Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable technologies, exoskeletons, and neural interfaces, boosting productivity and safety in manufacturing environments. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, enables precise production of complex parts layer by layer, reducing waste and accelerating prototyping. Explore how these innovations reshape manufacturing processes and drive industry transformation.
Why it is important
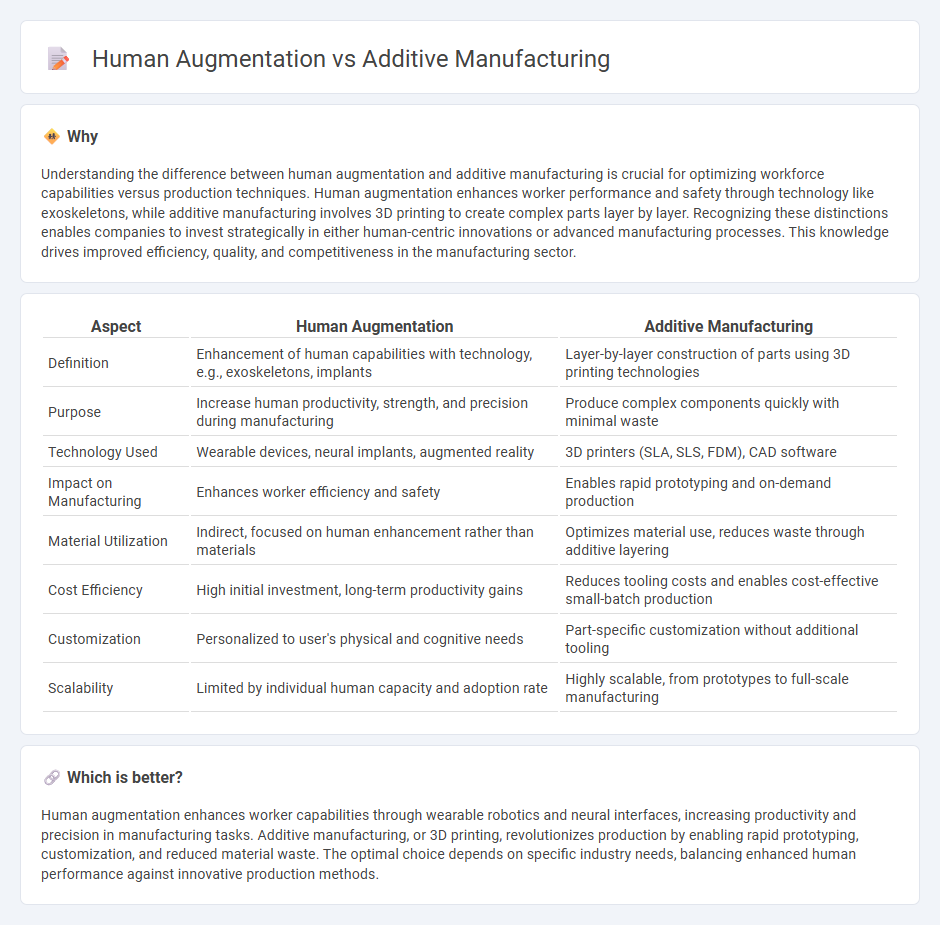
Understanding the difference between human augmentation and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing workforce capabilities versus production techniques. Human augmentation enhances worker performance and safety through technology like exoskeletons, while additive manufacturing involves 3D printing to create complex parts layer by layer. Recognizing these distinctions enables companies to invest strategically in either human-centric innovations or advanced manufacturing processes. This knowledge drives improved efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in the manufacturing sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Human Augmentation | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancement of human capabilities with technology, e.g., exoskeletons, implants | Layer-by-layer construction of parts using 3D printing technologies |
| Purpose | Increase human productivity, strength, and precision during manufacturing | Produce complex components quickly with minimal waste |
| Technology Used | Wearable devices, neural implants, augmented reality | 3D printers (SLA, SLS, FDM), CAD software |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Enhances worker efficiency and safety | Enables rapid prototyping and on-demand production |
| Material Utilization | Indirect, focused on human enhancement rather than materials | Optimizes material use, reduces waste through additive layering |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment, long-term productivity gains | Reduces tooling costs and enables cost-effective small-batch production |
| Customization | Personalized to user's physical and cognitive needs | Part-specific customization without additional tooling |
| Scalability | Limited by individual human capacity and adoption rate | Highly scalable, from prototypes to full-scale manufacturing |
Which is better?
Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities through wearable robotics and neural interfaces, increasing productivity and precision in manufacturing tasks. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, revolutionizes production by enabling rapid prototyping, customization, and reduced material waste. The optimal choice depends on specific industry needs, balancing enhanced human performance against innovative production methods.
Connection
Human augmentation enhances workers' physical and cognitive abilities, enabling more precise operation and maintenance of additive manufacturing technologies. Additive manufacturing relies on skilled human-technology interaction, where augmented reality (AR) and wearable devices improve focus and reduce errors during complex 3D printing processes. This synergy advances production efficiency, customization capabilities, and innovation in manufacturing workflows.
Key Terms
Additive Manufacturing:
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, revolutionizes production by enabling layer-by-layer construction of complex parts with high precision and minimal waste, crucial in aerospace, automotive, and healthcare industries. It accelerates prototyping, reduces costs, and allows customization that traditional subtractive methods cannot match. Explore how additive manufacturing drives innovation and sustainability across sectors.
3D Printing
3D printing in additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and complex part fabrication by layering materials, transforming industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. In human augmentation, 3D printing customizes prosthetics and implants, enhancing biocompatibility and personalization for patients. Explore how advancements in 3D printing technology bridge the gap between manufacturing innovation and human augmentation solutions.
Layer-by-Layer Fabrication
Layer-by-layer fabrication in additive manufacturing enables precise construction of complex geometries by depositing materials sequentially, optimizing strength and material usage. In contrast, human augmentation focuses on integrating bio-compatible layers and electronic components to enhance physiological functions or sensory capabilities. Explore the latest advancements in layer-by-layer techniques for cutting-edge applications and breakthroughs.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing builds objects one layer at a time from digital designs, enabling complex, customized products with minimal waste, and is commonly referred to as 3D printing.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (AM) fabricates three-dimensional products directly from digital files by depositing materials layer by layer, offering advantages like design complexity, material efficiency, and potential for mass customization.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation Software - Additive manufacturing uses various technologies--such as powder bed fusion, material extrusion, and photopolymerization--to create parts directly from 3D CAD models, supporting rapid prototyping and functional end-use production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com