Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) enhance manufacturing efficiency by seamlessly transporting materials with precision and minimal errors, reducing labor costs and operational downtime. Human-operated carts offer flexibility and adaptability in complex environments but depend heavily on operator skill, making them prone to inconsistencies and safety risks. Explore how integrating AGVs in your production lines can optimize logistics and improve overall productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and human-operated carts is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and safety. AGVs use precise navigation technology to reduce labor costs and minimize errors, while human-operated carts offer flexibility for complex tasks. Selecting the appropriate system impacts workflow automation, productivity, and operational scalability. Manufacturers can enhance supply chain management and reduce downtime by leveraging the specific advantages of each transport method.
Comparison Table
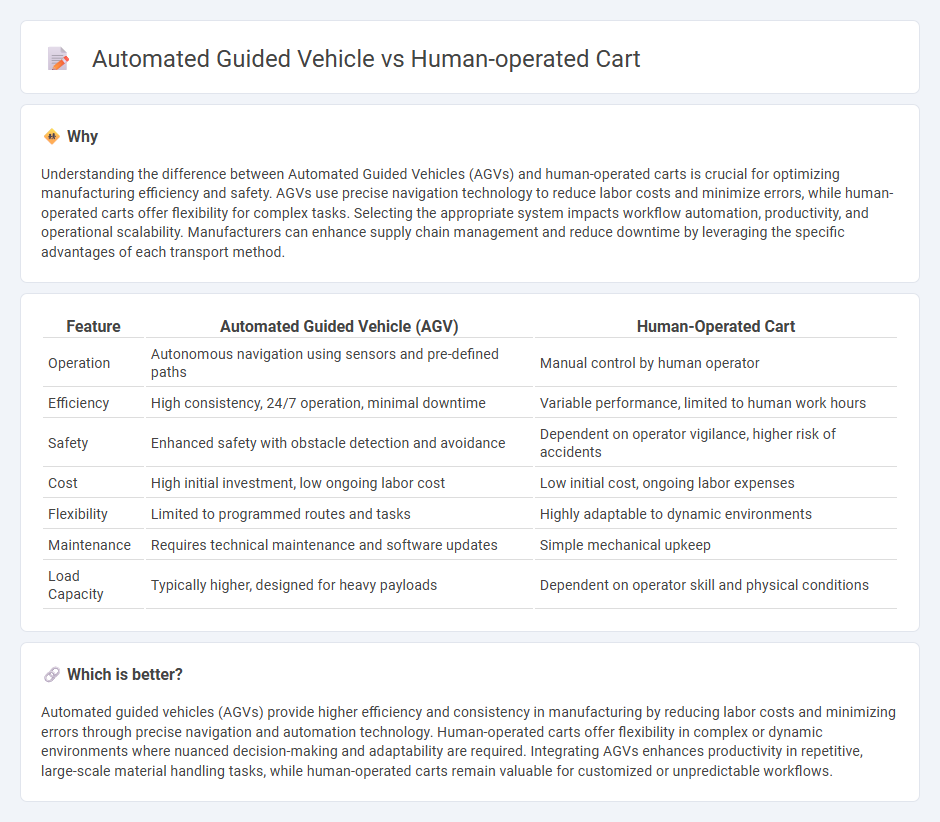
| Feature | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) | Human-Operated Cart |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Autonomous navigation using sensors and pre-defined paths | Manual control by human operator |
| Efficiency | High consistency, 24/7 operation, minimal downtime | Variable performance, limited to human work hours |
| Safety | Enhanced safety with obstacle detection and avoidance | Dependent on operator vigilance, higher risk of accidents |
| Cost | High initial investment, low ongoing labor cost | Low initial cost, ongoing labor expenses |
| Flexibility | Limited to programmed routes and tasks | Highly adaptable to dynamic environments |
| Maintenance | Requires technical maintenance and software updates | Simple mechanical upkeep |
| Load Capacity | Typically higher, designed for heavy payloads | Dependent on operator skill and physical conditions |
Which is better?
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) provide higher efficiency and consistency in manufacturing by reducing labor costs and minimizing errors through precise navigation and automation technology. Human-operated carts offer flexibility in complex or dynamic environments where nuanced decision-making and adaptability are required. Integrating AGVs enhances productivity in repetitive, large-scale material handling tasks, while human-operated carts remain valuable for customized or unpredictable workflows.
Connection
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and human-operated carts are interconnected in manufacturing through their complementary roles in material handling and workflow optimization. AGVs enhance efficiency by autonomously transporting goods along predefined routes, while human-operated carts provide flexibility for tasks requiring manual intervention or complex decision-making. Integrating these systems creates a hybrid logistics approach that improves productivity, reduces labor costs, and ensures continuous material flow on the production floor.
Key Terms
Labor Efficiency
Human-operated carts rely on manual labor for navigation and load handling, which can limit productivity due to physical fatigue and increased error rates. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) enhance labor efficiency by providing consistent, precise transport without the need for breaks, reducing downtime and operational costs. Explore how integrating AGVs can transform your workflow and optimize labor utilization.
Automation
Human-operated carts rely on manual control, requiring constant human intervention for navigation and load management, which limits efficiency and increases labor costs. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) utilize sensors, navigation systems, and software to autonomously transport goods, enhancing productivity and reducing errors in material handling operations. Discover the transformative benefits of AGV automation in supply chain optimization and warehouse management.
Flexibility
Human-operated carts excel in flexibility, easily adapting to changing routes, load types, and unexpected obstacles without requiring reprogramming. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) offer consistent performance but are limited to pre-defined paths and require updates for route adjustments, which can reduce operational agility. Explore more about optimizing warehouse logistics and improving material handling efficiency.
Source and External Links
The Human Powered Car - Hammacher Schlemmer - A hybrid vehicle powered by electricity generated by human effort via rowing bars, enabling up to four operators to propel the vehicle and store energy to power an engine reaching speeds up to 60 mph.
Human-powered land vehicle - Wikipedia - Land vehicles propelled by human power through drivetrains, lateral motion, or direct ground contact, including carts or wagons designed for carrying people or goods.
FOLO-200 Heavy Duty 100KG Four-wheel Cargo Trolley Automatic Human Following Cart Robot - A four-wheel cargo trolley capable of carrying 100 kg, designed with AI technology to follow a person automatically using sensors and wireless control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com