Smart dust and wireless sensor networks represent cutting-edge advancements in manufacturing monitoring and automation, with smart dust consisting of tiny, autonomous microelectromechanical sensors that can detect environmental changes at a granular level. Wireless sensor networks rely on interconnected sensor nodes that communicate data wirelessly to optimize processes and ensure real-time production efficiency. Explore how these innovative technologies transform manufacturing operations by enhancing precision and reducing downtime.
Why it is important
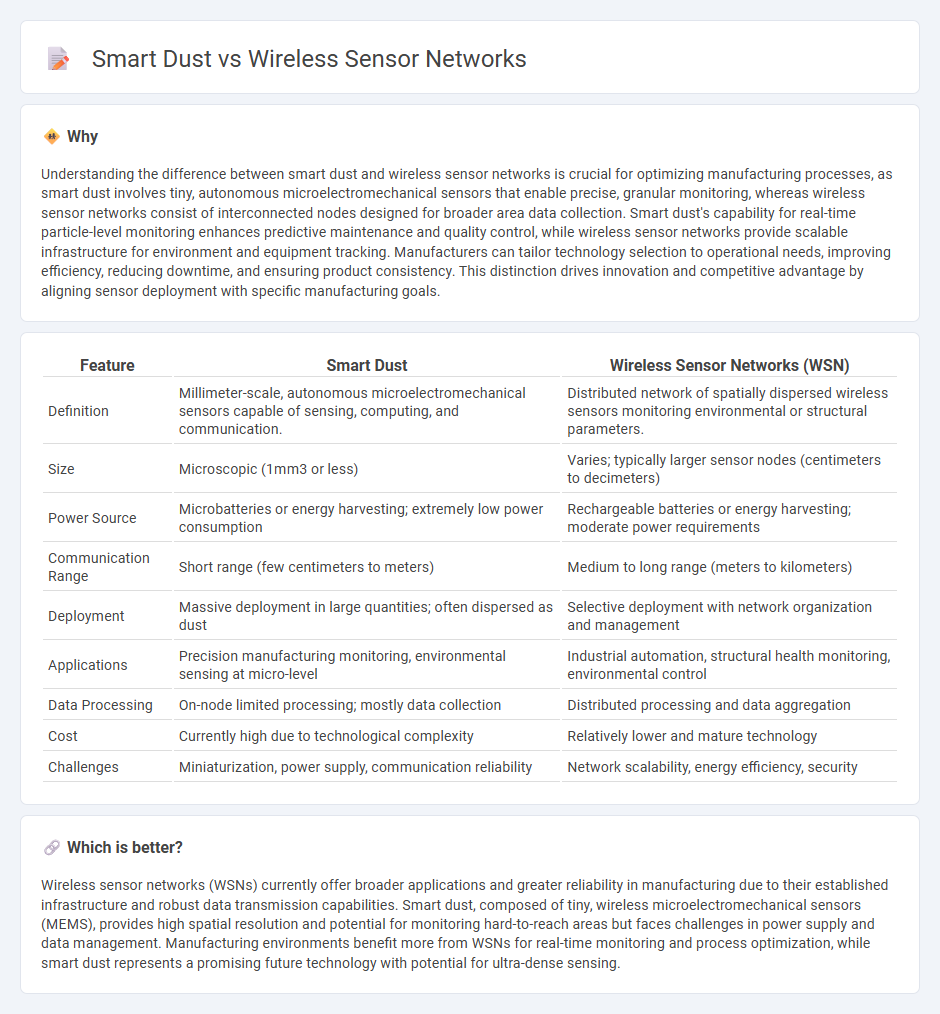
Understanding the difference between smart dust and wireless sensor networks is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as smart dust involves tiny, autonomous microelectromechanical sensors that enable precise, granular monitoring, whereas wireless sensor networks consist of interconnected nodes designed for broader area data collection. Smart dust's capability for real-time particle-level monitoring enhances predictive maintenance and quality control, while wireless sensor networks provide scalable infrastructure for environment and equipment tracking. Manufacturers can tailor technology selection to operational needs, improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and ensuring product consistency. This distinction drives innovation and competitive advantage by aligning sensor deployment with specific manufacturing goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Dust | Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Millimeter-scale, autonomous microelectromechanical sensors capable of sensing, computing, and communication. | Distributed network of spatially dispersed wireless sensors monitoring environmental or structural parameters. |
| Size | Microscopic (1mm3 or less) | Varies; typically larger sensor nodes (centimeters to decimeters) |
| Power Source | Microbatteries or energy harvesting; extremely low power consumption | Rechargeable batteries or energy harvesting; moderate power requirements |
| Communication Range | Short range (few centimeters to meters) | Medium to long range (meters to kilometers) |
| Deployment | Massive deployment in large quantities; often dispersed as dust | Selective deployment with network organization and management |
| Applications | Precision manufacturing monitoring, environmental sensing at micro-level | Industrial automation, structural health monitoring, environmental control |
| Data Processing | On-node limited processing; mostly data collection | Distributed processing and data aggregation |
| Cost | Currently high due to technological complexity | Relatively lower and mature technology |
| Challenges | Miniaturization, power supply, communication reliability | Network scalability, energy efficiency, security |
Which is better?
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) currently offer broader applications and greater reliability in manufacturing due to their established infrastructure and robust data transmission capabilities. Smart dust, composed of tiny, wireless microelectromechanical sensors (MEMS), provides high spatial resolution and potential for monitoring hard-to-reach areas but faces challenges in power supply and data management. Manufacturing environments benefit more from WSNs for real-time monitoring and process optimization, while smart dust represents a promising future technology with potential for ultra-dense sensing.
Connection
Smart dust consists of tiny, wireless sensors that form highly scalable Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) for real-time data collection in manufacturing environments. These networks enable precise monitoring of equipment status, environmental conditions, and process parameters, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Integration of smart dust with WSNs facilitates seamless communication and granular analytics, driving Industry 4.0 advancements in smart factories.
Key Terms
Nodes
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) consist of spatially distributed nodes equipped with sensors to monitor environmental conditions, characterized by their moderate size, power consumption, and processing capabilities. Smart dust nodes, or motes, are ultra-miniaturized sensor devices with minimal power requirements and advanced microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology, enabling deployment at micro-scale densities. Explore the technological distinctions and application potentials of these node types for enhanced monitoring solutions.
Communication Protocols
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) utilize protocols like Zigbee, Bluetooth Low Energy, and IEEE 802.15.4 to enable efficient data transmission and energy management across distributed nodes. Smart dust communication protocols emphasize ultra-low power consumption and miniaturized hardware integration, often relying on millimeter-wave or optical communication for high-density deployment. Explore deeper into the specific protocol architectures and their impact on scalability and latency in both technologies.
Data Aggregation
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) utilize structured nodes to collect and aggregate data efficiently, optimizing energy consumption and reducing communication overhead through hierarchical data aggregation protocols. Smart dust, consisting of ultra-small, autonomous sensor particles, faces challenges in data aggregation due to limited processing power and storage but leverages dense deployment for spatial data fusion. Explore detailed comparisons of data aggregation strategies in WSNs and smart dust architectures to understand their unique efficiencies.
Source and External Links
Wireless sensor network - Wikipedia - Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are networks of spatially distributed sensors that monitor environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and pollution, and transmit collected data wirelessly to a central location.
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) - GeeksforGeeks - WSNs are infrastructure-less networks deployed with numerous wireless sensors in an ad-hoc manner to monitor physical or environmental conditions, with sensor nodes processing data and communicating to a base station connected to the internet.
An Overview on Wireless Sensor Networks Technology and Evolution - WSNs enable innovative applications through low-complexity, energy-efficient devices, with research and standardization focusing on balancing communication and processing capabilities for long network lifetime.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com