Mass customization merges the efficiency of make-to-stock production with personalized product features, enabling manufacturers to meet individual customer demands without sacrificing scale. Make-to-stock relies on forecast-driven inventory, producing goods in advance to ensure immediate availability but may result in overstock or stockouts due to demand variability. Discover how these manufacturing strategies reshape production dynamics and consumer satisfaction.
Why it is important
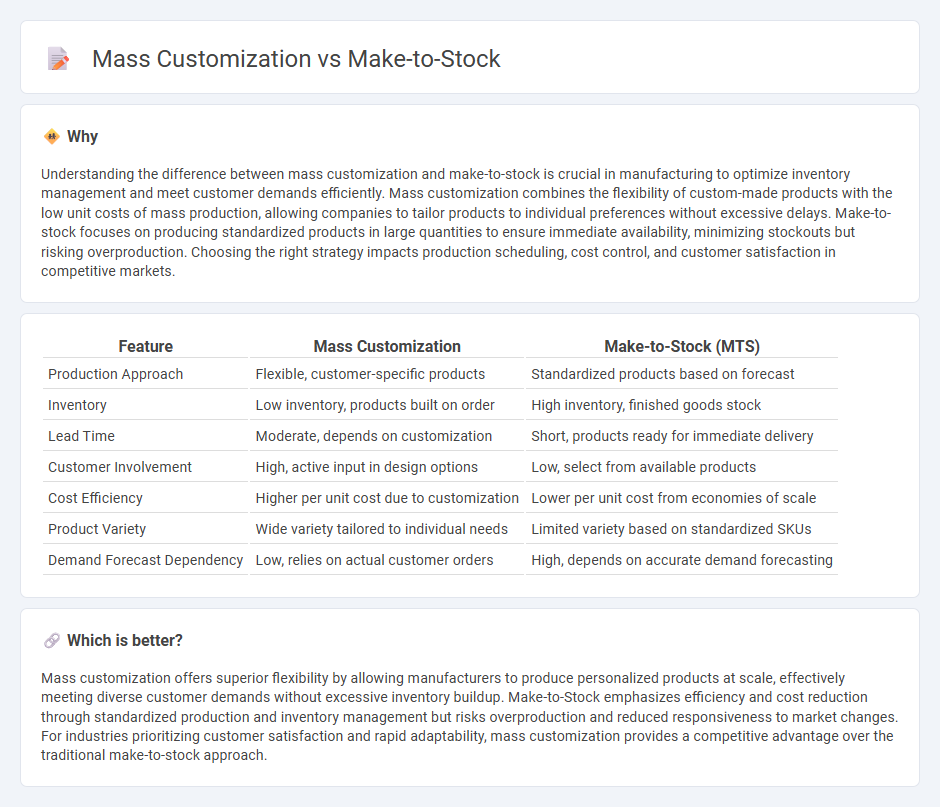
Understanding the difference between mass customization and make-to-stock is crucial in manufacturing to optimize inventory management and meet customer demands efficiently. Mass customization combines the flexibility of custom-made products with the low unit costs of mass production, allowing companies to tailor products to individual preferences without excessive delays. Make-to-stock focuses on producing standardized products in large quantities to ensure immediate availability, minimizing stockouts but risking overproduction. Choosing the right strategy impacts production scheduling, cost control, and customer satisfaction in competitive markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Mass Customization | Make-to-Stock (MTS) |
|---|---|---|
| Production Approach | Flexible, customer-specific products | Standardized products based on forecast |
| Inventory | Low inventory, products built on order | High inventory, finished goods stock |
| Lead Time | Moderate, depends on customization | Short, products ready for immediate delivery |
| Customer Involvement | High, active input in design options | Low, select from available products |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher per unit cost due to customization | Lower per unit cost from economies of scale |
| Product Variety | Wide variety tailored to individual needs | Limited variety based on standardized SKUs |
| Demand Forecast Dependency | Low, relies on actual customer orders | High, depends on accurate demand forecasting |
Which is better?
Mass customization offers superior flexibility by allowing manufacturers to produce personalized products at scale, effectively meeting diverse customer demands without excessive inventory buildup. Make-to-Stock emphasizes efficiency and cost reduction through standardized production and inventory management but risks overproduction and reduced responsiveness to market changes. For industries prioritizing customer satisfaction and rapid adaptability, mass customization provides a competitive advantage over the traditional make-to-stock approach.
Connection
Mass customization leverages Make-to-Stock (MTS) strategies by producing standardized components in bulk while allowing personalized configurations during final assembly, optimizing inventory and reducing lead times. MTS ensures product availability through forecasting and stockpiling, supporting mass customization's demand for quick, tailored solutions. Integrating MTS with advanced production technologies enables scalable, cost-effective manufacturing that meets diverse consumer preferences.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Make-to-Stock (MTS) relies on forecasting and maintaining large inventory levels to meet anticipated customer demand, optimizing production efficiency but risking overstock or stockouts. Mass customization balances inventory by producing standardized components in bulk while assembling final products based on specific customer orders, reducing excess stock and enhancing responsiveness. Explore detailed strategies in inventory management for both approaches to optimize supply chain performance.
Production Flexibility
Make-to-Stock production prioritizes efficiency by manufacturing goods based on forecasted demand, resulting in limited flexibility to accommodate individual customer preferences or sudden changes in market trends. In contrast, mass customization leverages advanced manufacturing technologies and flexible processes to produce personalized products at scale, balancing high variety with streamlined operations. Explore deeper insights to understand how production flexibility impacts supply chain responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
Customer Demand Segmentation
Make-to-Stock relies on forecasting aggregated customer demand to produce standardized products in large volumes, optimizing inventory turnover but risking mismatch with specific preferences. Mass customization leverages real-time customer demand segmentation by utilizing flexible manufacturing systems, allowing personalized product variations that address niche market needs and enhance customer satisfaction. Discover how integrating advanced demand segmentation tools can transform your production strategy and better meet evolving consumer expectations.
Source and External Links
Make to Stock (MTS): Manufacturing Explained - Mingo Smart Factory - Make-to-Stock (MTS) is a production strategy where products are made in advance based on forecasted demand and stocked until sold, aiming to meet customer demand immediately but risking excess inventory or stockouts due to forecast errors.
Make-to-Stock (MTS): A Comprehensive Guide - Qoblex - MTS involves manufacturing products ahead of customer orders based on predicted demand, widely used for standardized products to enable quick delivery and reduced lead times, in contrast to Make-to-Order (MTO) which produces after orders are received.
Make-To-Stock (MTS): Definition, Advantages & How It Works - MTS is commonly applied in retail, manufacturing, and consumer goods industries to produce goods in anticipation of demand peaks, minimizing order delays and enhancing customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability at launch and beyond.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com