Smart dust technology involves the deployment of tiny, wireless sensors capable of monitoring manufacturing processes in real-time with high precision, enhancing data collection and operational efficiency. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds complex parts layer by layer from digital models, reducing material waste and enabling rapid prototyping and customization. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of smart dust and additive manufacturing to optimize your production strategies.
Why it is important
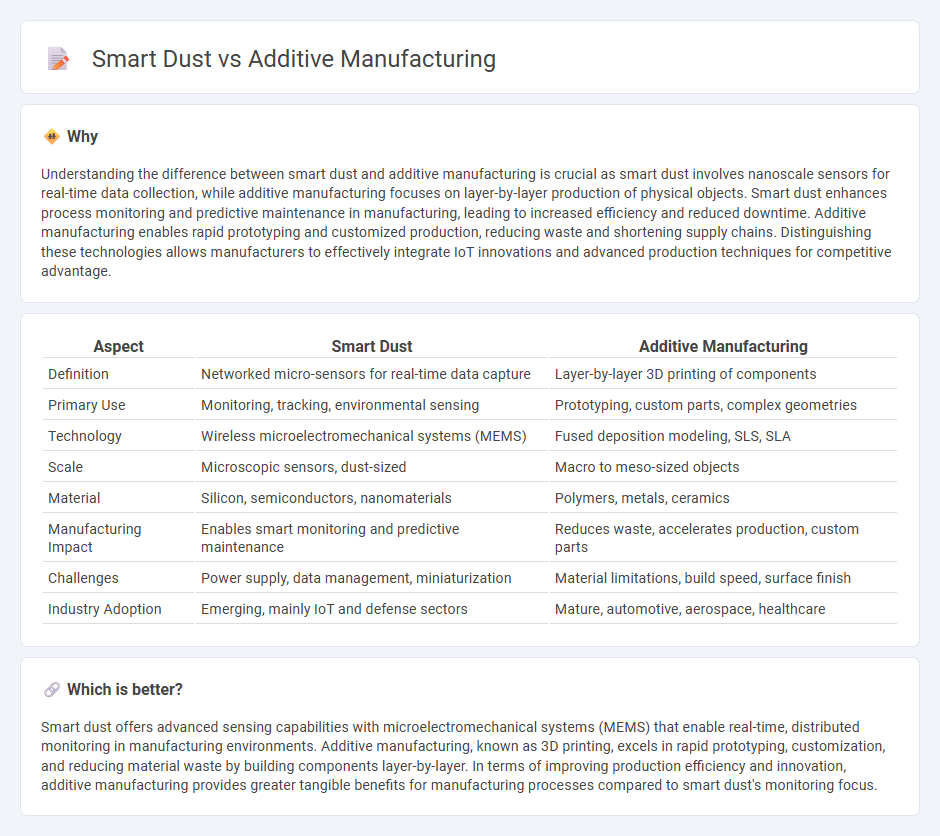
Understanding the difference between smart dust and additive manufacturing is crucial as smart dust involves nanoscale sensors for real-time data collection, while additive manufacturing focuses on layer-by-layer production of physical objects. Smart dust enhances process monitoring and predictive maintenance in manufacturing, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime. Additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and customized production, reducing waste and shortening supply chains. Distinguishing these technologies allows manufacturers to effectively integrate IoT innovations and advanced production techniques for competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Dust | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Networked micro-sensors for real-time data capture | Layer-by-layer 3D printing of components |
| Primary Use | Monitoring, tracking, environmental sensing | Prototyping, custom parts, complex geometries |
| Technology | Wireless microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) | Fused deposition modeling, SLS, SLA |
| Scale | Microscopic sensors, dust-sized | Macro to meso-sized objects |
| Material | Silicon, semiconductors, nanomaterials | Polymers, metals, ceramics |
| Manufacturing Impact | Enables smart monitoring and predictive maintenance | Reduces waste, accelerates production, custom parts |
| Challenges | Power supply, data management, miniaturization | Material limitations, build speed, surface finish |
| Industry Adoption | Emerging, mainly IoT and defense sectors | Mature, automotive, aerospace, healthcare |
Which is better?
Smart dust offers advanced sensing capabilities with microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) that enable real-time, distributed monitoring in manufacturing environments. Additive manufacturing, known as 3D printing, excels in rapid prototyping, customization, and reducing material waste by building components layer-by-layer. In terms of improving production efficiency and innovation, additive manufacturing provides greater tangible benefits for manufacturing processes compared to smart dust's monitoring focus.
Connection
Smart dust enhances additive manufacturing by providing real-time monitoring of 3D printing processes through microscopic sensors dispersed within materials. These sensors collect data on temperature, stress, and humidity, enabling precise control and quality assurance during production. Integrating smart dust accelerates innovation in manufacturing by improving customization, reducing defects, and optimizing resource usage.
Key Terms
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing, a leading form of additive manufacturing, creates objects layer by layer from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping and customized production in industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive. Smart dust consists of microelectromechanical sensors that collect and transmit environmental data, focusing on real-time monitoring rather than physical creation. Explore how 3D printing revolutionizes manufacturing efficiency and design innovation by learning more about its applications and future potential.
Microelectromechanical Systems (Smart Dust)
Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS), often referred to as smart dust, consist of tiny sensors and actuators that monitor and interact with their environments at a microscale, revolutionizing data collection and automation. Additive manufacturing enables the precise fabrication of complex MEMS structures with enhanced material properties and scalability, bridging the gap between conceptual design and functional deployment. Explore the advancements and applications of MEMS within additive manufacturing to understand their transformative potential.
Sensors
Additive manufacturing enables precise fabrication of complex sensor geometries through layer-by-layer deposition of materials, enhancing customization and miniaturization in sensor design. Smart dust consists of ultra-small, wireless sensor nodes capable of real-time environmental monitoring, relying on advanced microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology for sensing and communication. Explore how these cutting-edge sensor technologies revolutionize IoT applications and environmental data collection.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained - Additive manufacturing is a process that builds objects one layer at a time from digital designs, typically using 3D printing technology, and is the opposite of traditional subtractive manufacturing where material is removed to create a product.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing fabricates three-dimensional products layer by layer directly from digital files, allowing for complex designs and less material waste compared to conventional methods.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Additive manufacturing encompasses seven main process categories, including VAT photopolymerisation, material jetting, and binder jetting, each differing in technique and materials used for layer-by-layer construction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com