The Industrial Internet integrates advanced sensors and cloud computing to enable real-time data analytics and enhanced equipment connectivity, driving smarter manufacturing processes. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) focus on optimizing production workflows by tracking and managing operations on the factory floor, improving efficiency and reducing errors. Explore how combining Industrial Internet capabilities with MES can revolutionize your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
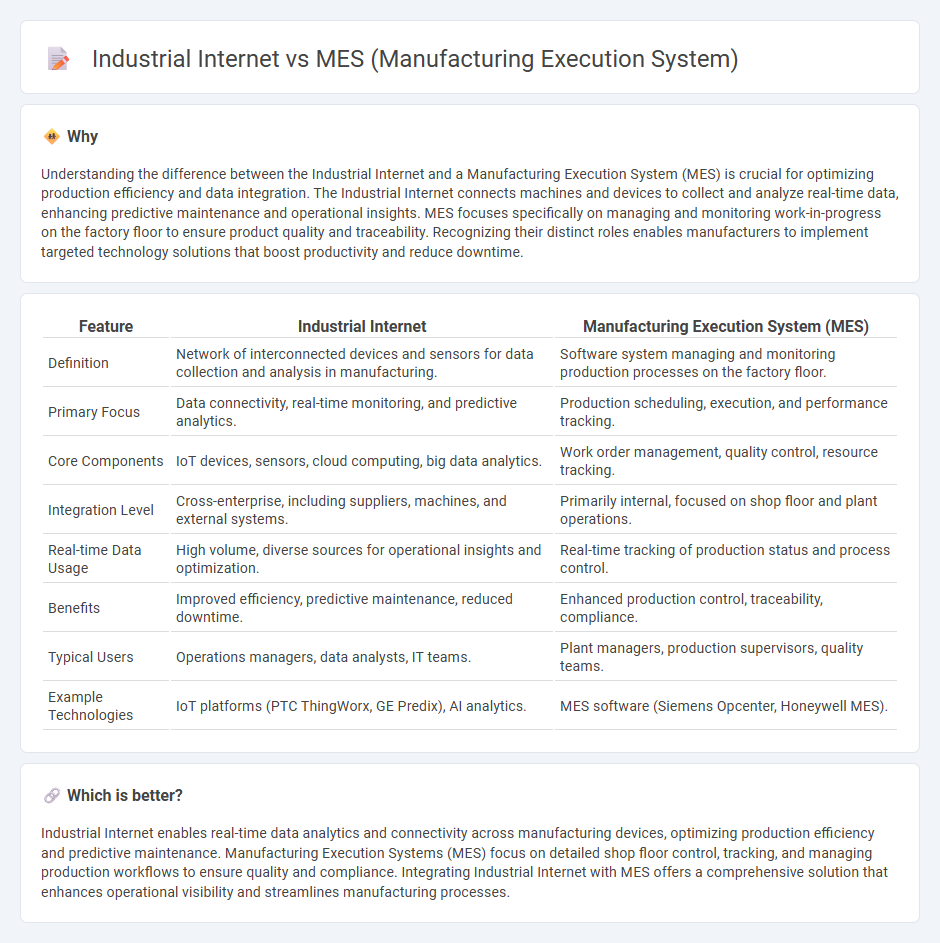
Understanding the difference between the Industrial Internet and a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and data integration. The Industrial Internet connects machines and devices to collect and analyze real-time data, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational insights. MES focuses specifically on managing and monitoring work-in-progress on the factory floor to ensure product quality and traceability. Recognizing their distinct roles enables manufacturers to implement targeted technology solutions that boost productivity and reduce downtime.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Internet | Manufacturing Execution System (MES) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of interconnected devices and sensors for data collection and analysis in manufacturing. | Software system managing and monitoring production processes on the factory floor. |
| Primary Focus | Data connectivity, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics. | Production scheduling, execution, and performance tracking. |
| Core Components | IoT devices, sensors, cloud computing, big data analytics. | Work order management, quality control, resource tracking. |
| Integration Level | Cross-enterprise, including suppliers, machines, and external systems. | Primarily internal, focused on shop floor and plant operations. |
| Real-time Data Usage | High volume, diverse sources for operational insights and optimization. | Real-time tracking of production status and process control. |
| Benefits | Improved efficiency, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime. | Enhanced production control, traceability, compliance. |
| Typical Users | Operations managers, data analysts, IT teams. | Plant managers, production supervisors, quality teams. |
| Example Technologies | IoT platforms (PTC ThingWorx, GE Predix), AI analytics. | MES software (Siemens Opcenter, Honeywell MES). |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet enables real-time data analytics and connectivity across manufacturing devices, optimizing production efficiency and predictive maintenance. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) focus on detailed shop floor control, tracking, and managing production workflows to ensure quality and compliance. Integrating Industrial Internet with MES offers a comprehensive solution that enhances operational visibility and streamlines manufacturing processes.
Connection
The Industrial Internet integrates smart sensors, devices, and analytics to create interconnected manufacturing environments that optimize real-time data flow. MES (Manufacturing Execution System) acts as the central software platform within this ecosystem, managing and monitoring production processes to enhance operational efficiency and quality control. This synergy enables manufacturers to achieve precise process tracking, predictive maintenance, and agile decision-making through seamless data exchange.
Key Terms
Real-time Production Monitoring
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide comprehensive real-time production monitoring by tracking shop floor activities, machine performance, and quality metrics with data integration from various manufacturing processes. Industrial Internet leverages IoT sensors, edge computing, and cloud platforms to enhance real-time visibility and predictive analytics across interconnected industrial equipment and networks. Explore deeper insights into how MES and Industrial Internet technologies transform real-time production monitoring and operational efficiency.
IIoT Connectivity
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) streamlines production processes by tracking and controlling manufacturing operations in real-time, while the Industrial Internet emphasizes IIoT connectivity to integrate machines, sensors, and systems for enhanced data-driven decision-making. IIoT connectivity enables seamless communication between devices, facilitating predictive maintenance, energy efficiency, and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) within smart factories. Explore how leveraging both MES and IIoT connectivity can revolutionize industrial productivity and operational intelligence.
Data Integration
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) centralizes real-time production data to optimize manufacturing workflows, while the Industrial Internet integrates vast sensor networks and IoT devices to enhance data collection across the entire industrial ecosystem. MES ensures precise control and traceability of shop floor operations, and the Industrial Internet enables scalable connectivity for predictive maintenance and advanced analytics. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how seamless data integration drives smarter manufacturing solutions.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing execution system - Wikipedia - MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is a computerized software system used in manufacturing to track and document the transformation of raw materials into finished products, providing real-time monitoring and control of production processes to enhance efficiency, quality, and decision-making on the plant floor.
What is a Manufacturing Execution System (MES)? - IBM - MES is a software-based solution bridging enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing operations, offering real-time visibility, control, and optimization of production activities, quality assurance, inventory management, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Top 10 benefits of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) - Infor - MES integrates production equipment with business systems, supports production order execution, enforces quality management, enables traceability, and provides data analytics to drive efficiency, responsiveness, and continuous improvement across manufacturing operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com