Circular manufacturing focuses on reducing waste through resource reuse, recycling, and sustainable design, aiming to minimize environmental impact and extend product life cycles. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds parts layer by layer, enabling complex geometries, material efficiency, and customization while reducing excess material waste. Explore the key differences and advantages of circular versus additive manufacturing to optimize your production strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing sustainability and efficiency in production processes. Circular manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste by reusing materials throughout the product lifecycle, promoting environmental responsibility. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer, enabling rapid prototyping and customization with minimal material waste. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses implement the most suitable strategies to reduce costs, lower environmental impact, and enhance innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
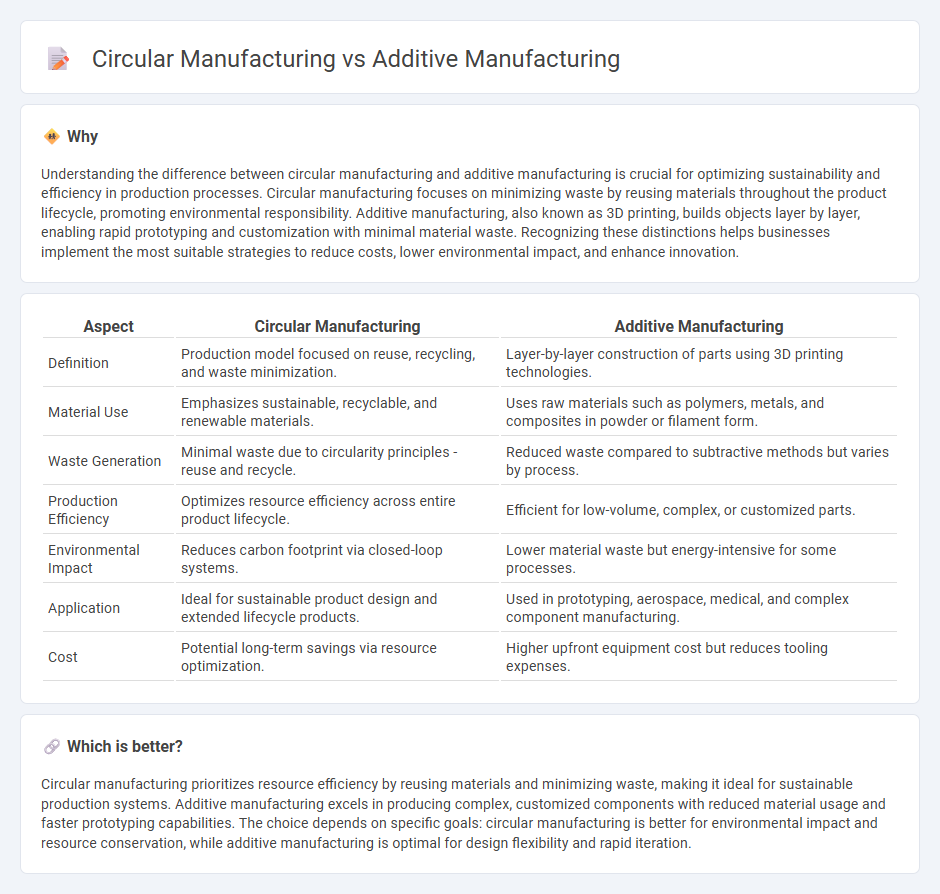
| Definition | Production model focused on reuse, recycling, and waste minimization. | Layer-by-layer construction of parts using 3D printing technologies. |
| Material Use | Emphasizes sustainable, recyclable, and renewable materials. | Uses raw materials such as polymers, metals, and composites in powder or filament form. |
| Waste Generation | Minimal waste due to circularity principles - reuse and recycle. | Reduced waste compared to subtractive methods but varies by process. |
| Production Efficiency | Optimizes resource efficiency across entire product lifecycle. | Efficient for low-volume, complex, or customized parts. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint via closed-loop systems. | Lower material waste but energy-intensive for some processes. |
| Application | Ideal for sustainable product design and extended lifecycle products. | Used in prototyping, aerospace, medical, and complex component manufacturing. |
| Cost | Potential long-term savings via resource optimization. | Higher upfront equipment cost but reduces tooling expenses. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing prioritizes resource efficiency by reusing materials and minimizing waste, making it ideal for sustainable production systems. Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex, customized components with reduced material usage and faster prototyping capabilities. The choice depends on specific goals: circular manufacturing is better for environmental impact and resource conservation, while additive manufacturing is optimal for design flexibility and rapid iteration.
Connection
Circular manufacturing enhances resource efficiency by prioritizing reuse, recycling, and waste reduction, closely aligning with additive manufacturing, which builds products layer by layer, minimizing material waste. Additive manufacturing enables customization and on-demand production, supporting circular principles by extending product life cycles and facilitating repair or remanufacturing. The synergy between these approaches drives sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing environmental impact and conserving raw materials.
Key Terms
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing, a core technology of additive manufacturing, builds objects layer by layer using digital models, minimizing raw material waste compared to traditional subtractive methods. Circular manufacturing incorporates 3D printing to enhance product lifecycle by enabling repair, remanufacturing, and recycling, supporting sustainable resource use and reducing landfill waste. Explore how integrating 3D printing within circular manufacturing models drives innovation and sustainability in industrial production.
Material Reuse (Circular Manufacturing)
Additive manufacturing enables precise material usage by building components layer-by-layer, significantly reducing waste compared to traditional subtractive methods. Circular manufacturing emphasizes material reuse by recovering and recycling materials within the production cycle, fostering sustainability and minimizing raw material consumption. Explore how integrating additive techniques with circular strategies can maximize resource efficiency and drive eco-friendly innovation.
Closed-Loop Supply Chain
Additive manufacturing enhances circular manufacturing by enabling closed-loop supply chains through efficient material reuse and reduction of waste in production processes. This technology supports sustainable resource management by facilitating on-demand production, minimizing inventory, and streamlining end-of-life product recycling. Explore how integrating additive manufacturing within circular manufacturing principles can transform closed-loop supply chain strategies.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing is a process of creating objects layer by layer using digital designs, often referred to as 3D printing, initially used for rapid prototyping and now employed to produce functional products across industries like aerospace and engineering.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing fabricates three-dimensional products by building layers from digital files, allowing complex designs with less material waste and enabling applications such as custom biomedical implants and lightweight aerospace parts.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Loughborough University - Additive manufacturing encompasses various processes classified into seven ASTM standard categories, including vat photopolymerisation, material jetting, and binder jetting, each differing in how layers and materials are deposited to build objects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com