Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing by facilitating resource sharing among industries, reducing waste through collaborative use of by-products and energy. Materials efficiency focuses on optimizing raw material use, minimizing scrap, and improving product design to lower environmental impact. Explore the differences and benefits of industrial symbiosis versus materials efficiency to boost sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
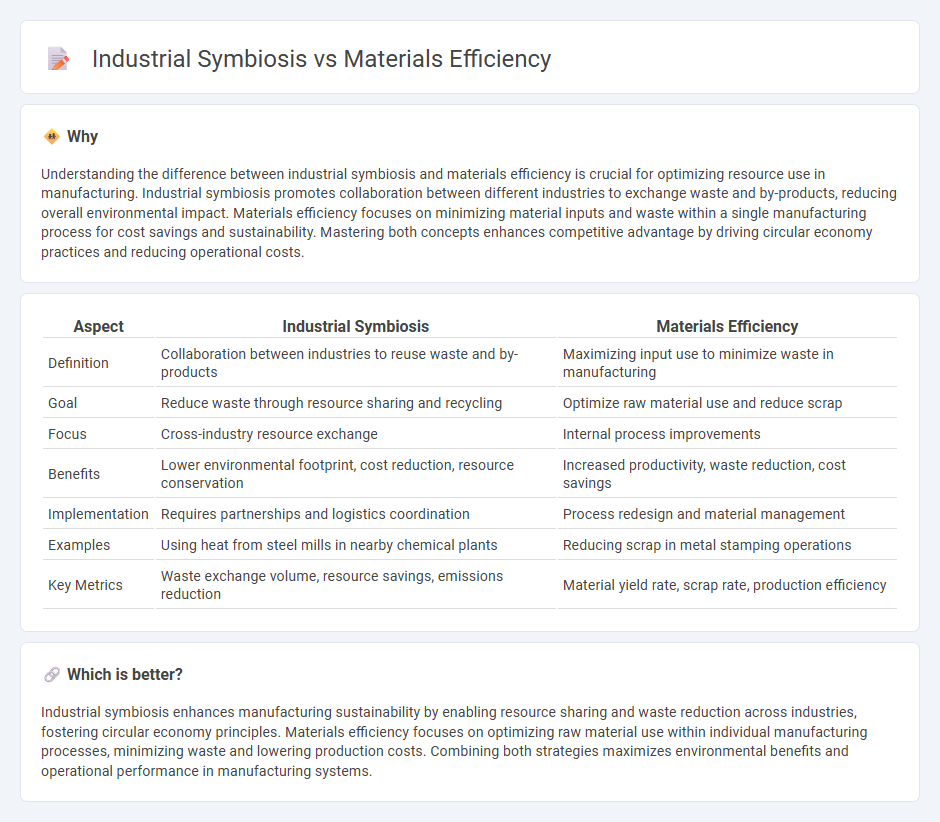
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and materials efficiency is crucial for optimizing resource use in manufacturing. Industrial symbiosis promotes collaboration between different industries to exchange waste and by-products, reducing overall environmental impact. Materials efficiency focuses on minimizing material inputs and waste within a single manufacturing process for cost savings and sustainability. Mastering both concepts enhances competitive advantage by driving circular economy practices and reducing operational costs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Materials Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaboration between industries to reuse waste and by-products | Maximizing input use to minimize waste in manufacturing |
| Goal | Reduce waste through resource sharing and recycling | Optimize raw material use and reduce scrap |
| Focus | Cross-industry resource exchange | Internal process improvements |
| Benefits | Lower environmental footprint, cost reduction, resource conservation | Increased productivity, waste reduction, cost savings |
| Implementation | Requires partnerships and logistics coordination | Process redesign and material management |
| Examples | Using heat from steel mills in nearby chemical plants | Reducing scrap in metal stamping operations |
| Key Metrics | Waste exchange volume, resource savings, emissions reduction | Material yield rate, scrap rate, production efficiency |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing sustainability by enabling resource sharing and waste reduction across industries, fostering circular economy principles. Materials efficiency focuses on optimizing raw material use within individual manufacturing processes, minimizing waste and lowering production costs. Combining both strategies maximizes environmental benefits and operational performance in manufacturing systems.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis enhances materials efficiency by promoting the reuse and exchange of waste streams between manufacturing processes, reducing raw material consumption and minimizing environmental impact. By integrating multiple industries, industrial symbiosis optimizes resource flow, leading to lower production costs and improved sustainability metrics in manufacturing. Efficient materials management within this collaborative framework drives circular economy principles and supports long-term industrial resilience.
Key Terms
Resource Optimization
Materials efficiency maximizes the use of raw materials by reducing waste and improving processing techniques, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits. Industrial symbiosis enhances resource optimization by facilitating the exchange of by-products, energy, and water between industries, transforming waste streams into valuable inputs. Explore how combining materials efficiency with industrial symbiosis drives sustainable industrial ecosystems and accelerates circular economy goals.
Waste Valorization
Materials efficiency maximizes resource use by reducing waste and improving production processes, while industrial symbiosis involves collaborative resource sharing among industries to transform waste into valuable inputs. Waste valorization plays a crucial role in both approaches by converting by-products into marketable materials, enhancing sustainability and economic gains. Explore innovative strategies to integrate materials efficiency with industrial symbiosis for advanced waste valorization.
By-product Exchange
Materials efficiency focuses on reducing waste and optimizing resource use within individual production processes to minimize environmental impact and cost. Industrial symbiosis enhances this by enabling by-product exchange, where waste or by-products from one industry become raw materials for another, creating interconnected resource loops and boosting overall sustainability. Explore how by-product exchange drives industrial symbiosis to maximize materials efficiency and promote circular economy initiatives.
Source and External Links
Material efficiency - Material efficiency refers to decreasing the amount of raw materials used in production through strategies like reduction, durability, lightweight design, and reuse, all aimed at reducing energy use, costs, and carbon emissions in industries such as steel and construction.
Material efficiency in clean energy transitions - Analysis - Material efficiency strategies can significantly reduce demand for key materials like steel, cement, and aluminum, contributing about 30% of emissions reductions in scenarios aligned with the Paris Agreement by minimizing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Industrial material efficiency - Material efficiency means meeting human needs with minimal material production through design innovations like light weighting, optimized and long-life designs, and reducing fabrication losses, thereby improving sustainability and extending product lifetimes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com