Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks in manufacturing by automating workflow processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in administrative and operational activities. Machine vision systems enable real-time inspection and quality control by using cameras and AI algorithms to detect defects and guide robotic actions on the production line. Explore deeper insights into how RPA and machine vision transform manufacturing operations and drive smart factory innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Machine Vision is crucial in manufacturing to optimize efficiency and quality control. RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry or inventory management, reducing human error and operational costs. Machine Vision focuses on inspecting products, detecting defects, and guiding robotic actions through image analysis, thereby ensuring high precision and consistency. Correctly deploying these technologies enhances production speed, accuracy, and overall competitiveness.
Comparison Table
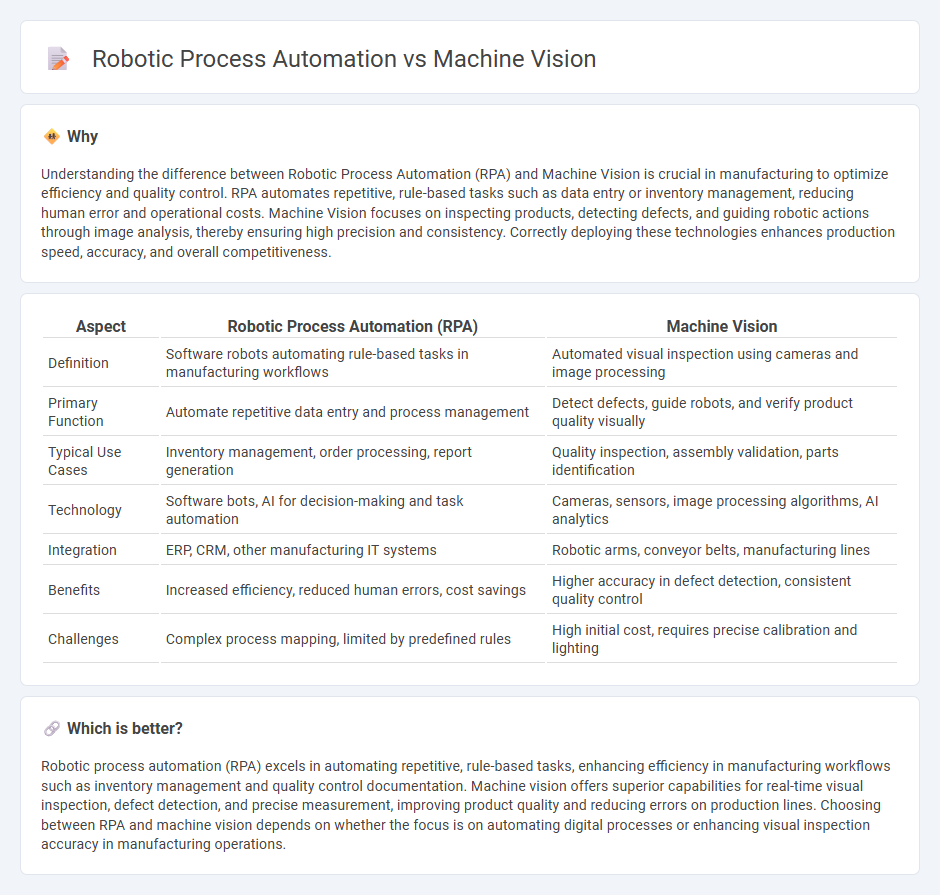
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Machine Vision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating rule-based tasks in manufacturing workflows | Automated visual inspection using cameras and image processing |
| Primary Function | Automate repetitive data entry and process management | Detect defects, guide robots, and verify product quality visually |
| Typical Use Cases | Inventory management, order processing, report generation | Quality inspection, assembly validation, parts identification |
| Technology | Software bots, AI for decision-making and task automation | Cameras, sensors, image processing algorithms, AI analytics |
| Integration | ERP, CRM, other manufacturing IT systems | Robotic arms, conveyor belts, manufacturing lines |
| Benefits | Increased efficiency, reduced human errors, cost savings | Higher accuracy in defect detection, consistent quality control |
| Challenges | Complex process mapping, limited by predefined rules | High initial cost, requires precise calibration and lighting |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) excels in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, enhancing efficiency in manufacturing workflows such as inventory management and quality control documentation. Machine vision offers superior capabilities for real-time visual inspection, defect detection, and precise measurement, improving product quality and reducing errors on production lines. Choosing between RPA and machine vision depends on whether the focus is on automating digital processes or enhancing visual inspection accuracy in manufacturing operations.
Connection
Robotic process automation (RPA) integrates with machine vision to streamline manufacturing workflows by enabling automated inspection, quality control, and real-time decision-making based on visual data analysis. Machine vision systems capture high-resolution images that RPA algorithms process to detect defects, verify assembly accuracy, and ensure compliance with standards, enhancing productivity and reducing human error. The synergy between RPA and machine vision accelerates manufacturing efficiency through precise, data-driven automation of repetitive and complex visual tasks.
Key Terms
Image Processing
Machine vision systems employ advanced image processing techniques to analyze and interpret visual data in real-time, enabling applications such as quality inspection, object recognition, and defect detection across manufacturing and logistics industries. Robotic Process Automation (RPA), while primarily centered on automating rule-based digital tasks, increasingly integrates image processing capabilities to handle unstructured data and enhance decision-making in document management and customer service. Explore the evolving convergence of machine vision and RPA to optimize automation strategies and achieve higher operational efficiency.
Workflow Automation
Machine vision enhances workflow automation by enabling real-time image analysis and quality control, significantly reducing errors in manufacturing and inspection processes. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based digital tasks such as data entry and report generation, improving operational efficiency across business functions. Explore how integrating machine vision with RPA can revolutionize end-to-end workflow automation by combining visual intelligence with digital task automation.
Quality Inspection
Machine vision systems utilize advanced image processing algorithms to detect defects and ensure product quality with high precision and speed in manufacturing environments. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive inspection tasks by integrating data from sensors and databases, enhancing overall inspection workflow efficiency but lacking direct visual defect analysis. Explore the latest advancements and comparative benefits of machine vision and RPA for quality inspection to optimize your production processes.
Source and External Links
Machine Vision Vs Computer Vision - Zebra Technologies - Machine vision is a subset of computer vision focused on practical applications like inspection and robot guidance, using image capture to trigger actions after analysis, often in industrial settings.
What Is Machine Vision? - Intel - Machine vision integrates smart cameras, industrial PCs, and AI to automate tasks such as quality inspection and robotic guidance in manufacturing, enabling robots to make real-time decisions.
Machine vision basics: definitions, uses, and benefits - Cognex - Machine vision enables automated systems to visually inspect, measure, and sort components with high speed and accuracy, improving product quality and factory efficiency through data generation and decision-making.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com