Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and advanced analytics to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing downtime. Preventive maintenance follows a fixed schedule based on time or usage intervals, aiming to prevent failures through regular inspections and part replacements. Explore the benefits and applications of both strategies to enhance manufacturing efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance is crucial for optimizing manufacturing operations and reducing downtime costs. Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and sensor monitoring to forecast equipment failures before they occur, increasing efficiency. Preventive maintenance relies on scheduled inspections and routine repairs to minimize unexpected breakdowns, ensuring consistent production. Differentiating these approaches enables manufacturers to implement cost-effective maintenance strategies that extend equipment lifespan and improve overall productivity.
Comparison Table
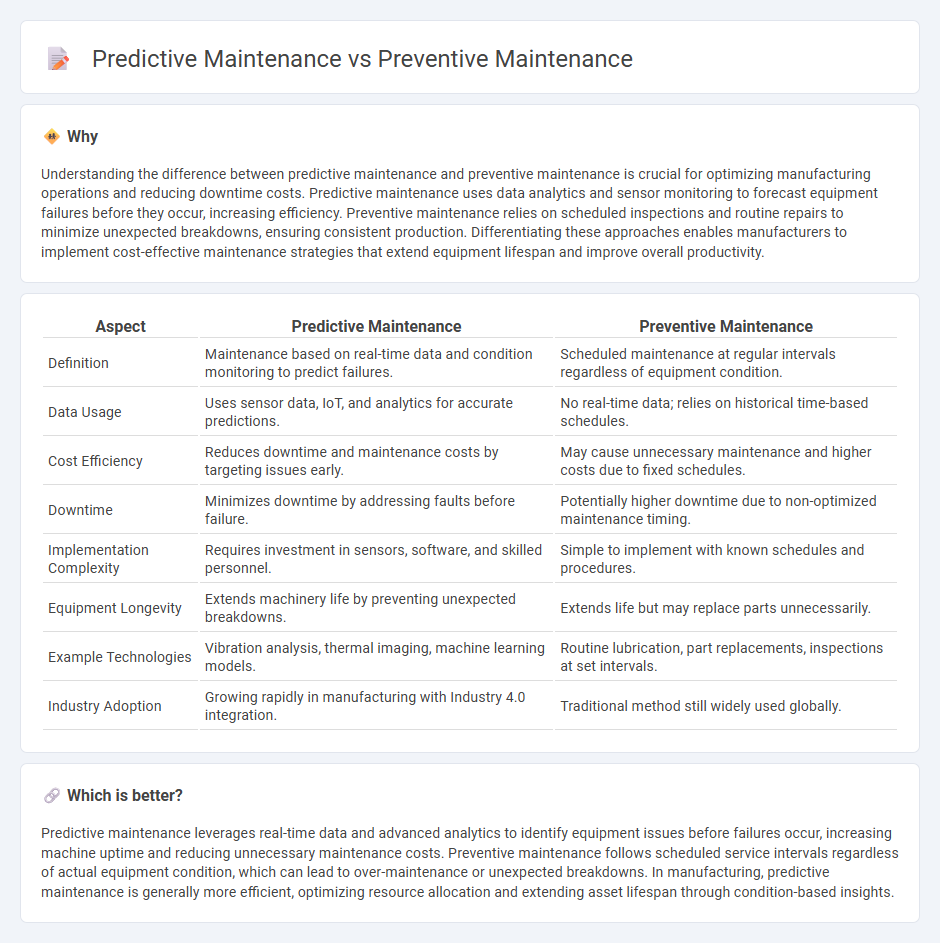
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance based on real-time data and condition monitoring to predict failures. | Scheduled maintenance at regular intervals regardless of equipment condition. |
| Data Usage | Uses sensor data, IoT, and analytics for accurate predictions. | No real-time data; relies on historical time-based schedules. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs by targeting issues early. | May cause unnecessary maintenance and higher costs due to fixed schedules. |
| Downtime | Minimizes downtime by addressing faults before failure. | Potentially higher downtime due to non-optimized maintenance timing. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires investment in sensors, software, and skilled personnel. | Simple to implement with known schedules and procedures. |
| Equipment Longevity | Extends machinery life by preventing unexpected breakdowns. | Extends life but may replace parts unnecessarily. |
| Example Technologies | Vibration analysis, thermal imaging, machine learning models. | Routine lubrication, part replacements, inspections at set intervals. |
| Industry Adoption | Growing rapidly in manufacturing with Industry 4.0 integration. | Traditional method still widely used globally. |
Which is better?
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to identify equipment issues before failures occur, increasing machine uptime and reducing unnecessary maintenance costs. Preventive maintenance follows scheduled service intervals regardless of actual equipment condition, which can lead to over-maintenance or unexpected breakdowns. In manufacturing, predictive maintenance is generally more efficient, optimizing resource allocation and extending asset lifespan through condition-based insights.
Connection
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that extend asset lifespan and reduce unplanned downtime. Preventive maintenance relies on scheduled, routine inspections and servicing based on historical data and manufacturer recommendations to maintain optimal equipment performance. Together, these strategies optimize maintenance efficiency by combining data-driven insights with systematic upkeep, minimizing operational disruptions in manufacturing.
Key Terms
Scheduled Inspections (Preventive)
Scheduled inspections in preventive maintenance involve routine checks at predetermined intervals to identify and address potential equipment issues before failure occurs. These inspections rely on fixed timelines rather than real-time data, ensuring consistent upkeep but sometimes leading to unnecessary maintenance or missed early-warning signs. Explore the benefits and limitations of scheduled inspections compared to data-driven predictive maintenance to optimize your maintenance strategy.
Condition Monitoring (Predictive)
Preventive maintenance schedules regular equipment servicing based on time or usage intervals to reduce the risk of unexpected failures, while predictive maintenance relies on Condition Monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis, temperature tracking, and oil analysis to assess real-time equipment health and predict potential breakdowns. Condition Monitoring leverages IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies early, enabling targeted interventions that optimize asset lifespan and minimize downtime. Explore more about how predictive maintenance transforms operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness through advanced Condition Monitoring.
Failure Patterns
Preventive maintenance schedules routine equipment inspections and replacements based on fixed time intervals, aiming to minimize unexpected failures by addressing known wear patterns before breakdowns occur. Predictive maintenance leverages IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time data, identifying specific failure patterns such as vibration anomalies, temperature spikes, and oil contamination that indicate imminent equipment malfunction. Explore deeper insights into failure pattern analysis and how predictive maintenance can reduce downtime and optimize operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
How To Develop A Preventive Maintenance Program - Accruent - Preventive maintenance aims to prevent equipment failure before it happens by scheduling inspections, servicing, and repairs to reduce downtime and extend asset lifespan, tailored to specific equipment needs.
What is Preventive Maintenance? - NEXGEN Asset Management - Preventive maintenance is planned maintenance performed to reduce the risk of asset failure and business interruptions, including types like usage-based, time-based, and predictive maintenance, typically supported by detailed checklists.
What Is Preventive Maintenance? [New for 2024] - OpenGov - Preventive maintenance consists of routine inspections and servicing aimed at avoiding failures and extending asset lifespan, helping organizations improve safety and operational efficiency by prioritizing critical tasks effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com