Cobotics integrates collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside human operators, enhancing flexibility and efficiency in manufacturing processes compared to traditional automated systems. Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on fixed automation and manual labor, often resulting in longer setup times and less adaptability to product variations. Discover how cobotic systems are revolutionizing production lines and boosting operational productivity.
Why it is important
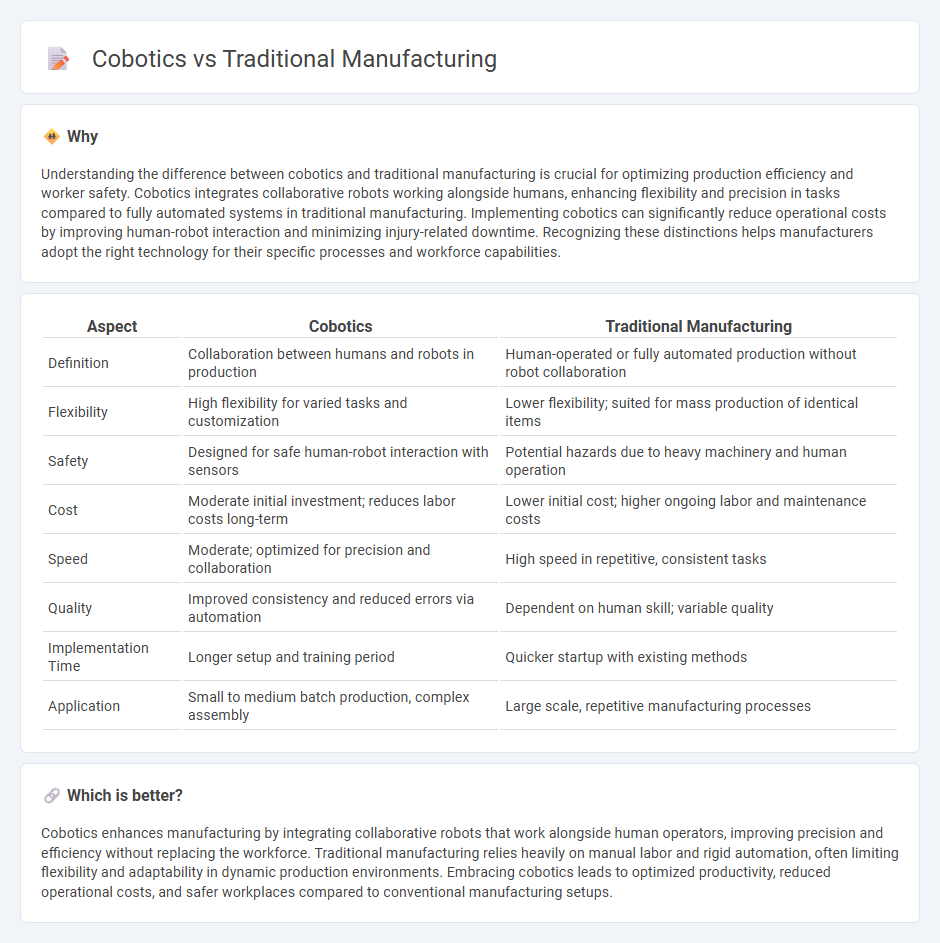
Understanding the difference between cobotics and traditional manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and worker safety. Cobotics integrates collaborative robots working alongside humans, enhancing flexibility and precision in tasks compared to fully automated systems in traditional manufacturing. Implementing cobotics can significantly reduce operational costs by improving human-robot interaction and minimizing injury-related downtime. Recognizing these distinctions helps manufacturers adopt the right technology for their specific processes and workforce capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cobotics | Traditional Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaboration between humans and robots in production | Human-operated or fully automated production without robot collaboration |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for varied tasks and customization | Lower flexibility; suited for mass production of identical items |
| Safety | Designed for safe human-robot interaction with sensors | Potential hazards due to heavy machinery and human operation |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; reduces labor costs long-term | Lower initial cost; higher ongoing labor and maintenance costs |
| Speed | Moderate; optimized for precision and collaboration | High speed in repetitive, consistent tasks |
| Quality | Improved consistency and reduced errors via automation | Dependent on human skill; variable quality |
| Implementation Time | Longer setup and training period | Quicker startup with existing methods |
| Application | Small to medium batch production, complex assembly | Large scale, repetitive manufacturing processes |
Which is better?
Cobotics enhances manufacturing by integrating collaborative robots that work alongside human operators, improving precision and efficiency without replacing the workforce. Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on manual labor and rigid automation, often limiting flexibility and adaptability in dynamic production environments. Embracing cobotics leads to optimized productivity, reduced operational costs, and safer workplaces compared to conventional manufacturing setups.
Connection
Cobotics integrates collaborative robots into traditional manufacturing environments to enhance productivity and precision by working alongside human operators. This synergy reduces manual labor, minimizes errors, and streamlines assembly processes across automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries. Data-driven cobotic systems enable adaptive workflows and real-time quality control, bridging the gap between conventional methods and Industry 4.0 innovations.
Key Terms
Human Labor
Traditional manufacturing heavily relies on human labor for repetitive and physically demanding tasks, often leading to fatigue and increased risk of injury. Cobotics integrates collaborative robots alongside workers, enhancing efficiency and safety while allowing employees to focus on higher-skilled roles. Explore the benefits of cobotics in transforming human labor dynamics.
Automation
Traditional manufacturing relies on manual labor and rigid machinery, often resulting in lower flexibility and higher operational costs. Cobotics integrates collaborative robots to automate repetitive tasks, enhancing productivity, accuracy, and worker safety by working alongside human operators. Explore how cobotics is revolutionizing automation and transforming manufacturing processes for greater efficiency.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on manual labor and rigid automation systems, which often lack flexibility and adaptability to changing production demands. Collaborative robots (cobots) enhance manufacturing efficiency by working safely alongside human operators, offering improved precision, reduced downtime, and scalable automation solutions. Explore the transformative impact of cobots on modern manufacturing processes and their integration.
Source and External Links
Lean Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing - Traditional manufacturing is a mass production approach that prioritizes high output volumes, economies of scale, and inventory accumulation, often resulting in longer lead times and excess inventory due to its push-based, forecast-driven system.
Which is Better? Traditional vs. On-Demand Manufacturing - Traditional manufacturing relies on established processes like casting, machining, and molding, offering reliability, consistency, and efficiency for high-volume production, with a broad selection of materials available for engineers.
Friends or Foes: Additive and Traditional Manufacturing - Traditional manufacturing enables rapid, high-volume production but often generates significant material waste, has limited design flexibility once tools are made, and incurs higher per-unit costs for small to medium production runs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com