Sustainable Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing process that recycles materials and waste within the production cycle to minimize raw material use. | Manufacturing approach focusing on reducing environmental impact, conserving resources, and enhancing social responsibility. |
| Primary Goal | Eliminate waste by reusing materials in a continuous loop. | Achieve long-term environmental, economic, and social sustainability. |
| Resource Management | Maximizes material recovery and reuse. | Promotes efficient use of energy, water, and raw materials. |
| Waste Treatment | Waste is reintegrated into production. | Waste is minimized, recycled, or disposed of responsibly. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces raw material extraction and landfill waste. | Reduces overall carbon footprint and pollution. |
| Implementation Scope | Focuses primarily on the product lifecycle and material loops. | Encompasses entire manufacturing operations, including supply chain and social aspects. |
| Examples | Remanufacturing, closed-loop recycling of metals. | Green manufacturing, energy-efficient production, ethical sourcing. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing focuses on recycling materials and minimizing waste by reusing outputs within the production cycle, enhancing resource efficiency. Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through energy conservation, reduced emissions, and eco-friendly practices across the entire product lifecycle. Sustainable manufacturing offers a broader approach by integrating environmental, social, and economic considerations beyond just material reuse.
Connection
Closed-loop manufacturing integrates recycling and reusing materials within production processes, significantly reducing waste and resource consumption. Sustainable manufacturing focuses on minimizing environmental impact by optimizing energy efficiency, reducing emissions, and fostering product lifecycle responsibility. The connection lies in their shared goal of promoting circular economy principles, where closed-loop systems enhance sustainability by enabling continuous material flow and reducing the need for virgin resources.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Sustainable manufacturing prioritizes reducing waste, energy consumption, and emissions throughout production processes to minimize environmental impact and promote resource efficiency. Closed-loop manufacturing specifically emphasizes recycling and reusing materials within the production cycle to create a circular economy that eliminates waste and maximizes resource conservation. Explore more to understand how these approaches transform industrial sustainability and resource management.
Waste Minimization
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact by optimizing resources and minimizing waste generation throughout the product lifecycle, while closed-loop manufacturing specifically targets waste minimization by recycling materials back into production processes to create a circular economy. Both approaches prioritize efficient resource use, but closed-loop manufacturing integrates advanced recycling technologies and product design innovations to achieve near-zero waste. Explore detailed strategies and case studies to understand how these manufacturing paradigms transform waste minimization efforts.
Circularity
Sustainable manufacturing emphasizes reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency, waste minimization, and resource conservation, ensuring long-term ecological balance. Closed-loop manufacturing specifically targets circularity by redesigning production processes to reuse materials and recover waste, creating a continuous recycling system that eliminates the concept of disposal. Explore how these approaches drive the transition to a circular economy and reshape industrial sustainability practices.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing | Sustainability Guide - Sustainable manufacturing focuses on creating products through processes that minimize environmental impacts, conserve energy and natural resources, and prioritize safety for employees, communities, and consumers by optimizing production, reducing waste, and fostering industrial symbiosis.
Sustainable Manufacturing | US EPA - The EPA defines sustainable manufacturing as producing goods through economically sound processes that reduce negative environmental impacts, conserve resources, enhance safety, and deliver substantial financial and competitive benefits for companies of all sizes and sectors.
5 Ways Manufacturers Can Become More Sustainable | Genius ERP - Manufacturers can increase sustainability by reducing energy use, adopting renewables, using recyclable materials, implementing lean practices, and partnering with sustainable suppliers to minimize waste and environmental impact throughout the supply chain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com