Digital twin technology creates dynamic, real-time virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, enabling precise monitoring and optimization throughout production. Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software organizes and manages product data, workflows, and processes from design through disposal, ensuring collaborative efficiency and compliance. Explore how integrating digital twins with PLM enhances manufacturing innovation and operational excellence.
Why it is important
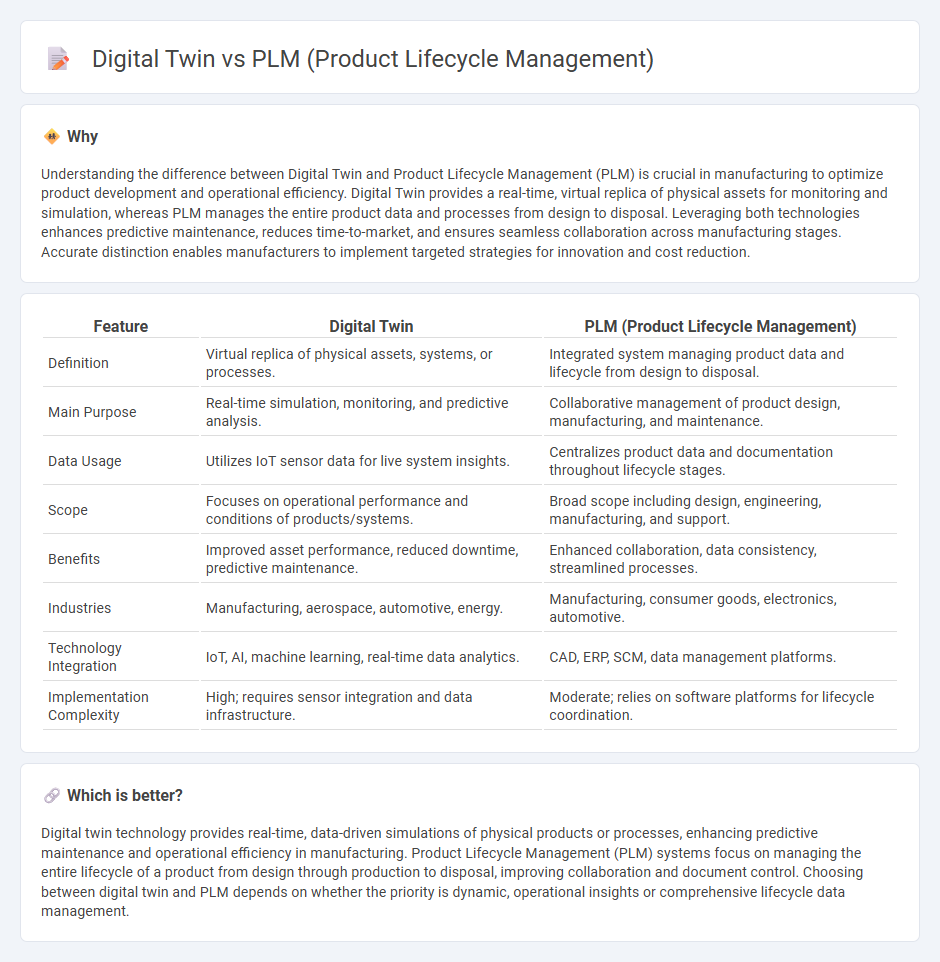
Understanding the difference between Digital Twin and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is crucial in manufacturing to optimize product development and operational efficiency. Digital Twin provides a real-time, virtual replica of physical assets for monitoring and simulation, whereas PLM manages the entire product data and processes from design to disposal. Leveraging both technologies enhances predictive maintenance, reduces time-to-market, and ensures seamless collaboration across manufacturing stages. Accurate distinction enables manufacturers to implement targeted strategies for innovation and cost reduction.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twin | PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets, systems, or processes. | Integrated system managing product data and lifecycle from design to disposal. |
| Main Purpose | Real-time simulation, monitoring, and predictive analysis. | Collaborative management of product design, manufacturing, and maintenance. |
| Data Usage | Utilizes IoT sensor data for live system insights. | Centralizes product data and documentation throughout lifecycle stages. |
| Scope | Focuses on operational performance and conditions of products/systems. | Broad scope including design, engineering, manufacturing, and support. |
| Benefits | Improved asset performance, reduced downtime, predictive maintenance. | Enhanced collaboration, data consistency, streamlined processes. |
| Industries | Manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, energy. | Manufacturing, consumer goods, electronics, automotive. |
| Technology Integration | IoT, AI, machine learning, real-time data analytics. | CAD, ERP, SCM, data management platforms. |
| Implementation Complexity | High; requires sensor integration and data infrastructure. | Moderate; relies on software platforms for lifecycle coordination. |
Which is better?
Digital twin technology provides real-time, data-driven simulations of physical products or processes, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency in manufacturing. Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems focus on managing the entire lifecycle of a product from design through production to disposal, improving collaboration and document control. Choosing between digital twin and PLM depends on whether the priority is dynamic, operational insights or comprehensive lifecycle data management.
Connection
Digital twin technology integrates with Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems by providing a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring and simulation throughout the product lifecycle. This connection allows manufacturers to enhance design accuracy, optimize production processes, and predict maintenance needs, leading to reduced costs and improved operational efficiency. Leveraging digital twins within PLM frameworks facilitates continuous data-driven decision-making from concept through end-of-life.
Key Terms
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management):
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) integrates data, processes, and business systems to manage a product's entire lifecycle from concept to disposal, enhancing collaboration and decision-making in product development. Unlike digital twins that create real-time virtual replicas for simulation and monitoring, PLM centralizes design, manufacturing, and maintenance information to optimize workflow efficiency and product quality. Discover how leveraging PLM systems can transform your product innovation and operational processes.
Lifecycle Data Management
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems centralize and manage all product-related data throughout design, manufacturing, and end-of-life stages, ensuring comprehensive lifecycle traceability. Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical products, enabling real-time monitoring and simulation by leveraging dynamic lifecycle data for enhanced decision-making. Explore more to understand how integrating PLM and digital twin optimizes lifecycle data management and operational efficiency.
Collaboration Platform
PLM systems centralize product data, streamline workflows, and enhance cross-functional collaboration by integrating design, engineering, and manufacturing teams on a unified platform. Digital twin technology provides real-time, dynamic simulation of physical products or processes, enabling predictive insights and operational optimization throughout the product lifecycle. Explore how combining PLM and digital twin platforms maximizes collaborative efficiency and drives innovation in product development.
Source and External Links
What Is Product Lifecycle Management? - IBM - PLM is a strategic approach and software that manages a product's journey from concept through design, production, service, and disposal by integrating people, data, processes, and business systems into a centralized system to optimize resource use, minimize waste, and enable faster innovation.
Product lifecycle - Wikipedia - PLM manages the entire product lifecycle from inception through engineering, design, manufacture, service, and disposal, providing an integrated information backbone for companies, with historical roots in automotive industry innovations from the 1980s.
What Is PLM Software? | Product Lifecycle Management - Oracle - PLM software manages information and processes throughout a product's lifecycle across global supply chains, supporting activities from ideation to disposal, and increasingly leveraging cloud-based platforms to unify product development and supply chain strategies for faster innovation and responsiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com