Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback and automation to continuously optimize production processes, reducing waste and improving product quality. Flexible manufacturing adapts quickly to changing product designs and volumes, enabling efficient production across diverse product types with minimal downtime. Explore the advantages and applications of closed-loop and flexible manufacturing to enhance your industrial operations.
Why it is important
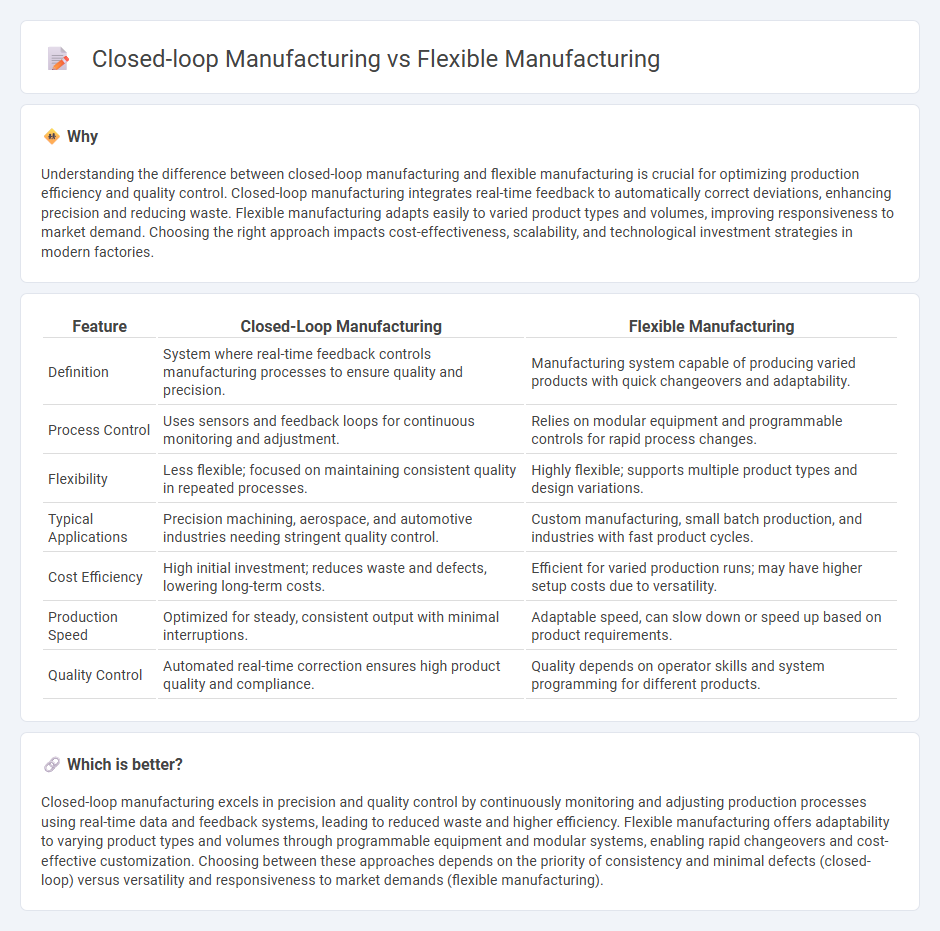
Understanding the difference between closed-loop manufacturing and flexible manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and quality control. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback to automatically correct deviations, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Flexible manufacturing adapts easily to varied product types and volumes, improving responsiveness to market demand. Choosing the right approach impacts cost-effectiveness, scalability, and technological investment strategies in modern factories.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Closed-Loop Manufacturing | Flexible Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System where real-time feedback controls manufacturing processes to ensure quality and precision. | Manufacturing system capable of producing varied products with quick changeovers and adaptability. |
| Process Control | Uses sensors and feedback loops for continuous monitoring and adjustment. | Relies on modular equipment and programmable controls for rapid process changes. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; focused on maintaining consistent quality in repeated processes. | Highly flexible; supports multiple product types and design variations. |
| Typical Applications | Precision machining, aerospace, and automotive industries needing stringent quality control. | Custom manufacturing, small batch production, and industries with fast product cycles. |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment; reduces waste and defects, lowering long-term costs. | Efficient for varied production runs; may have higher setup costs due to versatility. |
| Production Speed | Optimized for steady, consistent output with minimal interruptions. | Adaptable speed, can slow down or speed up based on product requirements. |
| Quality Control | Automated real-time correction ensures high product quality and compliance. | Quality depends on operator skills and system programming for different products. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing excels in precision and quality control by continuously monitoring and adjusting production processes using real-time data and feedback systems, leading to reduced waste and higher efficiency. Flexible manufacturing offers adaptability to varying product types and volumes through programmable equipment and modular systems, enabling rapid changeovers and cost-effective customization. Choosing between these approaches depends on the priority of consistency and minimal defects (closed-loop) versus versatility and responsiveness to market demands (flexible manufacturing).
Connection
Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time data feedback to continuously optimize production processes, enabling adaptive adjustments that align with flexible manufacturing principles. Flexible manufacturing systems use this dynamic data to quickly switch between different products or processes, enhancing responsiveness to market demands. Together, they create an interconnected manufacturing environment that maximizes efficiency, reduces waste, and improves product quality.
Key Terms
Adaptability
Flexible manufacturing enables rapid adjustment to product variations and demand shifts through modular equipment and programmable controls, enhancing responsiveness in dynamic markets. Closed-loop manufacturing incorporates real-time feedback systems to monitor and adjust processes, ensuring precision and minimizing defects but with less emphasis on quick adaptability. Explore further to understand how each manufacturing approach impacts operational efficiency and customization potential.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing systems leverage advanced automation technologies like robotics and CNC machines to quickly adapt production lines for varying product designs, ensuring high efficiency and reduced downtime. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems and automation to continuously monitor and adjust processes, enhancing precision and minimizing errors through data-driven control. Explore comprehensive insights on how automation reshapes both manufacturing models to optimize productivity and quality.
Feedback systems
Flexible manufacturing systems adapt production processes dynamically to handle varying product types and volumes, using real-time feedback to optimize efficiency and reduce downtime in diverse manufacturing environments. Closed-loop manufacturing incorporates continuous feedback control mechanisms, ensuring precise adjustment of operations by monitoring output quality and automatically correcting deviations, which enhances product consistency and minimizes waste. Discover how integrating advanced feedback systems can transform manufacturing efficiency and quality standards.
Source and External Links
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) - Autodesk - A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a computer-controlled setup designed to adapt to changes by rearranging production sequences or shifting tasks among machines, with types including dedicated, sequential, engineered, random, and modular systems tailored for various industries.
Flexible manufacturing system - Wikipedia - An FMS combines work machines, material handling, and central computer control to provide routing and machine flexibility, enabling adaptation to new products or operation sequences, resulting in lower costs, better efficiency, and improved quality.
Flexible manufacturing - TNO - Flexible manufacturing integrates smart robotics and software to enable the cost-effective production of varied, complex products without human intervention, though challenges include automated reprogramming and reconfiguration for zero-defect, fast changeovers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com