Smart factories leverage advanced digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to enable real-time data analysis, flexible automation, and enhanced production efficiency, contrasting with traditional mass production that relies on large-scale, repetitive processes with limited customization. While mass production emphasizes volume and cost reduction through standardized outputs, smart factories prioritize adaptability, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource utilization. Explore how the shift from mass production to smart factories revolutionizes manufacturing performance and competitiveness.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a smart factory and mass production is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and innovation. A smart factory integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to enable real-time data-driven decisions and flexible production. Mass production focuses on high-volume, standardized output with less adaptability and minimal technological integration. Identifying these distinctions helps businesses choose the right strategy to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and meet market demands.
Comparison Table
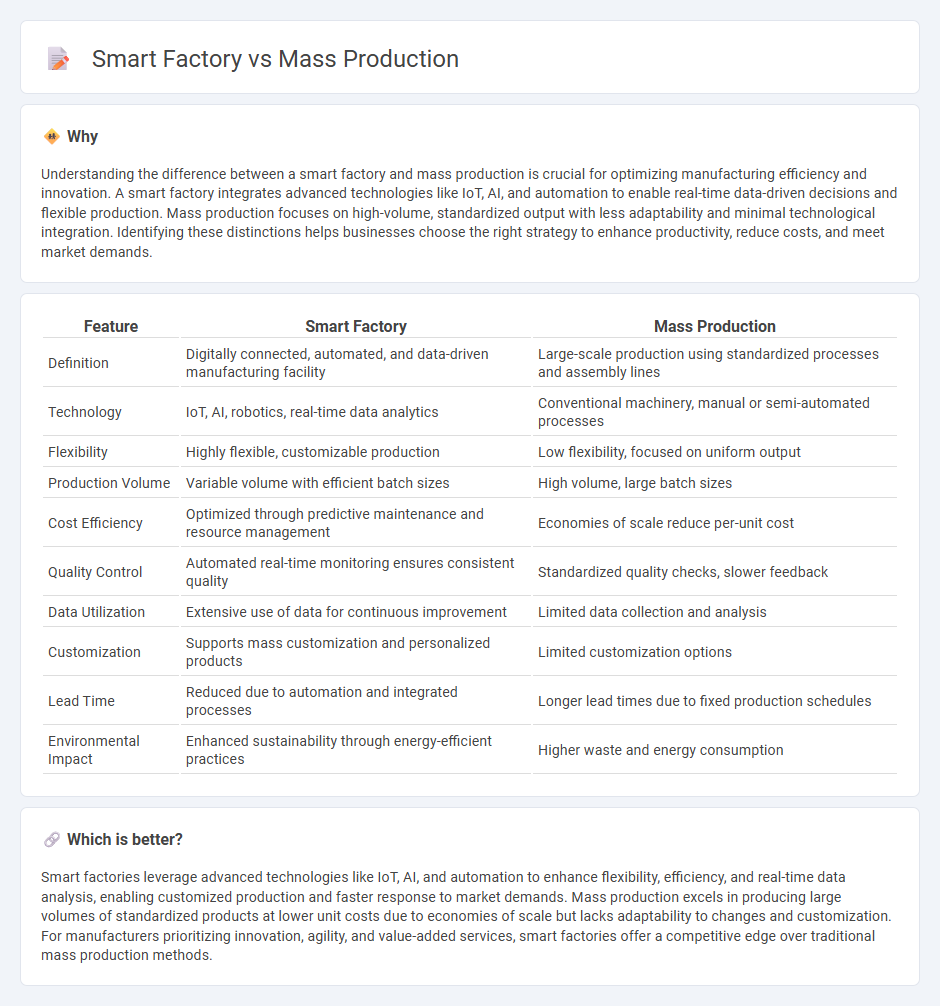
| Feature | Smart Factory | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitally connected, automated, and data-driven manufacturing facility | Large-scale production using standardized processes and assembly lines |
| Technology | IoT, AI, robotics, real-time data analytics | Conventional machinery, manual or semi-automated processes |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, customizable production | Low flexibility, focused on uniform output |
| Production Volume | Variable volume with efficient batch sizes | High volume, large batch sizes |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimized through predictive maintenance and resource management | Economies of scale reduce per-unit cost |
| Quality Control | Automated real-time monitoring ensures consistent quality | Standardized quality checks, slower feedback |
| Data Utilization | Extensive use of data for continuous improvement | Limited data collection and analysis |
| Customization | Supports mass customization and personalized products | Limited customization options |
| Lead Time | Reduced due to automation and integrated processes | Longer lead times due to fixed production schedules |
| Environmental Impact | Enhanced sustainability through energy-efficient practices | Higher waste and energy consumption |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to enhance flexibility, efficiency, and real-time data analysis, enabling customized production and faster response to market demands. Mass production excels in producing large volumes of standardized products at lower unit costs due to economies of scale but lacks adaptability to changes and customization. For manufacturers prioritizing innovation, agility, and value-added services, smart factories offer a competitive edge over traditional mass production methods.
Connection
Smart factories optimize mass production through real-time data analytics and automation, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Integration of IoT devices and AI-driven machinery enables adaptive manufacturing processes that reduce downtime and waste. This synergy transforms traditional mass production into a flexible, scalable system responsive to market demands.
Key Terms
Automation
Mass production relies heavily on repetitive manual tasks and mechanized assembly lines to achieve high output, whereas smart factories integrate advanced automation technologies like IoT sensors, AI, and robotics to optimize efficiency and flexibility. Automation in smart factories enables real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and adaptive workflows, significantly reducing downtime and operational costs. Explore how smart factory automation transforms traditional manufacturing processes to unlock unprecedented productivity gains.
Industrial IoT (Internet of Things)
Mass production relies on standardized processes and large-scale manufacturing, while smart factories integrate Industrial IoT technologies to enable real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and adaptive automation. Industrial IoT connects machines, sensors, and systems to enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize supply chains in smart factory environments. Explore how Industrial IoT transforms manufacturing by bridging mass production with intelligent automation and connectivity.
Production flexibility
Mass production emphasizes high-volume output with standardized processes, limiting production flexibility to accommodate customization or small batch sizes. Smart factories leverage advanced automation, IoT, and AI technologies to enable rapid reconfiguration and adaptive manufacturing, significantly enhancing production flexibility. Explore how smart factory innovations transform traditional manufacturing to meet dynamic market demands.
Source and External Links
What Is Mass Production? A Comprehensive Guide - Mass production is a manufacturing method designed to produce large quantities of standardized products efficiently through specialization, mechanization, and streamlined processes.
Mass production - Mass production involves making many copies of products quickly using assembly line techniques, where each worker focuses on a specific step, enabling high-volume output and consistent quality.
Mass Production - Overview, How It Works, Advantages - Mass production is the continuous manufacturing of standardized products using automation and assembly lines, which lowers costs, increases productivity, and meets large-scale consumer demand.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com