Biofabrication integrates biological materials and living cells to create functional tissues and organs, revolutionizing regenerative medicine and personalized healthcare. Continuous manufacturing streamlines production through ongoing, automated processes that enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product consistency across industries. Explore the innovative potentials and applications of biofabrication and continuous manufacturing to understand their impact on the future of production.
Why it is important
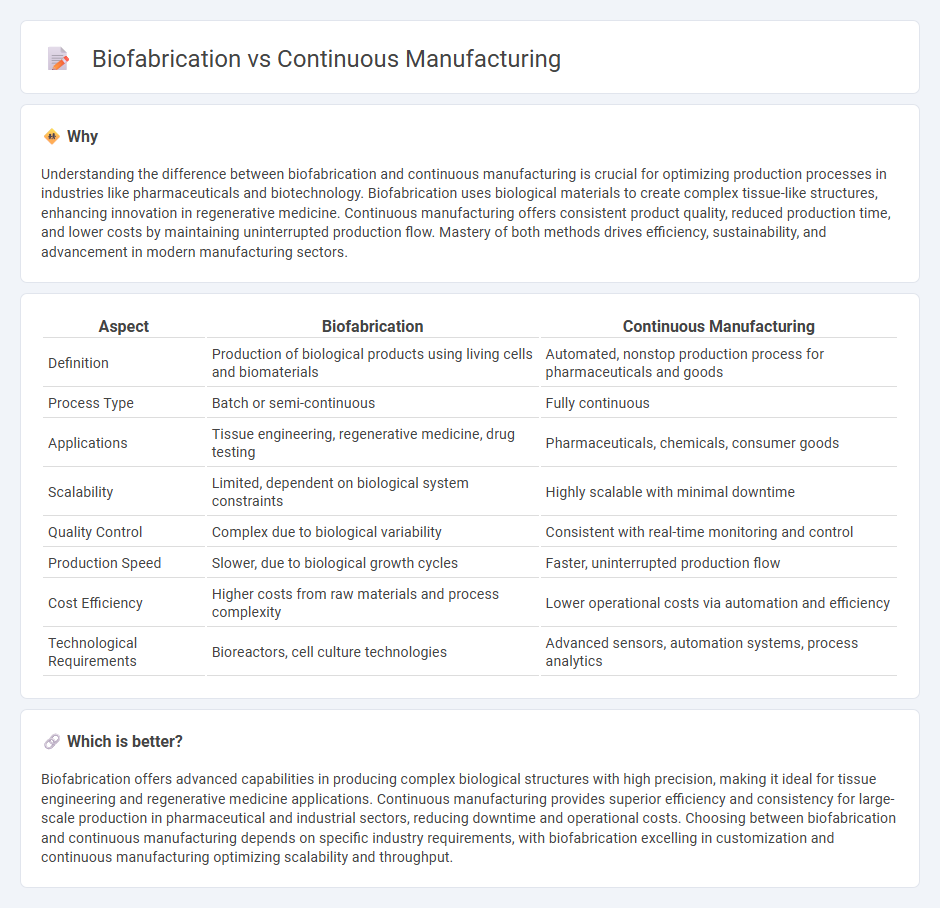
Understanding the difference between biofabrication and continuous manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production processes in industries like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. Biofabrication uses biological materials to create complex tissue-like structures, enhancing innovation in regenerative medicine. Continuous manufacturing offers consistent product quality, reduced production time, and lower costs by maintaining uninterrupted production flow. Mastery of both methods drives efficiency, sustainability, and advancement in modern manufacturing sectors.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biofabrication | Continuous Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production of biological products using living cells and biomaterials | Automated, nonstop production process for pharmaceuticals and goods |
| Process Type | Batch or semi-continuous | Fully continuous |
| Applications | Tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, drug testing | Pharmaceuticals, chemicals, consumer goods |
| Scalability | Limited, dependent on biological system constraints | Highly scalable with minimal downtime |
| Quality Control | Complex due to biological variability | Consistent with real-time monitoring and control |
| Production Speed | Slower, due to biological growth cycles | Faster, uninterrupted production flow |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher costs from raw materials and process complexity | Lower operational costs via automation and efficiency |
| Technological Requirements | Bioreactors, cell culture technologies | Advanced sensors, automation systems, process analytics |
Which is better?
Biofabrication offers advanced capabilities in producing complex biological structures with high precision, making it ideal for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Continuous manufacturing provides superior efficiency and consistency for large-scale production in pharmaceutical and industrial sectors, reducing downtime and operational costs. Choosing between biofabrication and continuous manufacturing depends on specific industry requirements, with biofabrication excelling in customization and continuous manufacturing optimizing scalability and throughput.
Connection
Biofabrication integrates living cells and biomaterials to create tissues and organs, revolutionizing the manufacturing of biomedical products. Continuous manufacturing streamlines production by enabling uninterrupted workflows, which enhances scalability and consistency. Combining biofabrication with continuous manufacturing accelerates bioprocesses and improves quality control in regenerative medicine and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Key Terms
Process Automation
Continuous manufacturing employs highly automated, real-time monitoring systems to enhance production efficiency and consistency in pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Biofabrication integrates automation technologies such as robotics and AI to precisely control cell and tissue assembly, improving scalability and reproducibility in regenerative medicine. Explore the advancements in process automation transforming these innovative production methodologies.
Bioprinting
Continuous manufacturing enhances bioprinting by enabling consistent layer deposition and scalable production of living tissues with precision. Biofabrication leverages bioprinting to create complex, cell-laden structures that mimic native tissue architecture and functionality. Explore the latest advancements in bioprinting technology to fully understand its transformative impact on continuous manufacturing and biofabrication.
Real-time Monitoring
Continuous manufacturing employs advanced real-time monitoring systems to ensure consistent quality and reduce production variability by analyzing critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. Biofabrication integrates real-time imaging and sensor technologies to monitor cellular behavior and tissue formation, enabling precise control over complex biological constructs. Explore the latest innovations in real-time monitoring to enhance manufacturing and biofabrication processes.
Source and External Links
Continuous Manufacturing and How To Do It -- Katana - Continuous manufacturing is a 24/7 production line process where raw materials are continuously processed into finished products in one location, commonly used in industries like oil refining and pharmaceuticals to minimize waste and cost while ensuring timely production.
Continuous Manufacturing: Batch to the Future - Continuous manufacturing enhances drug quality by using automated, real-time monitoring to prevent failures, reduce waste, and allow flexible batch sizes, improving production efficiency and responsiveness compared to traditional batch methods.
Continuous production - Wikipedia - Continuous production is a manufacturing method where materials flow uninterrupted through chemical or mechanical processes, typically operated 24/7, enabling large-scale production with minimal maintenance shutdowns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com