Microfactories focus on small-scale, flexible production with advanced automation and localized supply chains, enabling rapid customization and reduced waste. Macromanufacturing involves large-scale, centralized operations optimized for high volume output, utilizing extensive machinery and labor to achieve economies of scale. Explore more to understand how these manufacturing models impact efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
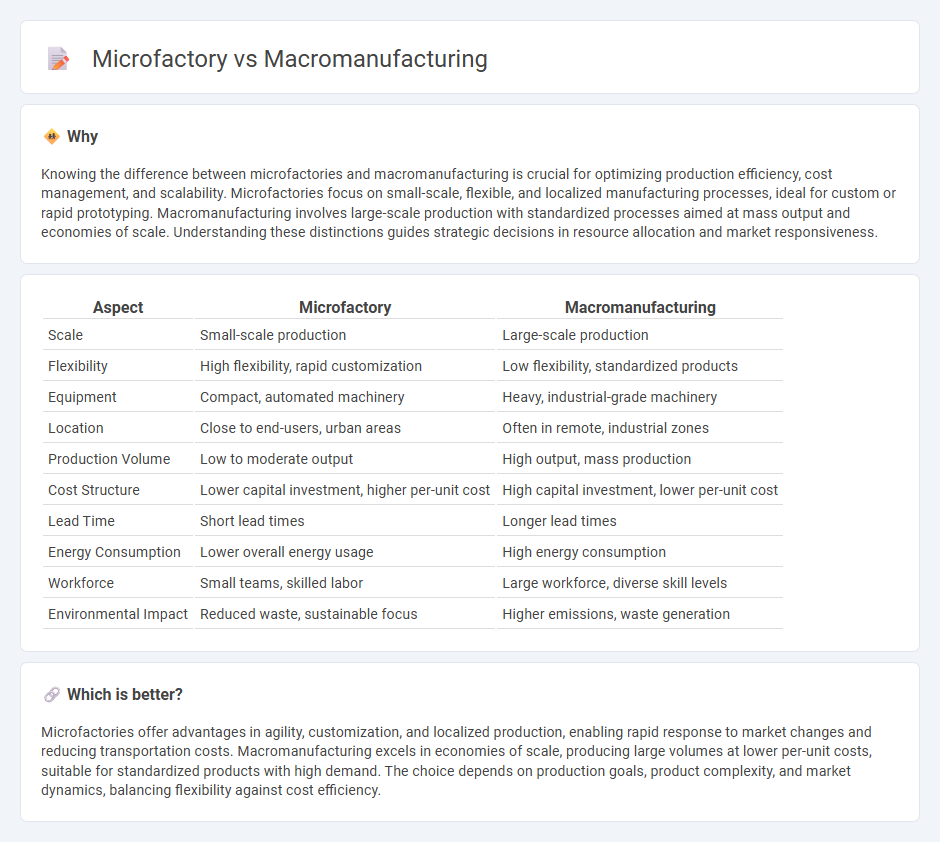
Knowing the difference between microfactories and macromanufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency, cost management, and scalability. Microfactories focus on small-scale, flexible, and localized manufacturing processes, ideal for custom or rapid prototyping. Macromanufacturing involves large-scale production with standardized processes aimed at mass output and economies of scale. Understanding these distinctions guides strategic decisions in resource allocation and market responsiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactory | Macromanufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Small-scale production | Large-scale production |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, rapid customization | Low flexibility, standardized products |
| Equipment | Compact, automated machinery | Heavy, industrial-grade machinery |
| Location | Close to end-users, urban areas | Often in remote, industrial zones |
| Production Volume | Low to moderate output | High output, mass production |
| Cost Structure | Lower capital investment, higher per-unit cost | High capital investment, lower per-unit cost |
| Lead Time | Short lead times | Longer lead times |
| Energy Consumption | Lower overall energy usage | High energy consumption |
| Workforce | Small teams, skilled labor | Large workforce, diverse skill levels |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced waste, sustainable focus | Higher emissions, waste generation |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer advantages in agility, customization, and localized production, enabling rapid response to market changes and reducing transportation costs. Macromanufacturing excels in economies of scale, producing large volumes at lower per-unit costs, suitable for standardized products with high demand. The choice depends on production goals, product complexity, and market dynamics, balancing flexibility against cost efficiency.
Connection
Microfactories and macromanufacturing are interconnected through integrated production systems where microfactories handle customized, small-batch manufacturing while feeding components and data into larger macromanufacturing operations for mass production. This synergy enhances supply chain agility by enabling rapid prototyping and localized production that supports large-scale manufacturing efficiency. Advanced technologies like IoT and AI facilitate seamless communication and coordination between micro-scale units and macro-scale factories, optimizing overall manufacturing output and responsiveness.
Key Terms
Scale
Macromanufacturing involves large-scale production facilities with high-capacity machinery designed to produce massive quantities of goods efficiently, leveraging economies of scale to reduce unit costs. Microfactories emphasize smaller, flexible, and often localized production units focused on agility, customization, and rapid response to market changes, typically utilizing automation and advanced robotics. Explore the evolving dynamics between macromanufacturing and microfactories to better understand their impact on industry scale and innovation.
Production Volume
Macromanufacturing typically involves large-scale production volumes often measured in millions of units per year, designed for mass-market supply chains with high automation and economies of scale. Microfactories focus on smaller production volumes, ranging from hundreds to thousands of units, emphasizing flexibility, customization, and localized manufacturing to reduce lead times and inventory costs. Explore how production volume impacts cost efficiency and scalability in different manufacturing models.
Flexibility
Microfactories offer superior flexibility by enabling localized, small-scale production with rapid adjustments to design and output, which contrasts with macromanufacturing's large-scale, fixed setups optimized for high-volume, consistent production. The agility of microfactories supports just-in-time manufacturing and customization without the extensive retooling costs typical in macromanufacturing. Explore detailed insights on how flexibility in these manufacturing models impacts innovation and efficiency.
Source and External Links
About - Macro Mfg. Co. - Macro Manufacturing is a CNC job shop specializing in milled and turned parts since 1970, serving various industries with a focus on quality, competitive pricing, and timely lead times.
MACRO Manufacturing - Located in Portland, Oregon, Macro Manufacturing offers CNC lathe and mill services delivering a wide range of precision machined parts for multiple industries, emphasizing cost efficiency and design for manufacturability.
Precision CNC Machining | Macro Manufacturing | Aberdeen - Macro Manufacturing Ltd, based in Aberdeen, UK, partners across industries like renewable energy and oil & gas to provide bespoke precision CNC machined components from prototype to production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com