Factory as a Service (FaaS) enables businesses to access flexible manufacturing resources on demand, reducing capital investment and accelerating production timelines. Mass customization focuses on producing individualized products at scale by integrating advanced technologies like automation and digital design. Explore the advantages and applications of these innovative manufacturing models to enhance your production strategy.
Why it is important
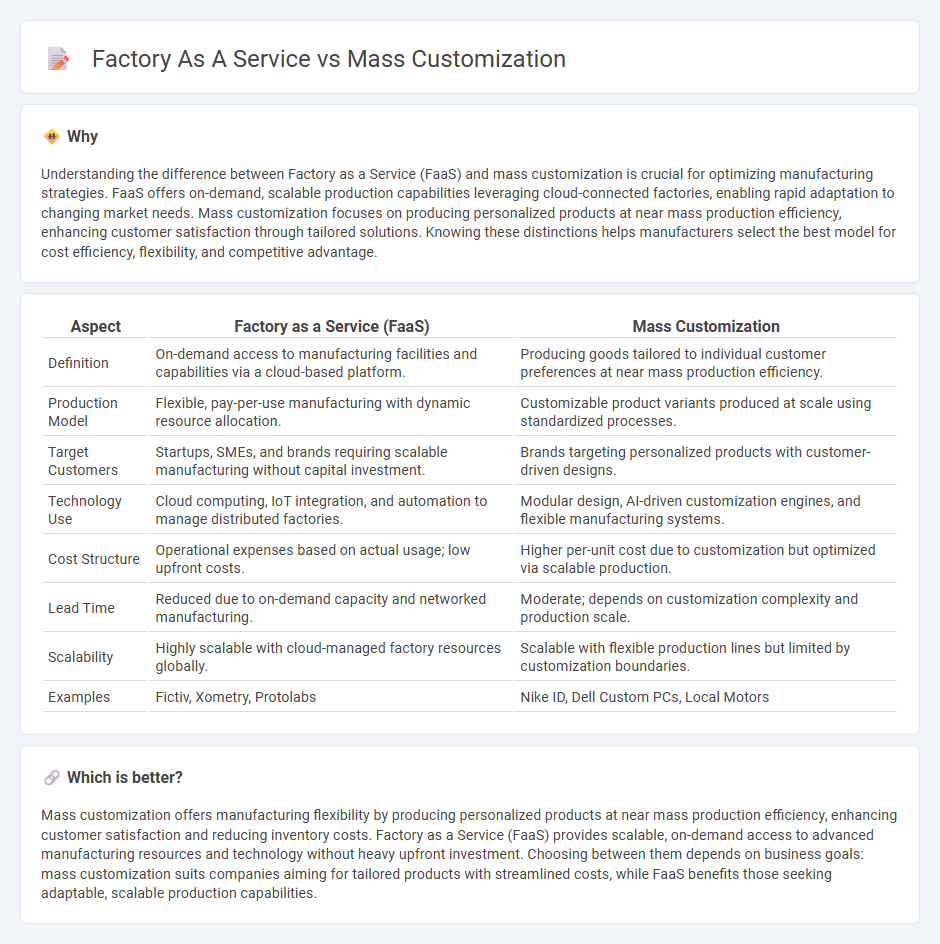
Understanding the difference between Factory as a Service (FaaS) and mass customization is crucial for optimizing manufacturing strategies. FaaS offers on-demand, scalable production capabilities leveraging cloud-connected factories, enabling rapid adaptation to changing market needs. Mass customization focuses on producing personalized products at near mass production efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction through tailored solutions. Knowing these distinctions helps manufacturers select the best model for cost efficiency, flexibility, and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Factory as a Service (FaaS) | Mass Customization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-demand access to manufacturing facilities and capabilities via a cloud-based platform. | Producing goods tailored to individual customer preferences at near mass production efficiency. |
| Production Model | Flexible, pay-per-use manufacturing with dynamic resource allocation. | Customizable product variants produced at scale using standardized processes. |
| Target Customers | Startups, SMEs, and brands requiring scalable manufacturing without capital investment. | Brands targeting personalized products with customer-driven designs. |
| Technology Use | Cloud computing, IoT integration, and automation to manage distributed factories. | Modular design, AI-driven customization engines, and flexible manufacturing systems. |
| Cost Structure | Operational expenses based on actual usage; low upfront costs. | Higher per-unit cost due to customization but optimized via scalable production. |
| Lead Time | Reduced due to on-demand capacity and networked manufacturing. | Moderate; depends on customization complexity and production scale. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cloud-managed factory resources globally. | Scalable with flexible production lines but limited by customization boundaries. |
| Examples | Fictiv, Xometry, Protolabs | Nike ID, Dell Custom PCs, Local Motors |
Which is better?
Mass customization offers manufacturing flexibility by producing personalized products at near mass production efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing inventory costs. Factory as a Service (FaaS) provides scalable, on-demand access to advanced manufacturing resources and technology without heavy upfront investment. Choosing between them depends on business goals: mass customization suits companies aiming for tailored products with streamlined costs, while FaaS benefits those seeking adaptable, scalable production capabilities.
Connection
Factory as a Service (FaaS) enables mass customization by providing scalable, on-demand manufacturing resources that adapt to specific customer requirements. This integration allows businesses to efficiently produce unique products in low volumes without investing in dedicated facilities. Leveraging advanced automation, cloud-based manufacturing platforms, and flexible production lines, FaaS supports responsive and cost-effective mass customization strategies.
Key Terms
**Mass Customization:**
Mass customization enables companies to produce personalized products at near mass production efficiency by leveraging advanced manufacturing technologies and flexible supply chains. This approach reduces inventory costs and enhances customer satisfaction by meeting individual preferences at scale. Explore how mass customization transforms manufacturing agility and customer engagement.
Modular Design
Mass customization leverages modular design to offer personalized products by combining standardized modules, enhancing flexibility and reducing costs. Factory as a Service (FaaS) employs modular design to enable scalable, on-demand manufacturing services, optimizing production efficiency through adaptable assembly units. Explore how modular design transforms both approaches by streamlining customization and manufacturing agility.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Mass customization leverages Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) to produce personalized products efficiently by integrating automation and real-time data processing, enabling quick adaptation to diverse customer specifications. Factory as a Service (FaaS) employs FMS to offer on-demand manufacturing capabilities, optimizing resource utilization through modular and scalable production units accessible via cloud platforms. Explore how Flexible Manufacturing Systems revolutionize production paradigms by visiting our in-depth analysis.
Source and External Links
Mass Customization: A Complete Guide - Deskera - Mass customization is a business strategy that blends mass production efficiency with personalized products, involving strategies like understanding customer needs, designing for scalability, and using automation and technology to deliver customized goods cost-effectively.
Mass customization - Wikipedia - Mass customization combines flexible computer-aided systems and modular design to produce individually customized products at near mass-production costs, balancing customer needs with manufacturing capabilities for economic value and strategic advantage.
Mass Customizations - Definition, How It Works, Types - Mass customization is a process that captures individual customer requirements to produce tailored goods efficiently using modularity, product platforms, and collaborative approaches to enable variety, reduce costs, and increase product reuse.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com