Cloud manufacturing leverages cloud computing technologies to enable on-demand access to distributed manufacturing resources and services, enhancing flexibility and scalability. Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) integrates computer-controlled machinery and automation systems to streamline production processes and improve precision. Explore how these advanced manufacturing paradigms transform industry operations and optimize efficiency.
Why it is important
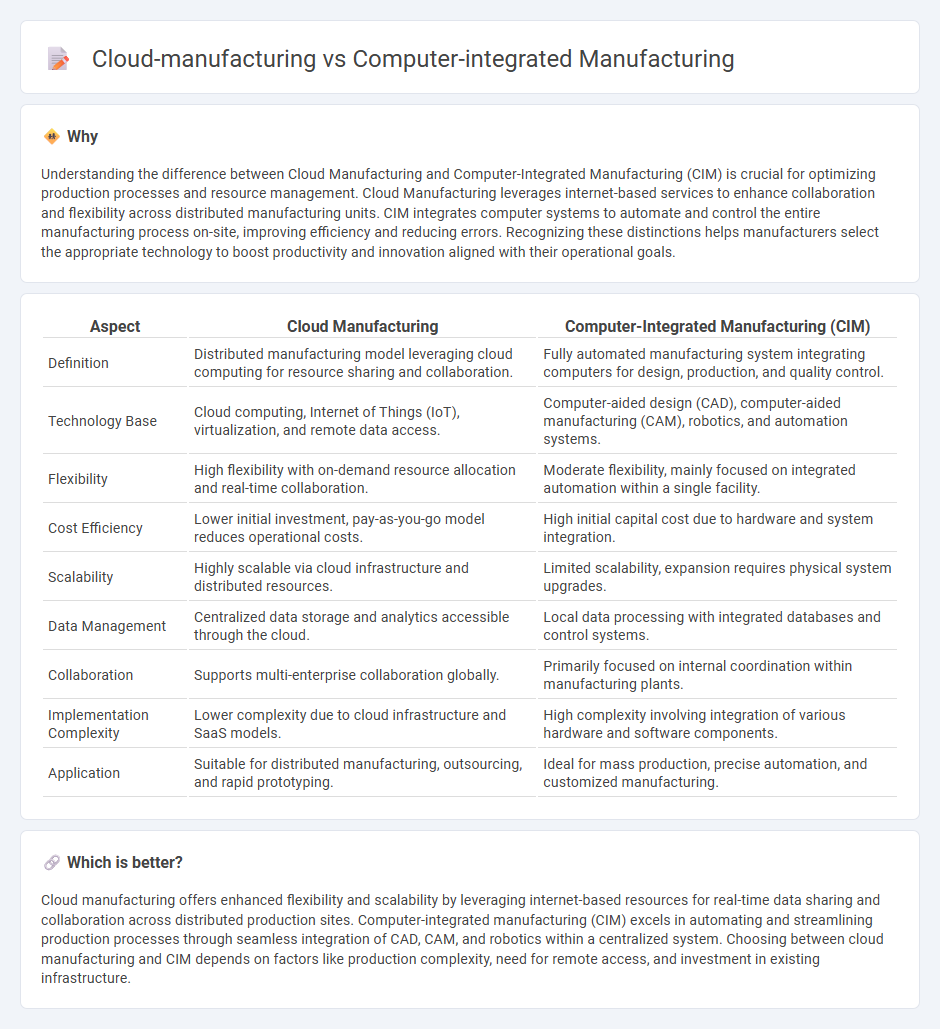
Understanding the difference between Cloud Manufacturing and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) is crucial for optimizing production processes and resource management. Cloud Manufacturing leverages internet-based services to enhance collaboration and flexibility across distributed manufacturing units. CIM integrates computer systems to automate and control the entire manufacturing process on-site, improving efficiency and reducing errors. Recognizing these distinctions helps manufacturers select the appropriate technology to boost productivity and innovation aligned with their operational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cloud Manufacturing | Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed manufacturing model leveraging cloud computing for resource sharing and collaboration. | Fully automated manufacturing system integrating computers for design, production, and quality control. |
| Technology Base | Cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT), virtualization, and remote data access. | Computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), robotics, and automation systems. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with on-demand resource allocation and real-time collaboration. | Moderate flexibility, mainly focused on integrated automation within a single facility. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment, pay-as-you-go model reduces operational costs. | High initial capital cost due to hardware and system integration. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via cloud infrastructure and distributed resources. | Limited scalability, expansion requires physical system upgrades. |
| Data Management | Centralized data storage and analytics accessible through the cloud. | Local data processing with integrated databases and control systems. |
| Collaboration | Supports multi-enterprise collaboration globally. | Primarily focused on internal coordination within manufacturing plants. |
| Implementation Complexity | Lower complexity due to cloud infrastructure and SaaS models. | High complexity involving integration of various hardware and software components. |
| Application | Suitable for distributed manufacturing, outsourcing, and rapid prototyping. | Ideal for mass production, precise automation, and customized manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing offers enhanced flexibility and scalability by leveraging internet-based resources for real-time data sharing and collaboration across distributed production sites. Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) excels in automating and streamlining production processes through seamless integration of CAD, CAM, and robotics within a centralized system. Choosing between cloud manufacturing and CIM depends on factors like production complexity, need for remote access, and investment in existing infrastructure.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing leverages cloud computing to provide scalable, on-demand access to manufacturing resources and data, enhancing flexibility and collaboration. Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) uses automated control systems and computer software to manage production processes seamlessly. The integration of cloud manufacturing with CIM enables real-time data exchange, remote monitoring, and optimized production workflows, driving efficiency and reducing operational costs in smart factories.
Key Terms
Automation
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) utilizes automated systems like CNC machines and robotics to streamline production processes within a physical factory environment. Cloud-manufacturing leverages cloud computing platforms to enable real-time data sharing, remote monitoring, and adaptive automation across distributed manufacturing sites. Discover how automation technologies transform industrial operations by exploring the distinct advantages of CIM and cloud-manufacturing.
Interoperability
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) relies on tightly coupled hardware and software systems within a centralized factory environment, emphasizing real-time data exchange through proprietary protocols for seamless interoperability. Cloud-manufacturing leverages distributed, internet-based platforms enabling scalable resource sharing and enhanced cross-organizational collaboration with standardized APIs and IoT integration for flexible interoperability across diverse systems. Explore the benefits and challenges of interoperability in both paradigms to optimize manufacturing efficiency.
Virtualization
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) employs automation and integrated hardware to streamline production processes on-site, enhancing efficiency through real-time data exchange and machine control. Cloud-manufacturing leverages virtualization technology to deliver manufacturing resources and capabilities via cloud platforms, enabling scalable, flexible, and distributed production environments accessible remotely. Explore deeper insights into how virtualization transforms manufacturing paradigms by comparing CIM and cloud-manufacturing architectures.
Source and External Links
Computer-integrated manufacturing - Wikipedia - Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) uses computers to control the entire production process, integrating functions like design, planning, and operations through real-time data exchange and automation.
Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM): Automation & ... - CIM automates and connects all facets of manufacturing--from product design and process planning to production control and quality assurance--using advanced software and IT systems to enhance efficiency and quality.
COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS - CIM encompasses the full range of product development and manufacturing activities, leveraging dedicated software and a common database to seamlessly integrate design, manufacturing, and business functions for improved performance and flexibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com