Lights-out manufacturing leverages automation and robotics to operate factories without human intervention, boosting efficiency and reducing labor costs. Batch manufacturing involves producing goods in fixed quantities or batches, allowing for flexibility in product changes but often leading to longer production cycles. Explore the advantages and challenges of both methods to determine the best fit for your manufacturing needs.
Why it is important
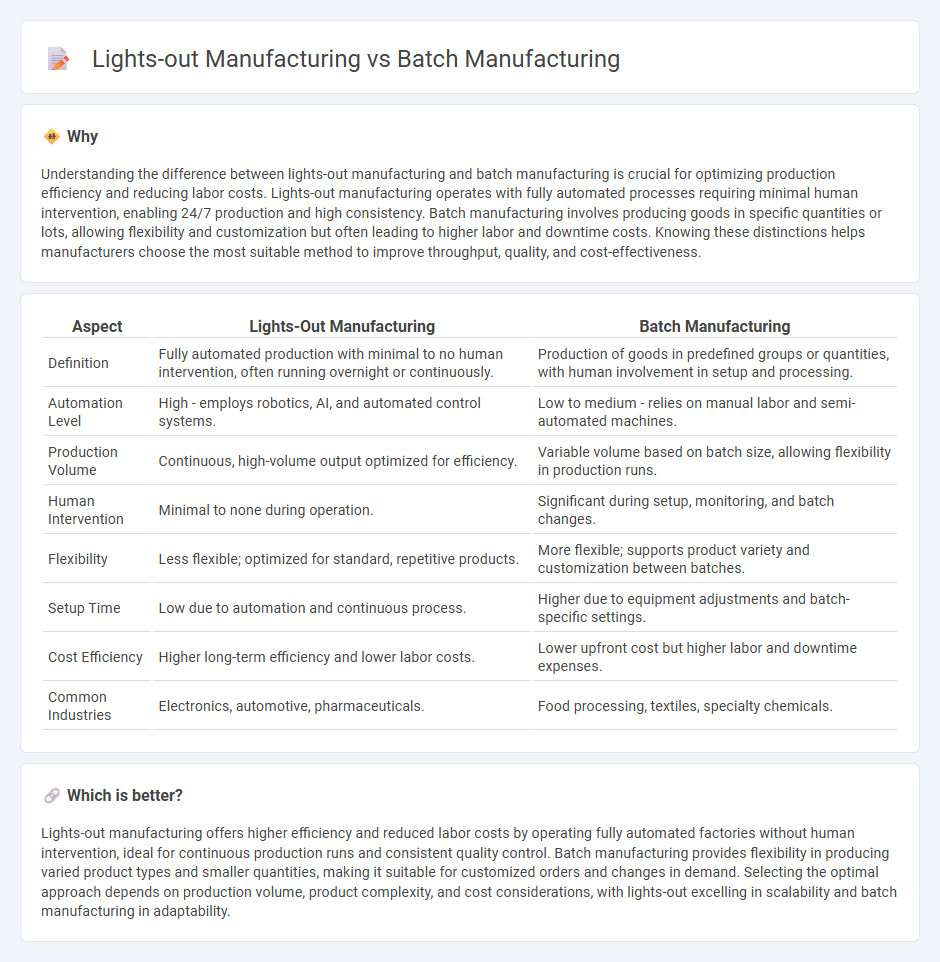
Understanding the difference between lights-out manufacturing and batch manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Lights-out manufacturing operates with fully automated processes requiring minimal human intervention, enabling 24/7 production and high consistency. Batch manufacturing involves producing goods in specific quantities or lots, allowing flexibility and customization but often leading to higher labor and downtime costs. Knowing these distinctions helps manufacturers choose the most suitable method to improve throughput, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lights-Out Manufacturing | Batch Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production with minimal to no human intervention, often running overnight or continuously. | Production of goods in predefined groups or quantities, with human involvement in setup and processing. |
| Automation Level | High - employs robotics, AI, and automated control systems. | Low to medium - relies on manual labor and semi-automated machines. |
| Production Volume | Continuous, high-volume output optimized for efficiency. | Variable volume based on batch size, allowing flexibility in production runs. |
| Human Intervention | Minimal to none during operation. | Significant during setup, monitoring, and batch changes. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; optimized for standard, repetitive products. | More flexible; supports product variety and customization between batches. |
| Setup Time | Low due to automation and continuous process. | Higher due to equipment adjustments and batch-specific settings. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher long-term efficiency and lower labor costs. | Lower upfront cost but higher labor and downtime expenses. |
| Common Industries | Electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals. | Food processing, textiles, specialty chemicals. |
Which is better?
Lights-out manufacturing offers higher efficiency and reduced labor costs by operating fully automated factories without human intervention, ideal for continuous production runs and consistent quality control. Batch manufacturing provides flexibility in producing varied product types and smaller quantities, making it suitable for customized orders and changes in demand. Selecting the optimal approach depends on production volume, product complexity, and cost considerations, with lights-out excelling in scalability and batch manufacturing in adaptability.
Connection
Lights-out manufacturing, characterized by fully automated production without human intervention, often integrates batch manufacturing processes to optimize efficiency and flexibility. Batch manufacturing allows production of goods in specific quantities, which facilitates precise automation control and minimizes downtime in lights-out systems. Combining these approaches enhances operational productivity and reduces costs in advanced manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Automation
Batch manufacturing involves producing goods in specified quantities using manual or semi-automated processes, often leading to downtime between batches and less efficient resource use. Lights-out manufacturing leverages full automation and advanced robotics, operating continuously without human intervention to maximize productivity and minimize errors. Explore the transformative impact of automation on manufacturing efficiency and scalability to learn more.
Human intervention
Batch manufacturing requires significant human intervention for tasks such as setup, quality checks, and changeovers, increasing the possibility of errors and downtime. In contrast, lights-out manufacturing operates autonomously with minimal or no human involvement, using automated systems and robotics to ensure continuous production and higher efficiency. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to optimize your manufacturing strategy.
Production scalability
Batch manufacturing offers flexible production scalability by allowing adjustments in batch sizes to meet varying demand, making it ideal for customized or seasonal products. Lights-out manufacturing enhances scalability through fully automated, continuous operations that minimize downtime and maximize output efficiency, especially in high-volume, standardized production environments. Explore further to determine which manufacturing method best matches your scalability and efficiency goals.
Source and External Links
What is Batch Production in Manufacturing? - Batch production is a manufacturing method where a group of identical products are produced together in a batch within a specific timeframe, with each batch going through production steps sequentially to ensure quality control and cost-effectiveness.
What is batch production in manufacturing? - Batch production involves producing groups of identical products simultaneously through all process stages before the next batch can begin, which allows for flexibility in product variations and efficient quality checks.
Batch Production: Examples, Advantages and Disadvantages - Batch production suits manufacturing of various consumer goods in multiple industries by enabling smaller quantities with product variety, cost-efficiency, reduced lead times, and enhanced quality control through stage-by-stage inspections.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com